- Blog >
- What Is a LiDAR Drone?
What Is a LiDAR Drone?
LiDAR drones are any drones made to carry a LiDAR sensor. They are used to collect data that can be used to make detailed 3D models for a variety of applications and industries.
Whether you’re surveying a forest, investigating the cause of a late-night automobile accident, or mapping an eroded shoreline, LiDAR sensors can help provide some of the most accurate and high resolution 3D models available.
And now, with the implementation of LiDAR drones, this technology is more accessible than ever.
 Credit: Wingtra
Credit: Wingtra
In the past, there have been three main ways to use LiDAR:
-
On the ground—carrying a LiDAR sensor in your hand or in a handheld mount.
-
On a plane—flying in an airplane or helicopter with a LiDAR sensor.
-
From space—using a satellite.
Up until recently, LiDAR technology of any kind was reserved for specialized and well-funded projects. However, as LiDAR sensors become more widely available due to decreases in cost and size, aerial LiDAR technologies—that is, LiDAR drones (as opposed to planes or helicopters)—are quickly growing more and more common.
In fact, drones with LiDAR sensors attached are now being used for everything from investigating insurance claims to helping make new archeological discoveries. Below, we’ll take a look at the many different ways that LiDAR is currently being used, and we’ll also look at the best LiDAR drone sensors currently on the market.
What Is LiDAR?
How can a laser measure the height of a tree? How does LiDAR even work?
The term LiDAR comes from the phrase Light Detection and Ranging—basically, using lasers to collect data about a surface, which can then be processed into 3D models.
LiDAR technology is relatively new. It was first developed in the early 1960s, when engineers and land surveyors began using it to produce maps of rivers, streams, and other geographic locations.
[Related read: What Is Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)?]
In those early days, the term LiDAR wasn’t an acronym, but merely a combination of the words “light” and “radar.”
Back then, LiDAR sensors were incredibly expensive and almost exclusively attached to large, manned airplanes. These planes could cover a lot of ground at once, but their operation was manual and expensive, and their results were far from accurate.
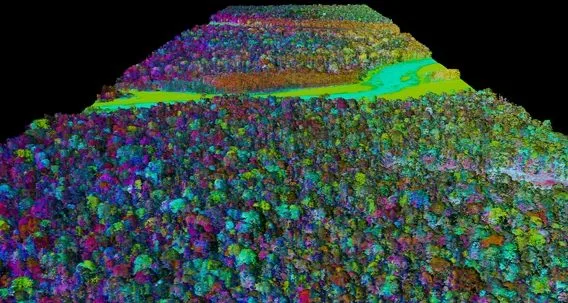
3D LiDAR map created by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
LiDAR is notably different from other 3D modeling systems like photogrammetry, which involves taking hundreds or even thousands of individual photographs and stitching them into one detailed model.
Instead, LiDAR uses light energy and sophisticated lasers to scan and measure a target from a distance. When attached to a high-flying drone, LiDAR can cut through or around foliage and other debris in a way that photogrammetry systems cannot, which makes it a powerful tool for discovering new sites in a field like archaeology.
But how exactly does it work?
The process is similar to how sonar or radar detect objects, which rely on bouncing a sound or radio wave off an object and measuring the time it takes to return in order to understand how far away the object is, or what its dimensions are.
With LiDAR, a high-powered laser shoots precise pulses at a target, and measures the pulse that bounces back in order to collect data about the target.
To create an understanding of an object in three dimensions, LiDAR sensors measure:
-
Time—how long it takes for the pulse to return.
-
Intensity—the return strength of the laser pulse.
-
Angle of the reflection—the ways the surface being measured change as indicated by the angle of reflection.
After collecting these data points, specialized 3D mapping software processes this information along with GPS (Global Positioning System) data and INS (Inertial Navigation System) data to create detailed and precise 3D models of a targeted area or object.
[Learn more about LiDAR in this guide.]
What Is a LiDAR Drone?
A LiDAR drone is any aerial drone with a LiDAR sensor attached.
In recent years, innovation in LiDAR technology has dramatically lowered both the cost and size of LiDAR sensors, making it more feasible to attach a LiDAR payload to a drone. And as LiDAR drones become more common, the information they can provide is far more accurate and far less expensive.
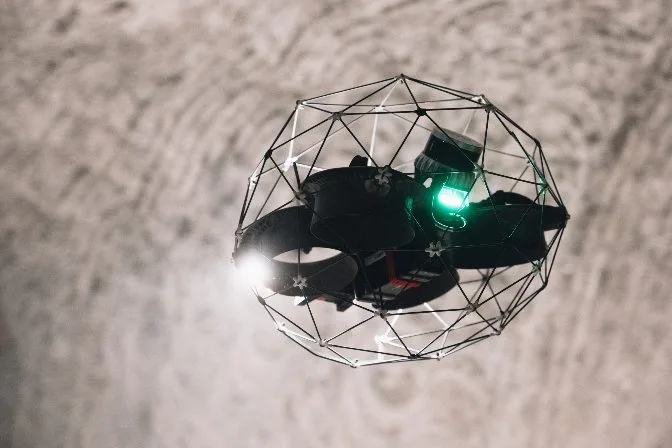 The Elios 3 equipped with a LiDAR sensor made by Ouster
The Elios 3 equipped with a LiDAR sensor made by Ouster
These developments, along with advancements in the technology used to integrate drones with LiDAR data, has led to a rapid increase in companies deploying drones equipped with LiDAR as an all-in-one, full-scale 3D-mapping system.
A LIDAR sensor attached to a fixed-wing drone can cover up to four square miles in one flight, with an absolute accuracy of 4 inches horizontally and 2 inches vertically. This is some of the highest fidelity data currently achievable by any aerial surveying method.
But it’s important to note that no two LiDAR drones are alike.
Different combinations of LiDAR sensors and drone models and designs will yield different types of results, and in some cases LiDAR isn’t the best method to use for 3D modeling.
In long, uniform environments, for instance, such as tunnels or sewer pipes, LiDAR data can fail to create a reliable 3D rendering if not flown by a professional drone pilot.
LiDAR Drone Uses
LiDAR drones are being used in a multitude of different ways across a wide range of industries.
Below are the most common areas in which LiDAR scanner drones are revolutionizing the world of 3D-mapping.
Accident Scenes
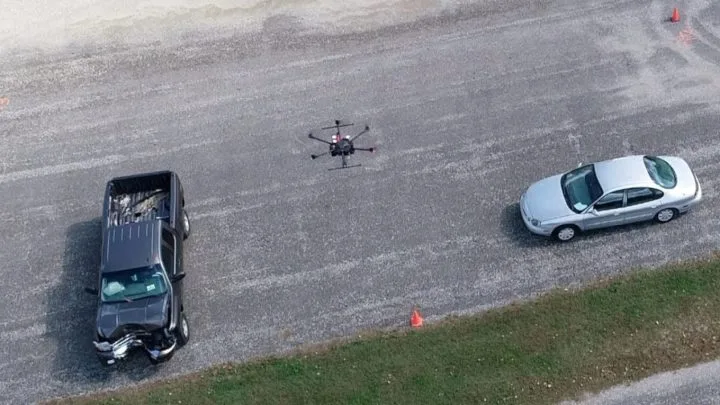 Credit: John Bullock and Erin Easterling / Purdue University
Credit: John Bullock and Erin Easterling / Purdue University
LiDAR systems typically use ultraviolet or near-infrared signals to map an area, meaning that they can operate with little to no external light—and this makes them perfect for use at night, especially in emergency situations like automobile accidents.
In a single pass, LiDAR drones can capture and produce a comprehensive 3D map of any accident that may require emergency services. Whether it's a late-night Interstate pileup or a fender bender on a snowy rural road, a LiDAR drone can create an accurate and exhaustive report of any emergency situation before first responders even arrive.
Benefits of LiDAR drones for accident scenes
-
Triage assistance. With accurate information and a sweeping knowledge of visual details that otherwise may have been unknown, emergency services on the scene can spend those first critical minutes rescuing citizens and saving lives instead of spending time assessing the situation.
-
Accident reconstruction. In addition to creating 3D models of an accident scene using LiDAR data, most LiDAR drones have a visual camera in addition to a LiDAR payload, and the visual data they collect can be presented as evidence in court as an accurate and neutral account reflecting the potential cause or result of an accident.
-
Clean up. The maps that LiDAR drones provide can help wreckers or sanitation crews deal with the fallout of an accident at a much faster rate.
-
Savings. LiDAR drones are typically cheaper than alternate methods for accident reconstruction. And, by helping reduce the amount of time in which secondary accidents might happen, they save cities money by reducing the total amount of accidents with which they have to deal.
-
Safer roads. Secondary accidents are common at crash scenes, and the longer it takes to clean up a crash, the bigger the window for these accidents. By speeding the clean up process, LiDAR drones can help keep roads safer.
Agriculture
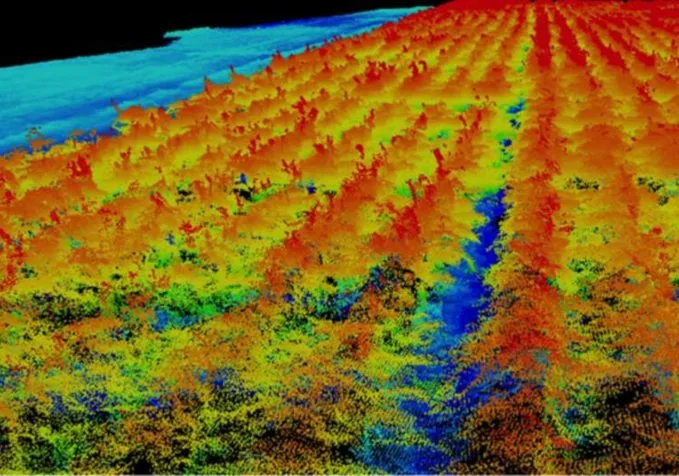 Credit: Texas A&M Agrilife photo
Credit: Texas A&M Agrilife photo
Another industry that stands to greatly benefit from the hyper-accurate maps provided by drones with LiDAR is agriculture.
The use of drones and other robotics technologies to improve farming is typically referred to as precision agriculture—and LiDAR data is a key element in this new movement.
Benefits of LiDAR drones for agriculture
-
Crop production. Information provided via LiDAR drones can be used to make a number of maps that can inform agricultural decisions. These include maps that show high, medium, and low crop production areas, maps that inform where and when to use fertilizer (an expensive, valuable and often overused resource), and even maps that show areas of a farm that receive the most sunlight.
-
Irrigation. On properties like rice farms, which require intricate and precise levees to be built for proper irrigation, LiDAR-generated maps can be indispensable. Not only can the LiDAR enabled drones provide models with inch-wide accuracy, but they can do so even if the fields are flooded—previously, farmers would have to wait until the ground dried up to drive trucks full of equipment through the fields.
-
Livestock management. Keeping track of wandering or grazing livestock in a manner that is impossible to do at ground level, as well as keeping them safe from predators—even at night, when monitoring for such threats becomes much more difficult and dangerous.
-
Mapping. In a short period of time, a drone with a LiDAR payload can scan and map out the full acreage of a farm to a high degree of accuracy.
-
Savings. Reducing the cost and time associated with irrigation, crop production, and livestock management by quickly providing precise data to inform all of these activities.
Archeology
 LiDAR map of a ruin in Caracol | Credit: Arlen and Diane Chase
LiDAR map of a ruin in Caracol | Credit: Arlen and Diane Chase
One of the most novel and exciting areas in which LiDAR scanner drones are being used today is in the field of archeology.
Of course, the drones don’t actually help with the excavation of ancient artifacts, but they can greatly aid researchers in understanding previously uncovered sites or in their search for new ones.
In 2017, information gathered by LiDAR drone sensors helped to identify a sprawling road system in the El Mirador river basin, a vast plot of land deep within the jungles of Central America. These roads, used by the Mayans as early as 600 B.C.E., may have never been discovered if not for the use of LiDAR drones and the technology’s unique ability to gather data through dense and wide tree top canopies.
A similar story occurred in 2019, at The Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, in Colorado. Here, researchers were attempting to map Sand Canyon, what was thought to be an ancestral Pueblo site. Using aerial LiDAR, the team at Sand Canyon was able to collect more than 3.2 billion data points in their mapping of the area.
“The impact of this survey approach is truly astonishingIt removed the need for a painstaking ground survey and the speed of delivery of such detailed results is impressive. It has accelerated our understanding—the results indicate the Pueblo was more extensive than we had previously imagined.”
- Mark D. Varien, Executive Vice President of the Research Institute at Crow Canyon Archeological Center
Benefits of LiDAR drones for archeology
-
Quick site surveys. Drones equipped with LiDAR sensors help archeologists survey potential dig sites without even picking up a shovel.
-
No damage. LiDAR allows archeologists to examine areas of interest without the fear of destroying what may be below the surface, which is a pressing concern in the field.
-
Reveal what’s hidden. Researchers can find hidden, overgrown, or nearly buried evidence that may have been invisible to the naked eye. In fact, LiDAR sensors can spot everything from foot paths to burial plots without ever disturbing the ground.
Conservation
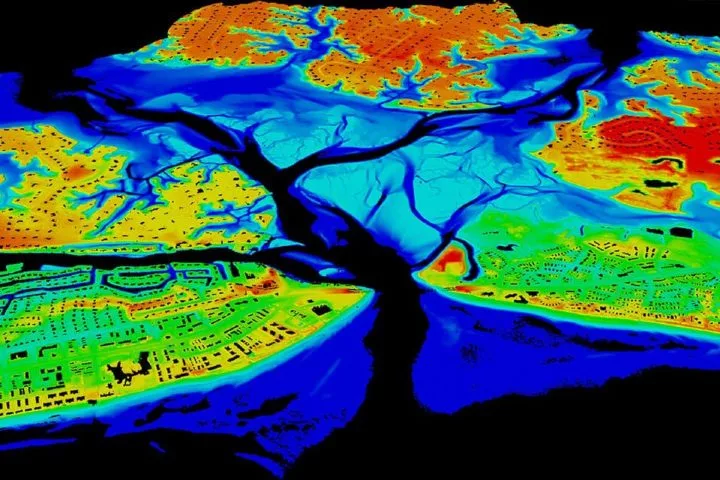 3D map of an inlet created by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
3D map of an inlet created by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
The information provided by LiDAR sensor drones can be incredibly effective in helping governments and other institutions maintain and conserve their natural resources.
In fact, a number of U.S. states have already begun using aerial LiDAR scanners to better understand the assets within their own borders. This intensive, accurate data collection allows for better documentation, which, in turn, can lead to better protection of our natural resources.
Other states, like Iowa, have entire databases filled with information collected from LiDAR sensors. The state’s Geographic Information System (GIS) is full of data collected from LiDAR systems under the issue of The Iowa Department of Natural Resources.
“LiDAR data, including derivatives like contour maps, digital elevation models, hill shade projections, and others, are assisting with a wide range of natural resource conservation applications.”
- University of Minnesota Water Resource Center
Benefits of LiDAR drones for conservation
-
Forest conservation. Mapping forests to conserve and protect them.
-
Water conservation. LiDAR drones can map out everything from flood plains to water basins, and with accurate, high fidelity maps of these areas, state and local governments can both prepare for natural disasters and more accurately predict their yearly resource use.
-
Sand dune conservation. Mapping sand dunes to track their spread and incursion on bordering ecosystems, and to protect them.
Inspections
 Credit: Delair
Credit: Delair
The use cases for LiDAR drones in inspection and other infrastructure fields are obvious.
From surveying a construction site, to measuring the amount of vegetation growing around a power line, drones with a LiDAR payload can greatly reduce both the time and cost of a manual survey or inspection.
Right now, drones with LiDAR sensors are being used to inspect and perform maintenance on rails, pipelines, turbines and more.
Benefits of LiDAR drones for inspections
-
Historical record. Get a precise, 3D snapshot of the entirety of an asset, which can be compared to past and future conditions with the asset.
-
Planning. Getting a detailed 3D rendering of an asset or space can help plan future work and make sure no details are missed.
-
Safety. Avoid the need to manually enter dangerous confined spaces or work at height by using drone data instead of collecting data in person.
-
Savings. By speeding up inspections and reducing downtimes, 3D maps made with aerial LiDAR data can lead to huge savings for industrial inspections.
[Case study: Elios 3's Indoor 3D Mapping Helps City of Lausanne in Water Department Inspections]
Insurance

The very same maps that state governments are using for conservation efforts can also be used by the insurance industry to better and more accurately serve their customers and clients.
This is because the maps that LiDAR sensor drones provide help in crafting highly personalized quotes for things like flood or property insurance, and to investigate claims for these kinds of incidents.
Typically, insurance adjusters assess the damage after an event like a flood by going from door to door, asking questions and making notes.
But LiDAR drones completely revolutionize this process, as they allow for huge sections of urban areas to be mapped in just a few short minutes.
Benefits of LiDAR drones for insurance
-
Proof. When it comes to insurance claims, the record that a LiDAR sensor provides is evidence of what exactly happened in a given place impacted by extreme weather or other incidents.
-
Safety. In the case of roof inspections, aerial LiDAR can take the place of a person having to physically go onto a roof, thus improving safety in the inspection process.
-
Speed. Quickly investigating insurance claims.
Forestry
LiDAR 3D model of rainforest canopy in the Amazon | Credit: Carnegie Airborne Observatory
Foresters are already using LiDAR drones to measure everything from the height of a canopy to the area of a single leaf, and this data is being used to classify land, manage forest fires, understand ecosystems, and take inventory of commercial forests.
LiDAR is especially helpful in measuring the height and location of individual trees within a large, dense forest, and the technology’s ability to work its way around treetops also makes it perfect for collecting information on the ground.
Since LiDAR technology ignores the shadows cast by trees, its lasers can bounce all the way to the forest floor, offering insights about the ground level that other methods never could.
Benefits of LiDAR drones for forestry
-
Savings. Aerial LiDAR is much faster than walking an area on foot to do an arboreal survey—and thus much less expensive.
-
Speed. Traditional surveying methods for forests are inefficient, time-consuming, and nearly impossible to use without light.
-
Research. LiDAR data is crucial for improving our understanding of forests, from data on specific trees and entire groves.
-
Resource management. LiDAR data can help inventory, catalog, and track several important data points for forestry, including the amount of overall trees in an area, their type, their distribution, and even their health.
-
Improving business and conservation. Improving forestry data has implications both for conservation efforts and for industries that rely on the world’s forests, like the paper, syrup and furniture business.
Law Enforcement
 Credit: DJI
Credit: DJI
To most people, law enforcement may be the one area of life where they’ve already seen LiDAR technology in use.
Why is that?
Well, because since the turn of the century, police departments across the world have been trading in their radar guns for LiDAR guns, using the accurate and precise technology to better measure the speed of passing cars.
But the uses for LiDAR in law enforcement go far beyond speed guns. We’ve already talked about how LiDAR drones can help map out an accident scene, even in the dark—but they can also be critical for analyzing an active crime scene as well.
Benefits for LiDAR drones in law enforcement
-
Tactical information. In a hostage situation, police can use a LiDAR drone to get a full picture of the threat from afar. Whether it's day or night, officers can use drones to fully understand and assess a dangerous situation.
-
Search and rescue. Finding people lost in remote areas—even at night.
-
Water rescue. Using bathymetric LiDAR sensors (a type of LiDAR that produces a water-penetrating green light instead of the near-infrared laser of topographic LiDAR) first responders can quickly identify wreckage or even survivors who may be partially or fully submerged in water.
Mining
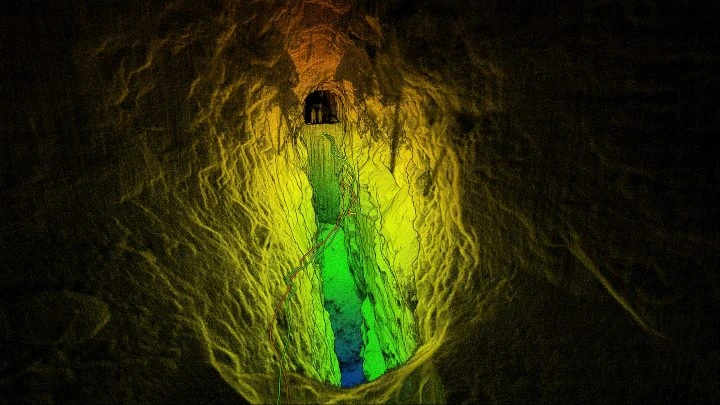 Credit: International Mining
Credit: International Mining
One final area in which LiDAR technology is making inspection, surveying, and mapping more efficient and safe is in the mining industry.
In mining, LiDAR-equipped drones are being used to inspect mines after planned detonations, in order to make sure the area is safe before sending in any human workers. LiDAR drones are also used to measure ore volumes and ore extraction spaces.
Underground mining environments render GPS operations impossible for drones, so LiDAR and visual sensors are crucial to make it possible for a drone to operate underground, without GPS.
Benefits of LiDAR drones in mining
-
Increased ore extraction. 3D maps made using LiDAR data can help identify potential remaining ore, which can lead to huge amounts of extra revenue for a mining company.
-
Planning. In tandem with scanners on the ground, LiDAR drones can compare new surface data with previous scans in order to determine what areas of the mine are rich with resources or should be targeted next.
-
Safety. Mapping unstable areas so that they can be evaluated for safety.
-
Savings. Improved understanding of crucial excavations in a mine can lead to more ore extraction and greater efficiency overall, leading to huge potential savings.
Best LiDAR Drones
The truth is, there’s no single best LiDAR drone. In fact, the phrase itself is a bit misleading.
The best drone for you depends on your situation and intended use. And when it comes to LiDAR, there are even more variables than usual.
With LiDAR drones, the drone itself, the LiDAR sensor, and the integration between the two are all equally important.
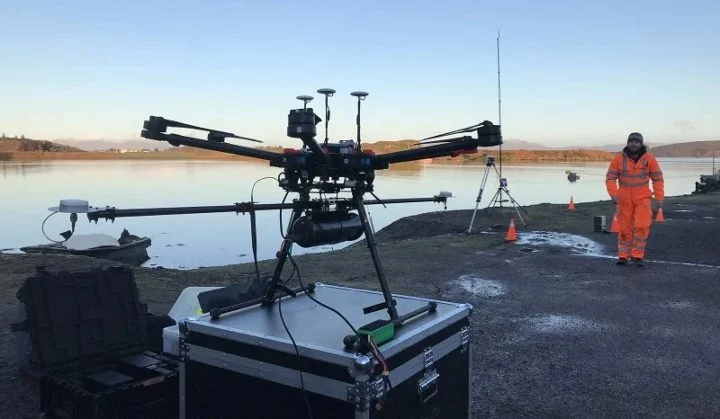 A DJI Matrice 600 mounted with a Routescene LidarPod
A DJI Matrice 600 mounted with a Routescene LidarPod
However, while there are all-in-one drones and full service LiDAR packages out there, the best investment for hobbyists, enthusiasts, or even smaller businesses is a high quality LiDAR sensor. High quality sensors ensure you get the data you need—the platform that carries it, whether it's a drone or just your open hand, isn’t necessarily as important as the data it can collect.
Below, you’ll find some of the best drone-compatible LiDAR sensors available. But before you buy one, we recommend really thinking about how you plan to use it.
Here are four questions to help guide your decision making:
1. How easy is it to use?
Keep in mind that when it comes to LiDAR scanner drones, there is a lot to learn and understand beyond the drone itself. Be sure that all the included software, including the operation and data collecting functionalities of the sensor, is something that you are either already familiar with or comfortable learning.
2. What will it be used for?
Different drones can be optimized for different functions, and the same is true for LiDAR sensors. The best LiDAR drone for building inspection may not be the best one for irrigation planning, so it’s important to know your intended use case before purchasing your LiDAR sensor.
3. How much does it weigh?
If you’re buying a LiDAR sensor for a drone already in your possession, it’s vital to know how much the sensor weighs and whether the payload is within your drone’s carrying capacity. Certain LiDAR sensors far outweigh the limit of some commercial drones, so be sure to do your homework.
4. Is LiDAR the Best Option?
While LiDAR sensor technology is impressive and cutting-edge, it isn’t always the best option when it comes to 3D mapping. In some cases, systems like photogrammetry may be a better solution.
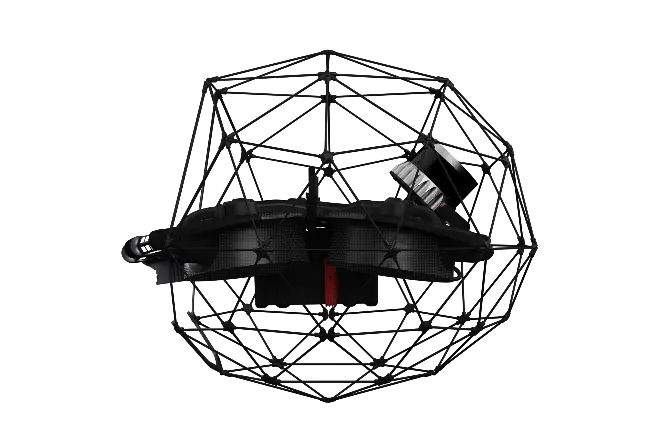 The Elios 3 has a modular payload with two ports
The Elios 3 has a modular payload with two ports
LiDAR Drone Sensors
Listed below are a number of different LiDAR sensors for use on small drones, in order from least to most expensive.
Keep in mind that these price points vary widely, and that each sensor has a number of different functionalities.
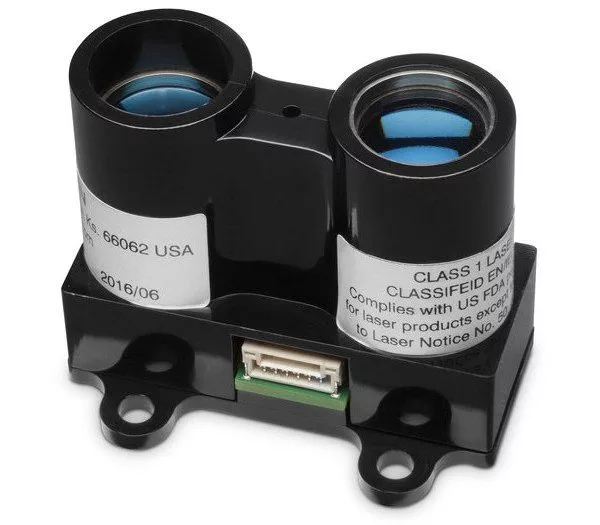
1. Garmin LiDAR-Lite v3
Price: $130
This sensor from Garmin is one of the best options for hobbyist or DIY LiDAR drone enthusiasts.
It’s lightweight, uses little power, and has a range of about 40 meters. It’s also on the lower end of price points for sensors of its kind, making it a great option for at-home LiDAR drones.
Learn more about the Garmin LiDAR Lite-V3.
2. LeddarTech Vu8

Price: $693
This LiDAR sensor detects targets up to a 215 meter range and comes in at a light 75 grams, making it a fantastic, lightweight LiDAR sensor that will work with a number of drones.
Learn more about the Leddartech VU8.
3. RPLIDAR A2M8 360° Laser Scanner
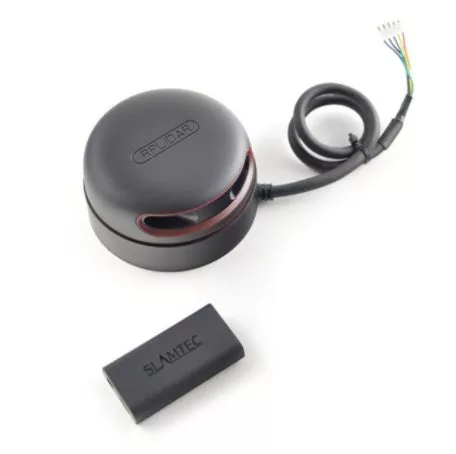

Price: $319
This LiDAR sensor comes in at 340 grams and has a range of about 6 meters.
Intended for use in robotics, obstacle avoidance and route planning, this sensor has limited viability with drones, but can still be the right option for certain functions or applications.
Learn more about the RPLiDAR A2M8 360° Laser Scanner.
4. Velodyne HDL-32E
Price: $1,400
This ruggedly built Velodyne LiDAR sensor has a range that reaches up to 100 meters. It has a 360° Horizontal FOV and comes in at less than 2kg, making it a sturdy LiDAR sensor for use on drones.
Learn more about the Velodyne HDL-32E.
5. Velodyne Puck VLP-16

Price: $2,100
This Velodyne sensor, created with mass production in mind, is one of the highest value LiDAR drone sensors currently on the market. More cost effective than sensors at a similar price, this is a great option for those looking to spend a bit more.
Learn more about the Velodyne Puck.
6. Ouster OS0-2
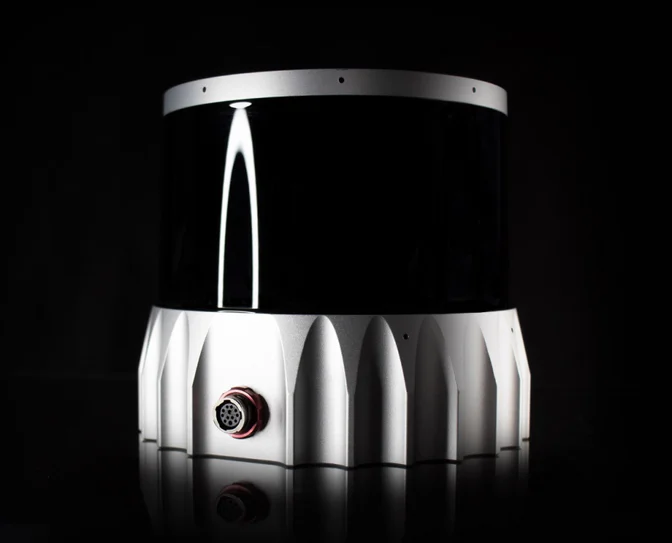

Price: Contact sales
This Ouster LiDAR sensor is meant for long-range applications and creates high definition 3D renderings. Designed for commercial use, with all weather capabilities, it's a great choice for drones with the appropriate payloads.
Learn more about the Ouster OSO 2.
LiDAR Drone Price
As is evident from the sensors listed above, the prices of LiDAR drones and sensors can vary widely depending on type and functionality.
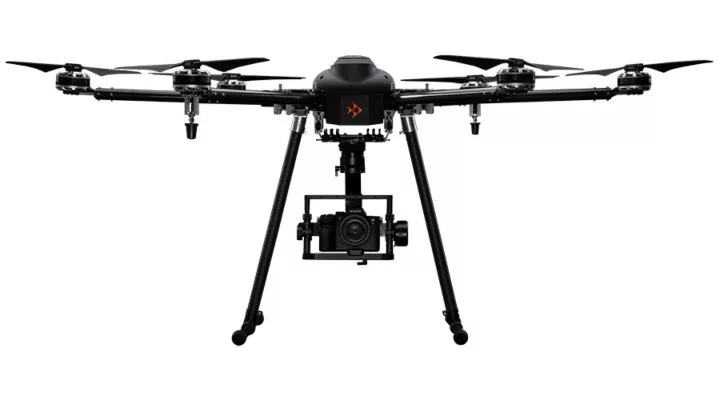

The Skyfish M6 can carry multiple types of payloads, including a LiDAR sensor
In addition to a large range of prices for sensors, the cost of the drone itself and any compatible software quickly adds up, especially for a hobbyist, making purchasing a LiDAR enabled drone quite the investment.
If you’re looking for an all-in-one system or a full service LiDAR solution, the cost is even steeper, with rental prices alone reaching a couple thousand dollars a month.
However, LiDAR tech that used to cost thousands of dollars now only costs a couple hundred, and, within the few years, even these LiDAR sensors will begin to drop in price.
As discussed above, LiDAR drones and their associated sensors can potentially save millions of dollars across a number of different sectors, so as the cost of entry continues to plummet, it’s all but certain that LiDAR drone technology will continue to be implemented across a number of industries.