- Blog >
- Stope Mining Guide: Techniques & Methods Explored
Understanding Stope Mining: A Comprehensive Guide
What is a Stope in Mining?
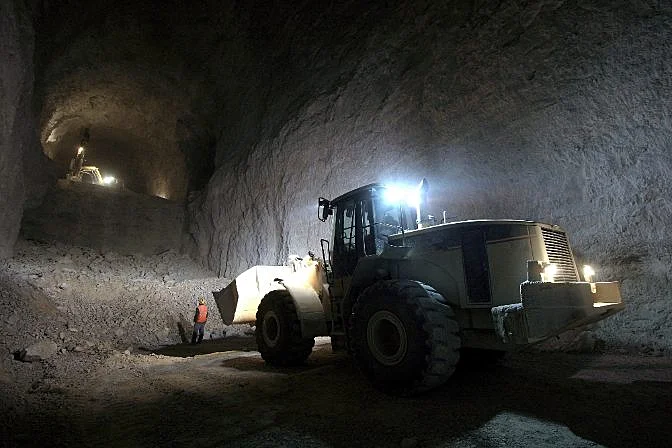
A stope is a dugout tunnel or space that contains the ore that is being mined. Clear stopes are essential for a mining industry operation to run smoothly.
The stope provides direct access to the orebody and routes ore and waste in an underground mine. Stopes are created by drilling holes, placing explosives, and blasting open a space, which produces a stope.
 Clearing a tunnel
Clearing a tunnel
Considerations for Creating Stopes
When creating stopes, it is common practice to dig vertical shafts down to the orebody. Once the ore is reached, horizontal levels are created to mine the ore. These levels are where stoping occurs.
When creating a stope, miners consider the following:
-
The grade of the ore
-
The width of the ore
-
The incline of the ore (tilted, vertical, or flat)
-
The strength of the surrounding rock
-
The cost for supporting the mine roofs
Depending on the orebody orientation, an underground mining technique will be selected to extract the greatest amount of ore from a stope.
See also: The efficient management of a stope requires lots of mining technology and equipment to be used to ensure the safety of staff. Discover how this Glencore Kidd Operations mine ensured safer and more efficient inspections within their mine.
Stoping Methods
Before blasting, an initial slot must be present to successfully extract the ore. A slot is the basis for creating the stope. The following are methods used to create a slot hole:
-
Raise bore. A raise bore is the bottom-up construction of a cylindrical shaft that is created by using mechanical rollers. This is a good technique when longer stopes are needed.
-
Longhole raise. A longhole raise (also called longhole stoping) is a series of smaller blast holes that are drilled either down or up. This is a good technique when shorter stopes are needed.
-
Airleg raise. An airleg drill is versatile and can be used to determine the condition of the rock before mining.
-
Boxhole boring machine. Boxhole boring machine creates slot holes with small diameters. This is similar to a raise bore, but differs in that the broken materials are extracted directly from the drill site.
 Airleg raise
Airleg raise
Long-Hole Stoping
Long-hole stoping is one of the most common ways to create stopes in a mine. This method drills preprogrammed holes up towards the surface. Explosives are planted and the hole is blasted. This is a highly automated and mechanical process.
Once the stope is blasted, it cannot be accessed by personnel, so blasted rock is designed to fall directly to a drawpoint.
Shrinkage Stope Mining
Shrinkage stoping moves from the bottom up, similar to cut and fill underground mining.
Shrinkage stope mining is used for steep bodies of ore, with 60% of the broken ore left in place for miners to work through. (The other 40% is removed in order to prove adequate working space for the miners to access the next ore slice.)
Once the ore is depleted from the bottom up using shrinkage stope mining, the mine may be backfilled depending on the rock conditions inside.
 Drilling from the bottom up
Drilling from the bottom up
Timbered-Stoping
Timbered-stoping uses timber to support the stope and to prevent cave-ins. Miners will also use the timber to work from, like makeshift scaffolding.
There are two types of timbered-stoping:
-
Square-set stoping. Square-set stoping uses timber that is set into stopes in a square pattern. This is then backfilled with tailings, or mining waste, and a binder like cement.
-
Stull stoping. Stull stoping uses seemingly random timbering, called stulls. The stulls are placed between the foot and hanging wall of the ore vein. Stull stoping is used in mines with strong rock support since the stulls don’t provide much structural support. Backfilling these stopes made by stull stoping with large voids can be extremely dangerous and can cause a mine to collapse.
Open Stope Mining
The open stoping mining method is unique in that it does not require artificial support.
There are four types of open stope mining:
-
Overhand stoping. Overhand stoping is an open stope mining method that works the ore deposit from the bottom upward. With the drill and blast technique, this is the typical direction used to create a stope.
-
Underhand stoping. Underhand stoping is an open stope mining approach that works the ore deposit from the top down and is used in cut and fill underground mining. This method was more widely used when miners predominantly used hand tools and could rely on gravity to collect ore.
-
Combined stoping. Combined stoping is an approach to open stoping that works the ore deposit from the top and bottom simultaneously.
-
Breast stoping. Breast stoping is an open stope mining method that works the horizontal orebodies. The breast stoping method is best used in stope and pillar mining.
Managing Stopes with Drones
As with any mine, the careful management of the tunnels, equipment, and infrastructure must come paramount in operations. Through ensuring the working condition of everything associated with the mine, it becomes possible to work efficiently and guarantee the safety of workers as much as possible.
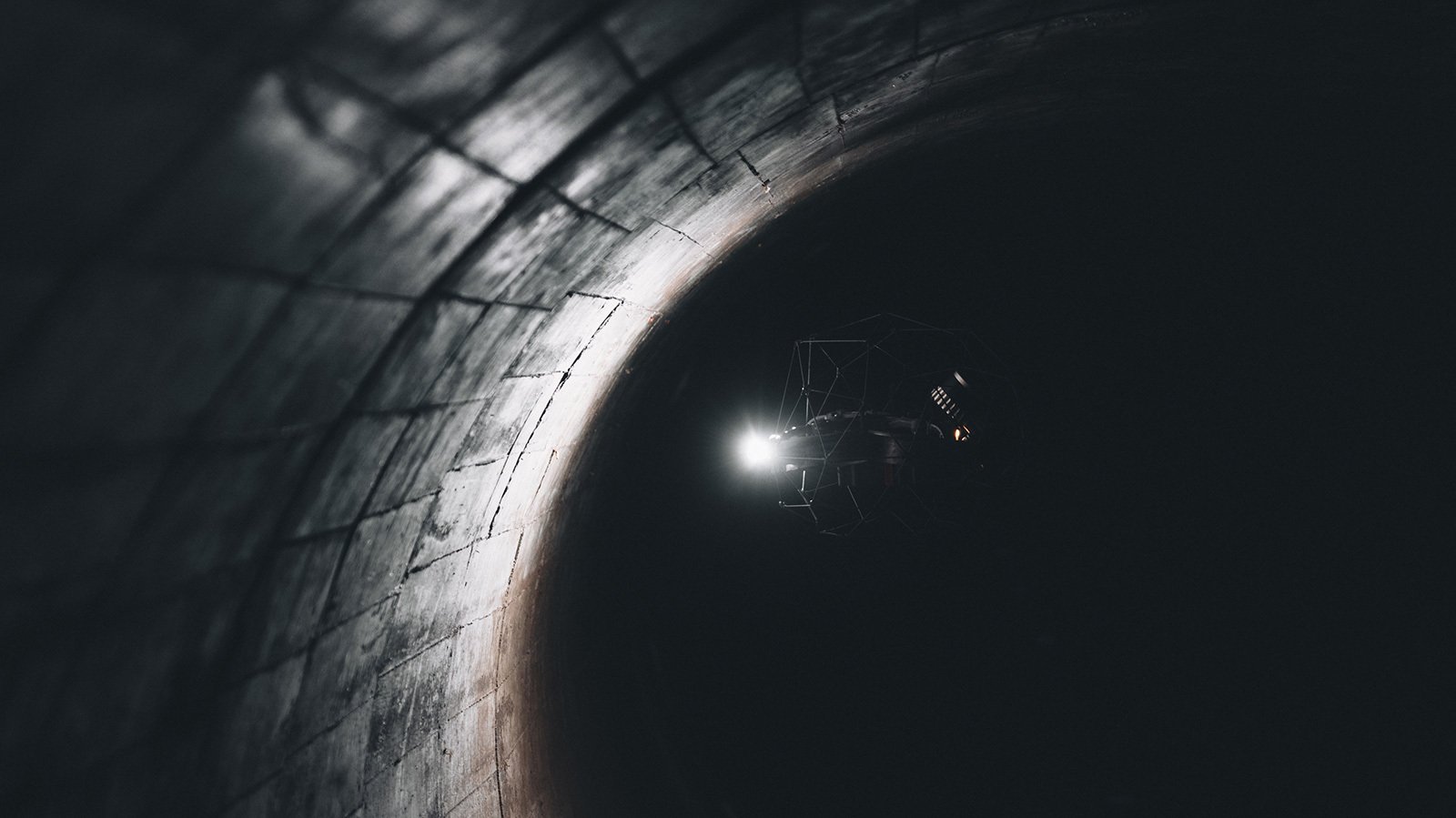
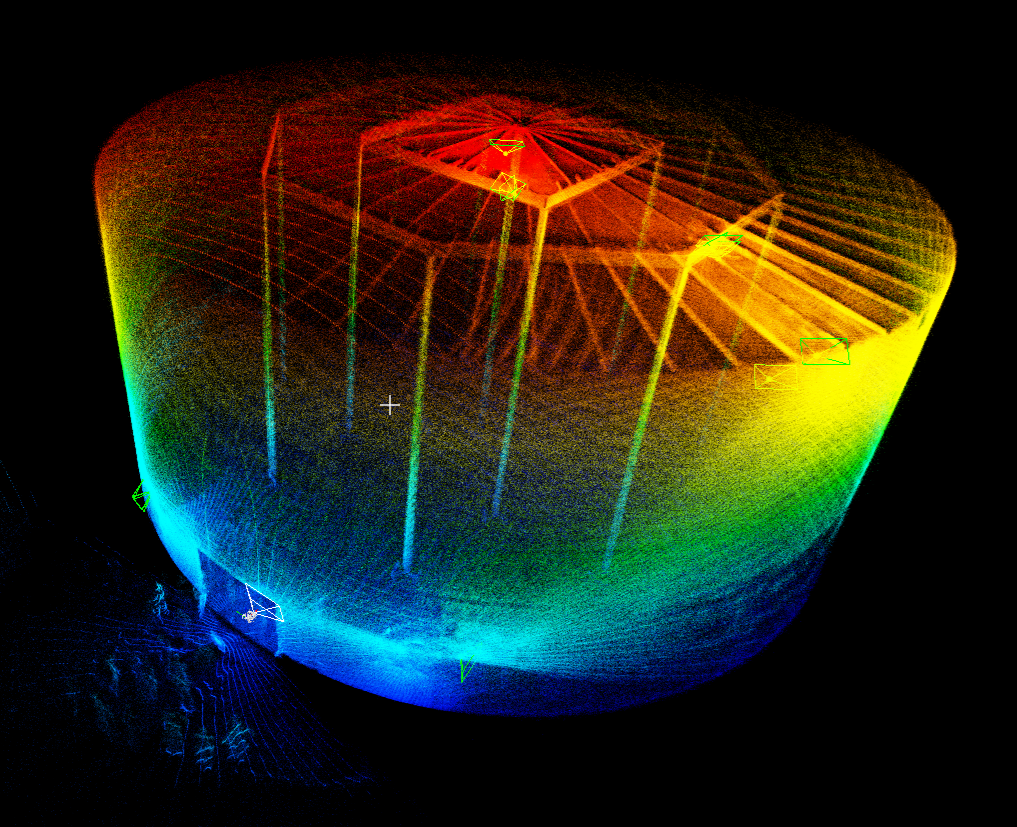
In some cases, this means not just managing the stope that is currently active but also monitoring old workings or excavations within the mine. Old workings can have outdated equipment, debris, and various unidentified hazards within them, and the structure of the stope may no longer be clear or guaranteed. For this reason, many mines require detailed records of the old workings to be created. In fact, drone surveys of old workings in underground mines with the Elios 3 drone have proven faster and safer than any other method and help keep staff safe.

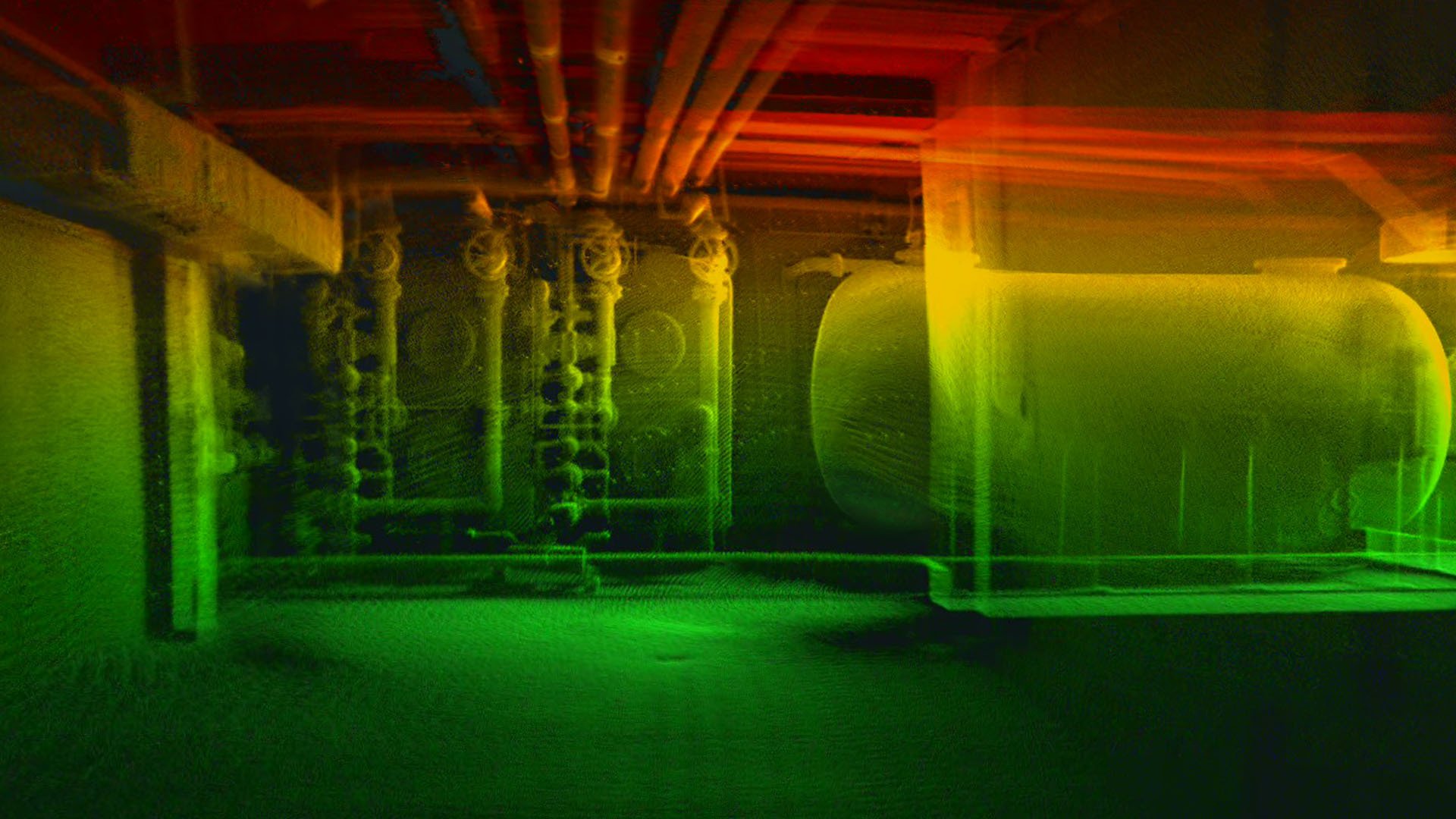
A drone survey completed with the Elios 3 drone provides inspectors with a LiDAR scan, photos, and detailed video feed of the drone’s flight. As a result, it gives remote access to surveyors. This is ideal for inspecting stopes as well as managing tunnels and connecting infrastructure. The drone can be deployed in minutes and complete quick scans while staff stay in safe locations, controlling it via the remote control which has a live video feed and 3D point cloud.
Afterwards, results from the Elios 3’s LiDAR scan can be as accurate as to within 1 centimeter, capturing 1 million points per second with a range of 100 meters. It can provide mover coverage than a standard laser scanner as it can be maneurevered more easily, ensuring there are not gaps in the data collected.
See how the Elios 3 and its LiDAR payload worked at an underground polyhalite mine.
When it comes to stope management, the outputs from the Elios 3 are clear, digital versions of the space that can be used to update records, track progress, and investigate concerns if there are any. This drone for mining is tailored for rugged, challenging environments such as inside stopes, and will provide critical data that helps with the overall management of the stope and wider mine.