- Blog >
- What Is Mineral Processsing in Mining?
What Is Mineral Processsing in Mining?
Mineral processing is a form of extractive metallurgy that separates valuable minerals from the ore into a concentrated, marketable product. Mineral processing is also known as mineral dressing.
Mineral processing is conducted at the site of the mine and is a highly mechanical process, with oversight from a central control room.

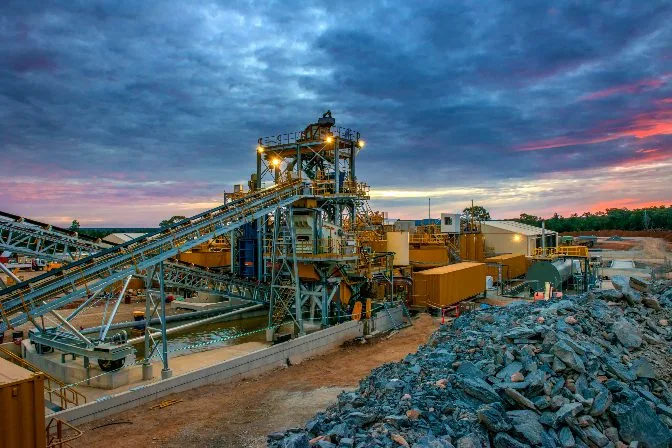
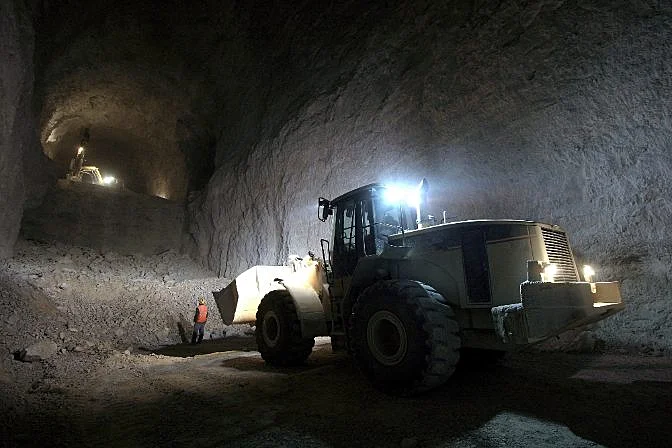
Gold mineral processing plant
Why Is Mineral Processing Important?
The profitability of a mine is based on how much concentrate of the desirable mineral can be extracted from the ore. As a result, mineral processing is designed to yield the maximum amount of mineral concentrate possible before products hit the market.
If the case cannot be made for profitable yields of valuable minerals, then a mine will not hit the development stage in the lifecycle of a mine.
Mineral processing is used to extract the following materials:
-
Metals, including aluminum, bauxite, chalcopyrite, chromite, copper, galena, gold, hematite, iron, lead, magnetite, molybdenum, nickel, platinum, silver, sphalerite, tin, and zinc
-
Rocks, including including building stone, coal, clay, granite, limestone, potash, marble, and sand
-
Industrial mineral ore, including apatite, barite, diamond, fluorite, garnet, gemstones, quartz, vermiculite, wollastonite, and zircon
Mineral processing is an important step in converting ore into a product that can be sold and used for everyday applications.
What Are the 4 Stages of Mineral Processing?
Aside from profitability, the main objective of mineral processing is to break down ore from its heterogeneous properties and turn it into a homogeneous product to sell. To do this, materials will undergo the following four stages of processing to extract the desired crude material:
1. Crushing and grinding. Crushing and grinding, also called comminution, is the process of reducing the particle size of large rocks to be further processed down the line.
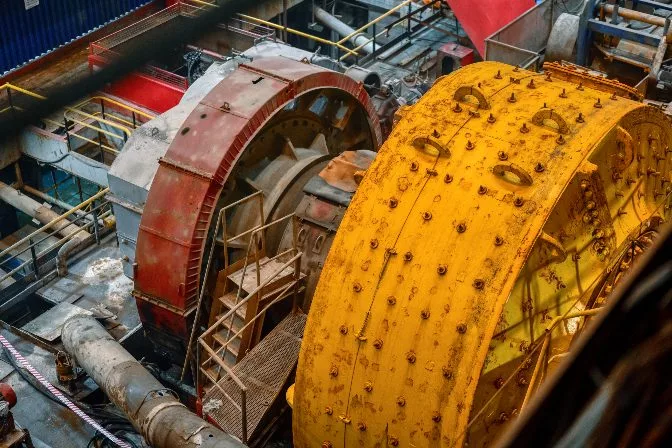 Wet grinding mill
Wet grinding mill
2. Sizing and classification. Sizing and classification is the process of separating different sizes of ore by screens. Finer materials are routed to different stages of the mine than coarser materials.
3. Concentration. Concentration is the process of breaking down the materials until the desired concentration of crude material is reached. There are several different techniques for accomplishing the target concentration including:
-
Automated ore sorting. Automated ore sorting uses optical sensors to sort the rock into categories. This technology is expanding to include more sensing parameters.
-
Electrostatic separation. Electrostatic separation consists of electrostatic separators and electrodynamic sensors, also known as high tension rollers. Since these separators rely on electric currents, ore material needs to be dry. Charges are run through the materials and separate from the gangue—the undesirable ore that is removed from the profitable minerals. These separators are used to separate mineral sands.
-
Froth flotation. Froth flotation uses a chemical collector and frother that forms bubbles on the surface of the slurry that hydrophobic materials bind to. The bubbles are collected off the surface of the frother. Activators are used to enable the flotation of one mineral ore while depressants are used to inhibit the flotation of the gangue.
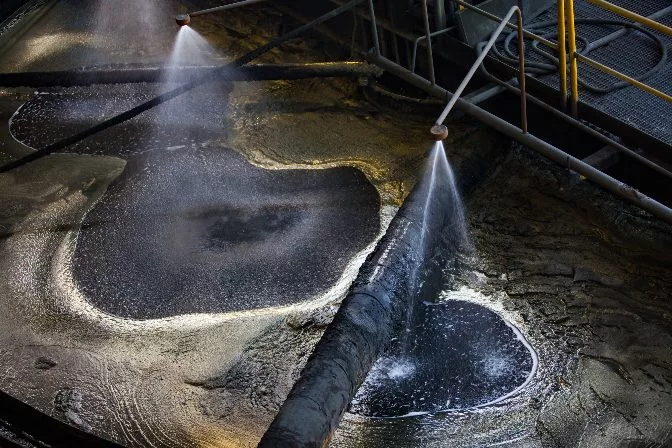 Froth flotation tank
Froth flotation tank
-
Gravity separation. Gravity separation is the process of separating two or more ore minerals in their respective responses to gravity paired with buoyant forces, centrifugal forces, and/or magnetic forces in a viscous substance.
-
Magnetic separation. Magnetic separation is the process of using electromagnets to extract the desired mineral ore from a conveyor belt. This process can be used with or without water.
4. Dewatering. Dewatering is the final process of removing the water content of the mineral in order to dispose of the gangue and reach the desired concentrate levels for marketability.
In the next section, we’ll take you through the ore’s journey from crushing to concentration.
How Does Mineral Processing Work?
Once the ore is transported to the surface of the mine, haulers feed the crushers with tonnes of large rocks, the first step in mineral processing.
After they are crushed to about 15 cm (6 in) in diameter, conveyor belts route the materials into stockpiles near the concentrator building for grinding.
A conveyor belt transports the crushed rock into the concentrator building to be further diminished by SAG grinding mills. There, the ore is either mixed in with water or kept dry and then undergoes the grinding process. Materials are ground to about 5 cm (2 in) in diameter.
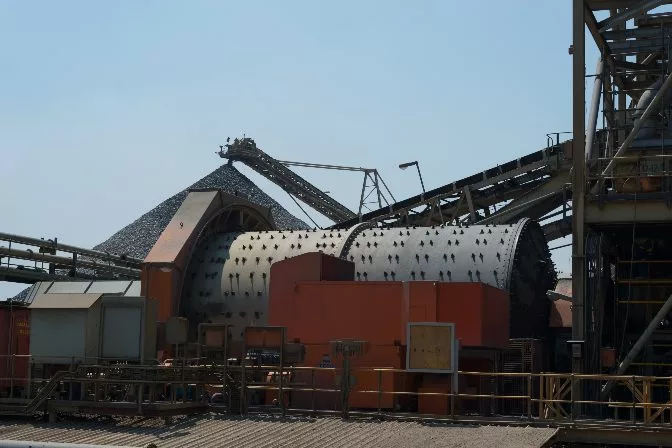 SAG grinding mill with a stockpile in the background
SAG grinding mill with a stockpile in the background
The now smaller materials are fed to screens that size ore, resulting in minerals less than 1.3 cm (½ in) to fall through the screens.
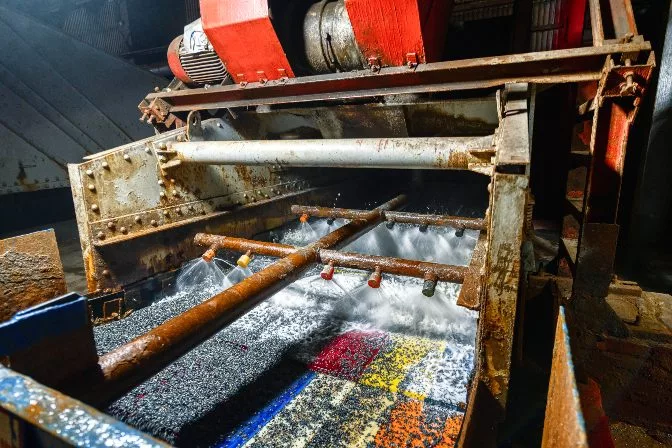 The screening process
The screening process
The smaller ore will go on to the ball grinding mills where they will be further ground down. The larger ore will be routed to a pebble crusher to reduce the size to 1.3 cm (½ in) and will return to the SAG mill stage.
The ball mill product is pumped to cyclones which separate out the coarse material with the fine ore. The coarse mineral ore is routed back to the ball mill stage while the fine minerals are routed to the concentration stage of mining.
 Minerals adhere to bubbles in the froth flotation concentration process
Minerals adhere to bubbles in the froth flotation concentration process
During the concentration stage, a cleaner and higher concentration of the desired mineral is produced and ground down to the consistency of talcum powder. This is sent to a thickener where the concentrate settles and dewatering begins.
At this point, the ore is still at about 50% water, so this material is pumped to a filter press to further dewater the mineral ore.
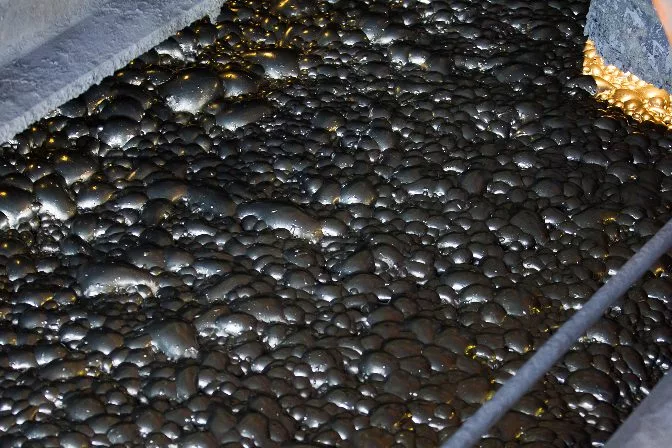
Finally, the minerals are dried to remove the remaining water. The final concentrated mineral percentage differs depending on the mineral and the concentration process used.
The crude material is transferred to another off-site processing plant that smelts or refines the mineral ore into the final raw material.
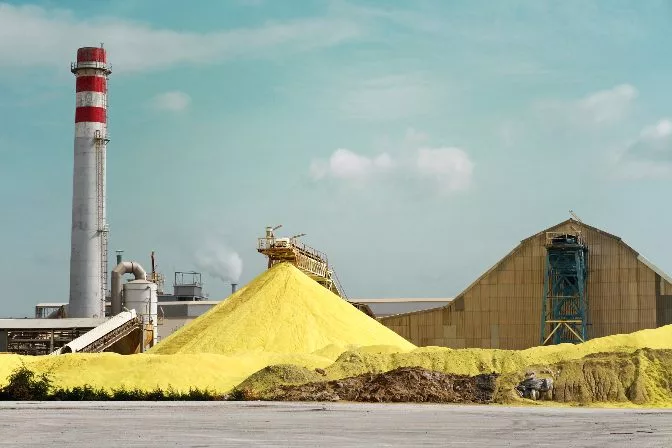
 Copper and gold concentrate
Copper and gold concentrate
Mineral Processing Equipment
Below is a list of equipment used at each stage of mineral processing:
-
Crushing and grinding equipment
-
Cone crushers
-
Gyratory crushers
-
Jaw crushers
-
SAG mill grinders
-
Rod mill grinders
-
Ball mill grinders
-
Pebble crushers
-
-
Sizing and classification equipment
-
Bar screens
-
Banana screens
-
Fine screens
-
Flip flop screens
-
Grizzlies
-
Multi-deck screens
-
Radial sieves
-
Vibratory screens
-
Wedge wire screens
-
Wire mesh screens
-
Fluidized classifiers
-
Spiral classifiers
-
Gas cyclones
-
Hydrocyclones
-
Ore sorters
-
Rake classifiers
-
Rotating trommels
-
-
Concentration equipment
-
Cleaners
-
Recleaners
-
Roughers
-
Scavengers
-
-
Dewatering equipment
-
Dewatering screens
-
Thickeners/clarifiers
-
Belt press/membrane filter press
-
Fluidised beds
-
Hearth dryers
-
Rotary dryers
-
Rotary tray dryers
-
Spray dryers
-