- Blog >
- 8 Key Benefits Of Drones For Wastewater Inspections
8 Key Benefits Of Drones For Wastewater Inspections
The deployment of drones for wastewater inspections can bring massive improvements in terms of safety, time, and cost-efficiency. Here's our list of the top 8 benefits of using drones for wastewater inspections.
Traditionally, sewer management companies rely on three different methods for conducting wastewater inspections. These methods are:
- Manned entry
- Raft or sled-mounted remote inspection, typically using CCTV cameras
- Robotic inspection, using CCTV cameras and/or other types of sensors (LiDAR, SONAR, and others)
Manned entry can help inspectors collect detailed data on the condition of the asset but presents safety concerns. It is also impossible in certain scenarios, due either to access issues or to the inability to get temporary bypass of flows.
CCTV on a raft or sled is one of the most common methods sewer inspectors use to collect visual data remotely. But once the camera is in the water there is no way to control where it’s pointed or how fast it moves through the system, and this lack of control leads to unreliable data capture.
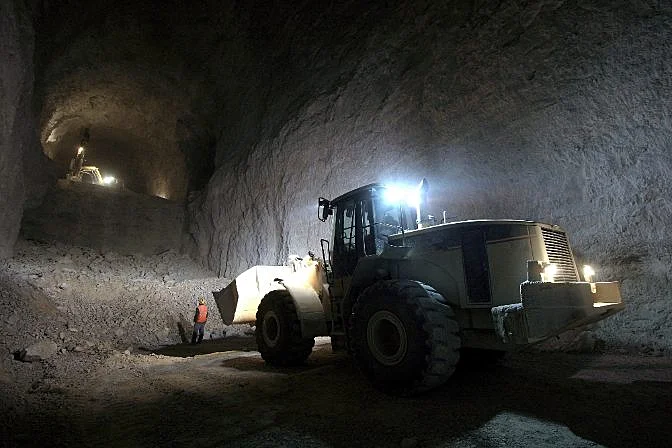
Robotic solutions with multi-sensor platforms (CCTV, SONAR, laser profiling, or LiDAR) can yield a huge amount of data, but are often very expensive. And their size can present significant issues with access—most robots used in sewer inspections are so big they need to be lowered into the sewer system with a small crane.
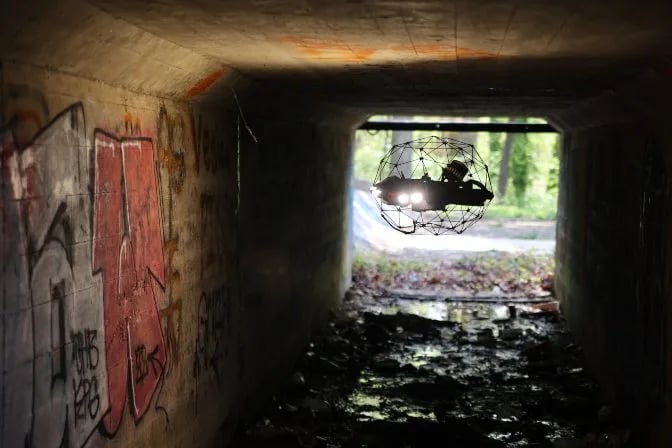

Indoor drones like the Elios 3 (pictured above) present a fourth solution.
Small, stable, and easy to control even in high flow conditions, a drone like the Elios 3 can enter a wastewater system and collect high quality visual data without any advance preparation, and at a relatively low cost.
Here are eight ways that indoor drones are changing wastewater inspections for the better.
1. Savings
Drones help make wastewater inspections more efficient by removing the need for inspectors to physically enter sewer systems, thereby eliminating extra personnel costs and helping inspectors realize significant savings.

Drone pilots preparing for a sewer inspection mission
Péter Kövessi, former Director of Client Services at Flind—a company that helps oversee the massive sewer infrastructure in the city of Barcelona—estimates that wastewater infrastructure inspections conducted by drone are twice as efficient as human inspections and 40% less expensive per meter of inspection.
Drones also have the potential to eliminate the need for using expensive robotics solutions like those described above, which can help inspectors realize even more savings.
2. Safety
The type of confined space entry required for wastewater inspections always presents a certain level of risk to inspectors.
In addition, sewers present specific safety hazards to inspectors in the form of rushing water and the potential presence of noxious gases, such as Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S). In some cases, inspectors must use scuba gear outfitted with PPE to protect them from the presence of raw sewage in order to conduct their inspections.
[Related reading— Safe sewer inspections in Sydney with the Elios 3]
Using an indoor drone to collect visual data can reduce or even eliminate the need for inspectors to enter a sewer system, vastly improving safety for the inspection process.
3. Data Localization
Another drawback to using CCTV or robotics solutions for collecting data within wastewater systems is that it can be hard to pinpoint the exact location of a defect identified by these methods—inspectors may see something that needs to be fixed, but they can’t always tell where it is in the asset.
But identifying a defect is only half the job of an inspection.
Inspectors also need to be able to tell their clients where defects are located in a way that can be shared with others, so that the defect can be evaluated and maintenance can be performed quickly and efficiently.
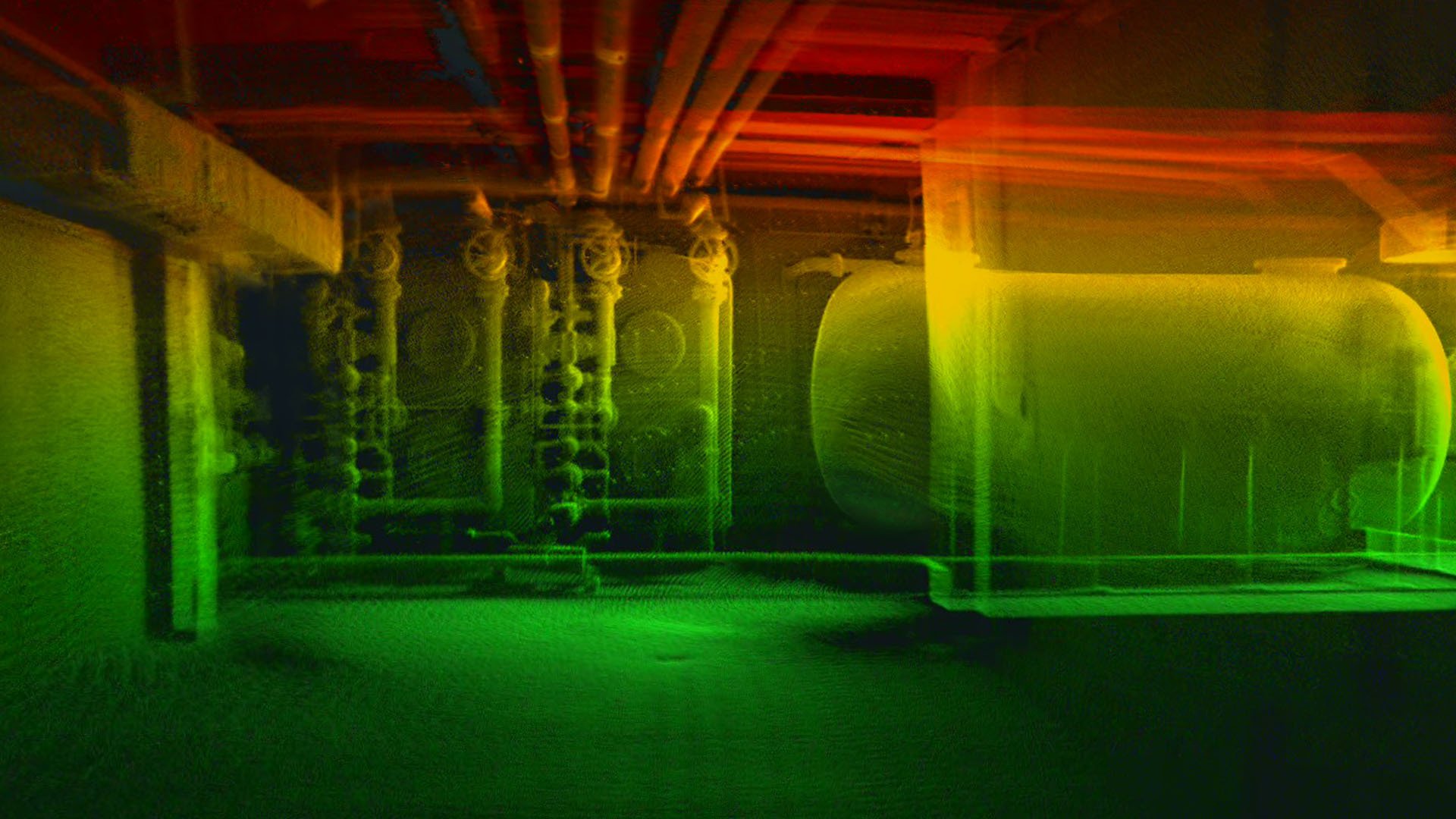
Flyability’s Inspector software allows inspectors to pinpoint the location of defects identified during inspection flights.
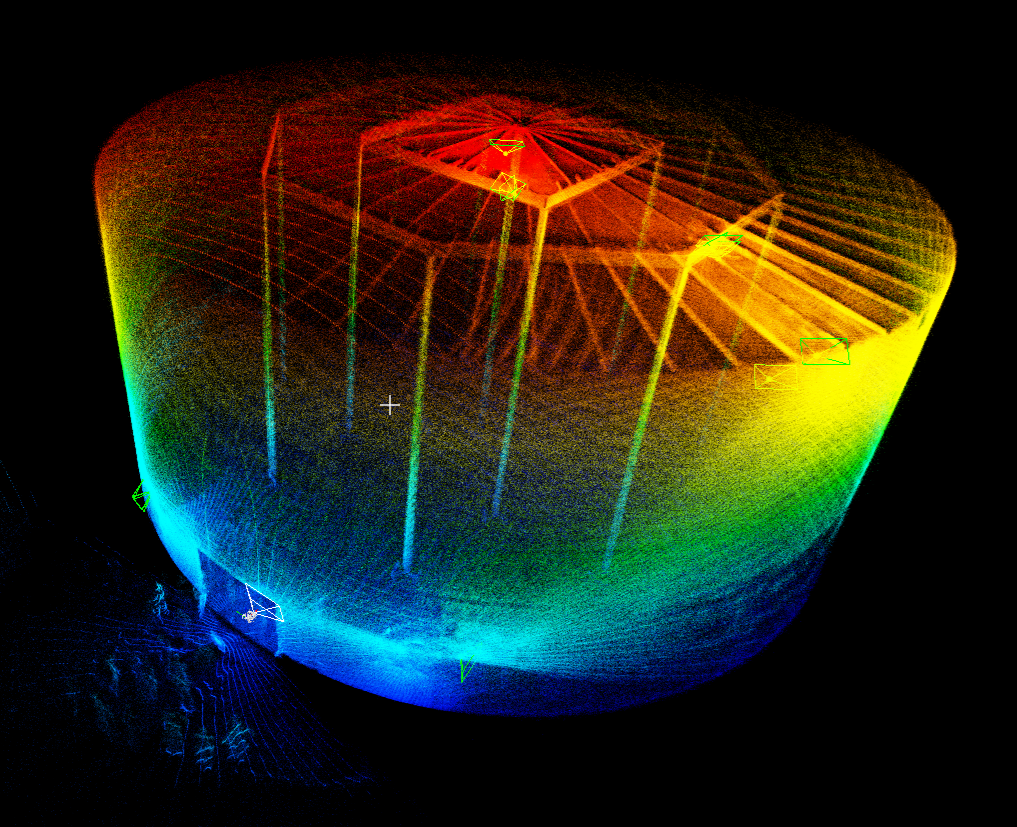
A point cloud of a sewer pipe created using Inspector
This data comes in the form of sparse point clouds that provide accurate, detailed data about the locations of defects found during a mission. These point clouds have highly accurate data, with the Elios 3's Surveying Payload achieving point clouds accurate to 1 centimeter, which allows wastewater inspectors to measure the size of the defects and pinpoint where further investigation or attention is required.
4. High Quality Visual Data
The quality of the images and video that can be captured using a drone is much higher than what can be captured using CCTV or other more expensive robotics solutions.
Inspectors working in wastewater systems have reported using the Elios 3 to capture “crystal clear” media of a quality they’ve never been able to achieve before. The Elios 3 has a 12MP camera and can capture video in 4K, providing a high level of detail that allows for remote close visual inspections.

The powerful lighting on the Elios 3 enables it to provide clear visual data for pilots doing wastewater inspections
A few other elements that contribute to the high quality of the drone’s images and videos are:
-
Lighting. The Elios carries 10'000 lumens of light, enough for it to light up a dark sewer system so that inspectors can see every part of it.
-
Camera control. Inspectors can control the speed and angle of the camera, swivelling 180 degrees up and down, allowing them to capture exactly what they need for inspection purposes.
-
Drone control. Inspectors can hover in one location, or fly back in order to investigate a defect further, allowing them to capture as much clear, high quality video footage of an area as they need.
-
Lighting control. Lighting can be shifted to provide an oblique lightsource that reveals pitting and depth, similar to the effect of an inspector moving a flashlight around the surface of an object.
5. Access
Manned entry is just not feasible in some wastewater inspection scenarios due to access requirements or to the need to temporarily bypass flows, which could be cost prohibitive or simply impossible (as in large diameter or trunk sewers). Robotic solutions also can’t enter some sewer inspection systems due to size limitations.
But the Elios can access sections of sewer systems through manholes and other small entry points, allowing inspectors to collect stable, high quality visual data regardless of access issues. The Elios 3 can enter spaces as small as 50x50 cm with ease.

An inspector controls an Elios drone inside a sewer system from the surface
6. Extended Range
The RVI techniques we mentioned above, like floating a CCTV or other type of camera from one manhole to another, can present range limitations, which can limit their usefulness in certain inspection scenarios.
Flyability’s Range Extender allows its indoor drones to fly farther from the pilot in order to perform inspections with greater efficiency. This can be vital when flying inside prolonged tunnels or areas inside wastewater assets where signal can be poor or obstructed.
The Elios 3 can fly in associated wastewater systems such as culverts or large drainage tunnels alongside sewers
7. Stability—Even in High Flows
Drones like the Elios are not only small and easy to deploy for wastewater inspections, but they’re also very stable in flight.
The Elios has been used in a wastewater system where the water was roaring through at an average velocity of 26 feet per second—a speed so fast that the power of the water generated airflow in the space between the water and the pipe that created turbulence for flying. Despite the high rate of flow the Elios remained stable in flight, capturing images and video for inspectors that were so clear they were able to completely eliminate the need for an inspector to enter the sewer.
.jpg?width=900&height=675&name=sewer-inspection-drone-shot%20(1).jpg)
An image taken by the Elios in a high flow wastewater system
8. Reduction of Emergency Response Time
Drones can help significantly reduce the amount of time it takes to identify the cause of a problem during a sewer emergency. This is because drones can be deployed quickly and easily, requiring fewer pre-deployment safety checks than traditional inspection methods. This means that in the case of a leak or tunnel collapse, the drone can be sent into the wastewater system for an inspection as soon as the pilot is on-site, providing immediate situational awareness and helping responders plan the next steps as well as determine if it is safe for people to enter the space.
For example, in Barcelona inspectors were faced with an urgent problem when a wastewater interceptor that served five different municipalities broke suddenly during a severe storm.

An inspector in Barcelona placing a drone into a manhole
Every moment counted in this emergency, since the damaged pipe was leaking raw sewage into the sea at a rate of 500 cubic meters per second. Although the broken pipe was ten feet in diameter, there was no way for inspectors to enter it because sewage was pouring out at such a rapid rate.
Inspectors were able to fly an Elios drone into the pipe through intact manholes, both upstream and downstream of the visible break, and quickly survey the entire area to identify the exact location of the break and extent of the damage.
Using this information, experts on the scene were able to ensure that the bypass was connected at the correct place to quickly stop the flow of waste into the sea and to avoid the risk of a future break.