- Case Studies >
- Sewer Inspections by Drone: How Suez RV Osis Uses the Elios...
Sewer Inspections By Drone: How Suez RV Osis Uses The Elios 2 To Ensure 100% Coverage When Inspecting Wastewater Infrastructure
Inspectors at Suez RV Osis are using the Elios 2 indoor drone to get full coverage in its sewer inspections. Here's how they're doing it.
Suez RV Osis is a company based in France that provides waste management services.
As part of its work, inspectors from RV Osis conduct periodic inspections of wastewater infrastructure. These inspections take place throughout the country, in both urban and rural environments.
The diversity of locations means that inspectors must know how to work in a variety of conditions, from huge citywide sewer systems to old systems in the country made out of masonry, which run directly under people’s homes.
These sewer inspections are crucial for the maintenance of the wastewater systems because they help:
-
Identify clogging in pipes through the accumulation of material or sediment.
-
Assess the current functionality of the network.
-
Identify any potential structural problems that could cause a collapse of masonry and lead to the failure of the sewer network.
French Law Requires Wastewater Inspections In All Major Cities By 2026
Sewer inspections are more important than ever in France right now because of a new national law that requires all major cities in the country to have their wastewater infrastructure inspected and diagnosed by 2026.
The law has put tremendous pressure on cities, making them turn to experts in the field like Suez RV Osis for help.
In Toulouse, for example, there are 2,229 miles (3,700 kilometers) of sewer pipes that must be inspected. The work has already started there, but the effort is massive and requires a huge team and budget for execution.
The pressure of compliance with the national law as well as advances in RVI (Remote Visual Inspection) technology have helped drive innovation at Suez RV Osis when it comes to how sewer inspections are conducted.

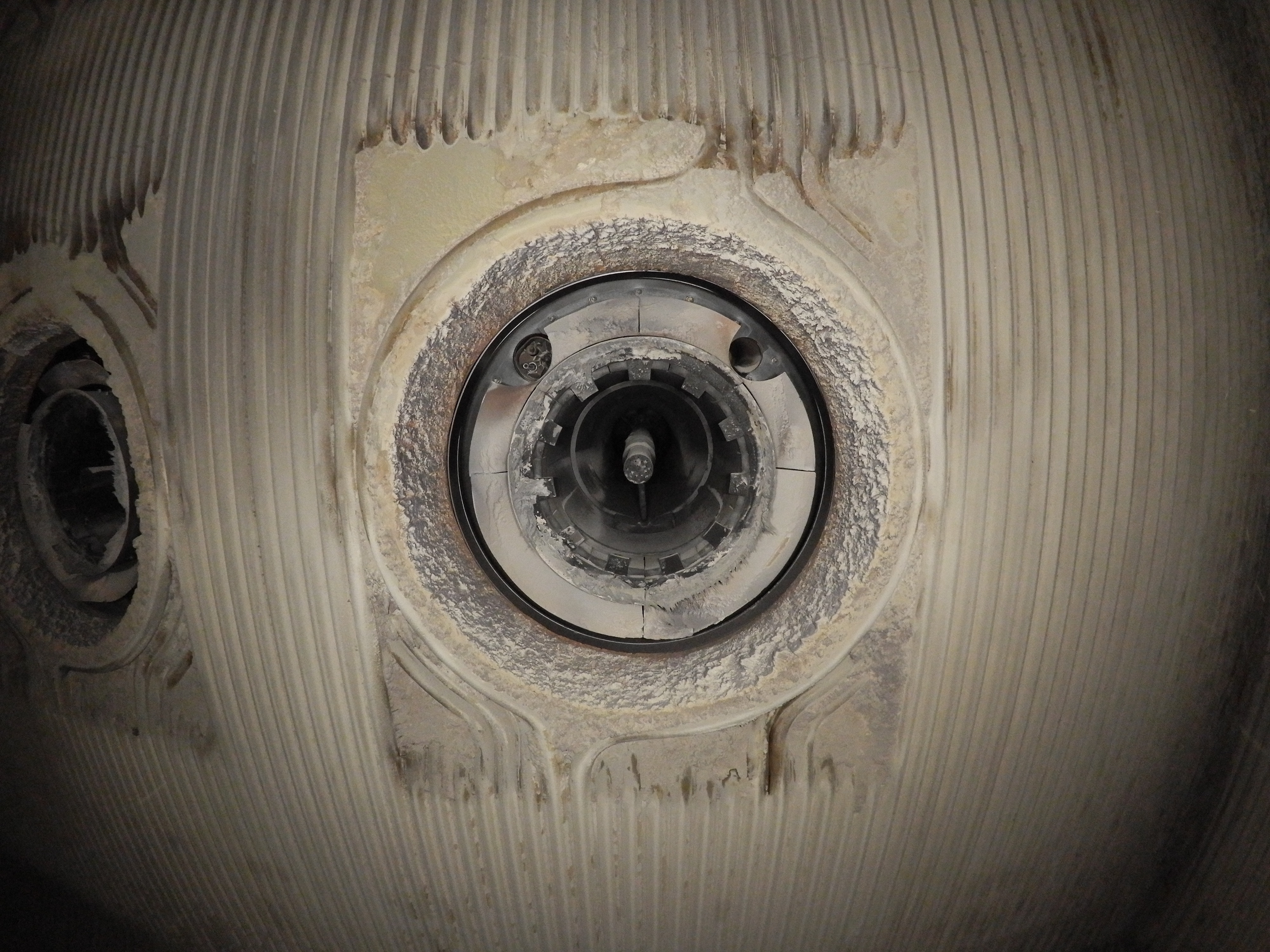
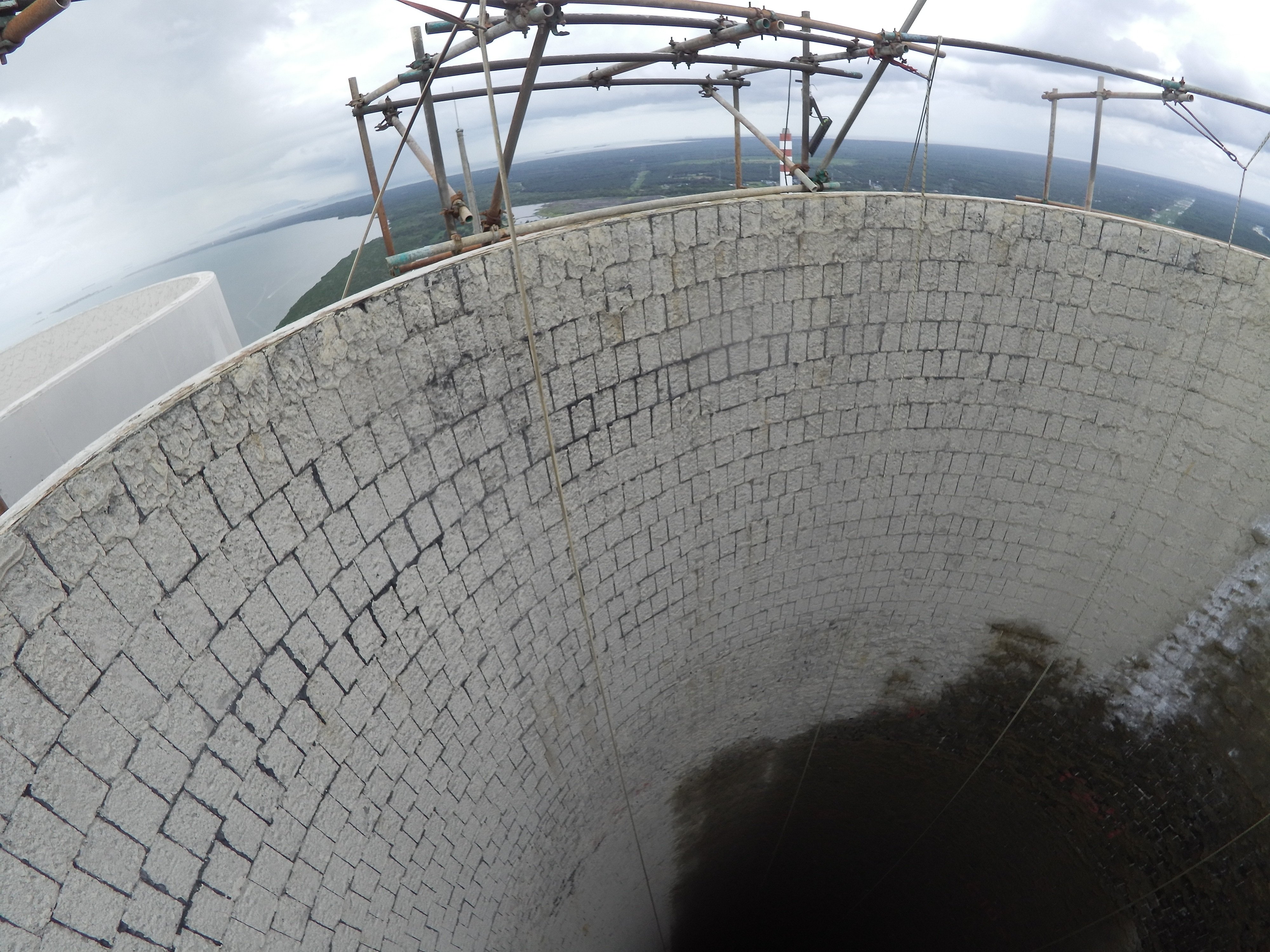
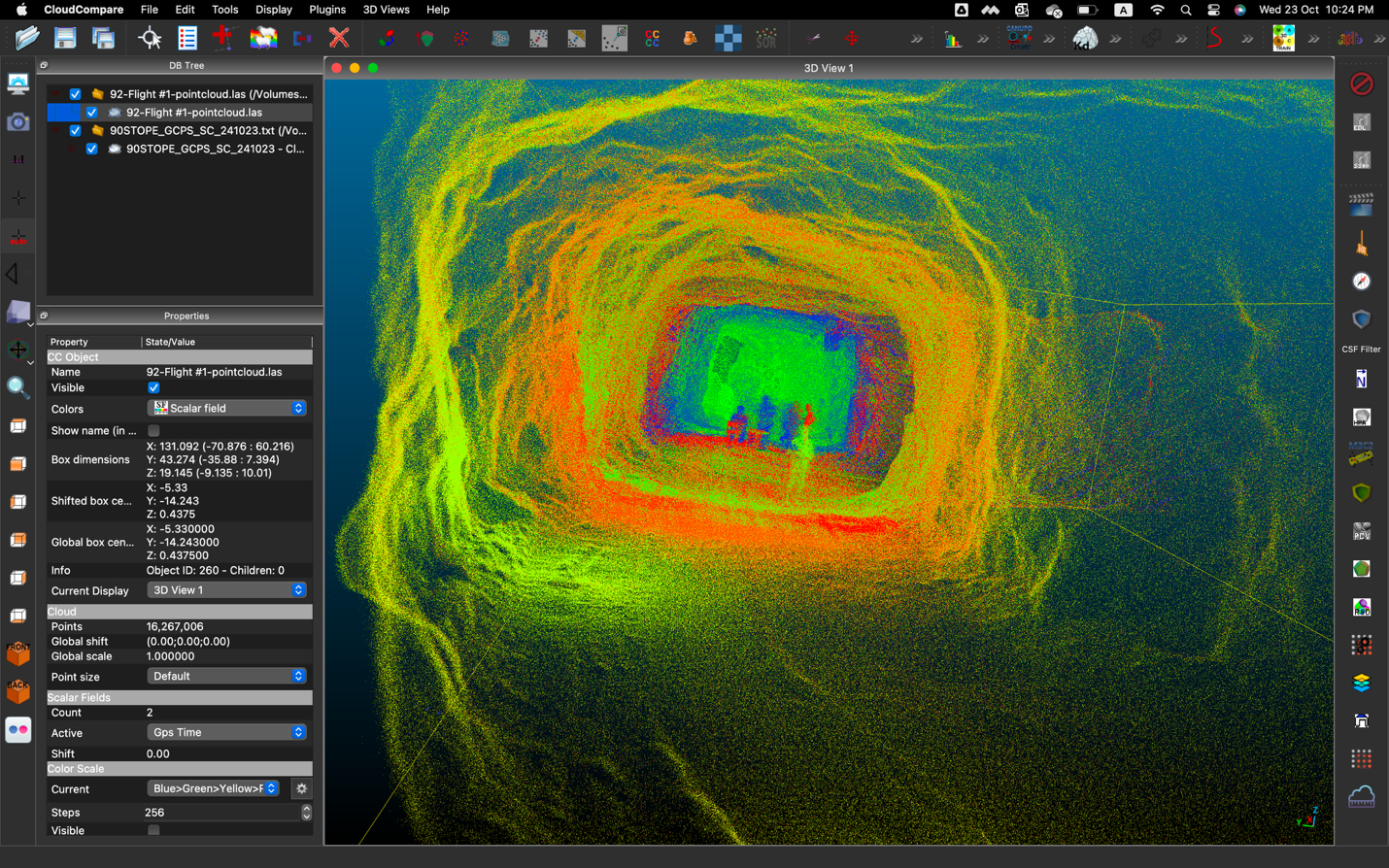
A picture taken by the Elios 2 during a Suez sewer inspection
Traditionally, inspectors at RV Osis have used a variety of methods to collect visual data inside sewers. These include using dollies or carts to roll a camera through a pipe, floating a CCTV camera inside the pipe, or having an inspector go through the pipe in person with a camera.
But these approaches are limited, and are only useful up to a certain point.
This is especially true for manual data collection, since many of the pipes that Suez personnel inspect present a significant danger for entry due to:
-
The risk of collapse caused by premature wear of the masonry
-
High water levels caused by heavy rains
-
Slippery areas, which increase the chances of falling
-
The potential presence of harmful gases like Hydrogen sulfide (H2s)
Because of these limitations, only about 80% of the wastewater systems that Suez oversees can be inspected using traditional methods.
Suez RV Osis’ Groundbreaking Work With Innovative Technologies
So how does Suez RV Osis inspect the remaining 20% of wastewater infrastructure?
By using innovative technologies, such as flying and floating drones, as well as special rovers. RV Osis is a leader when it comes to adopting new technologies for wastewater inspections, and it has invested heavily in using innovation to improve its data collection processes.

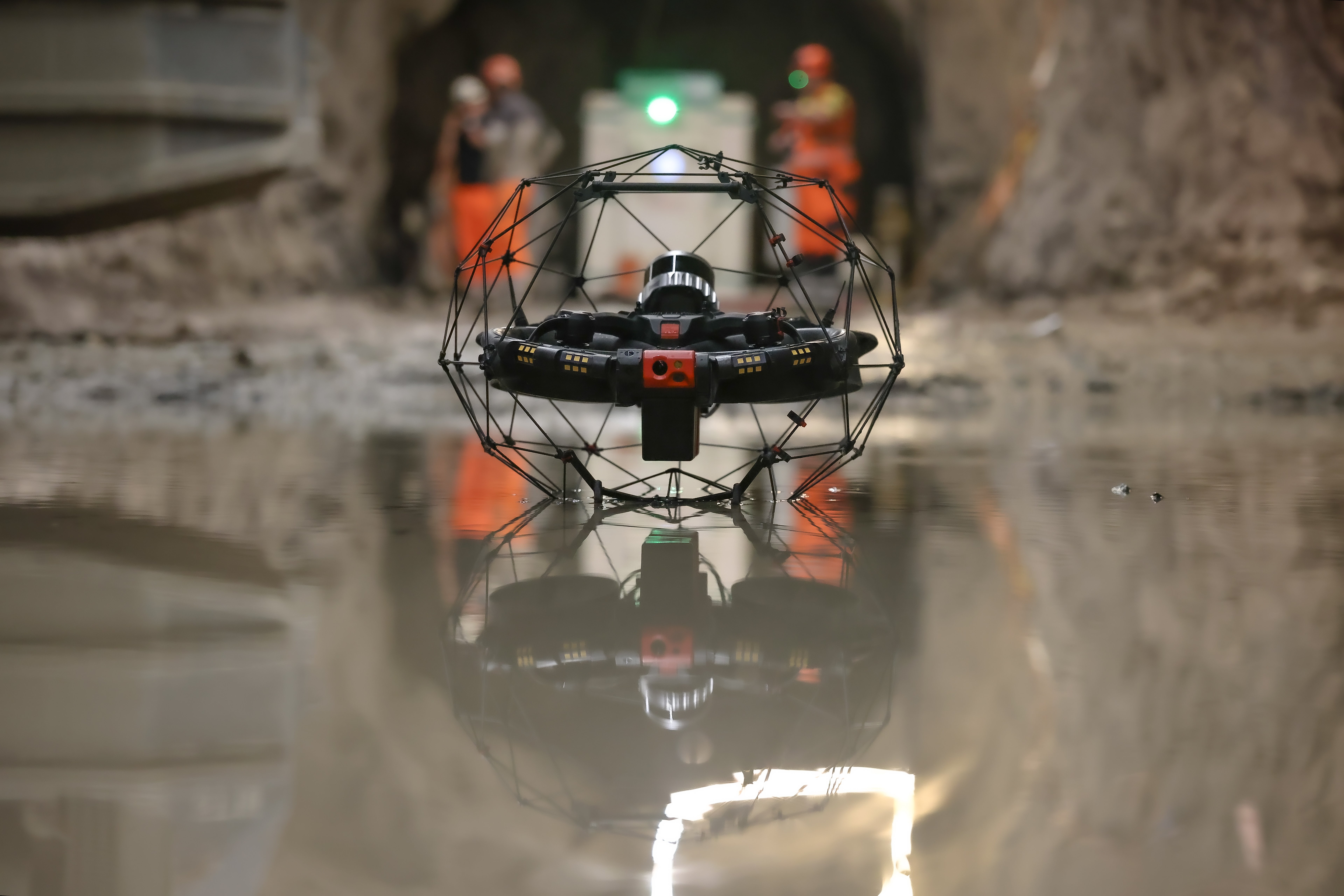
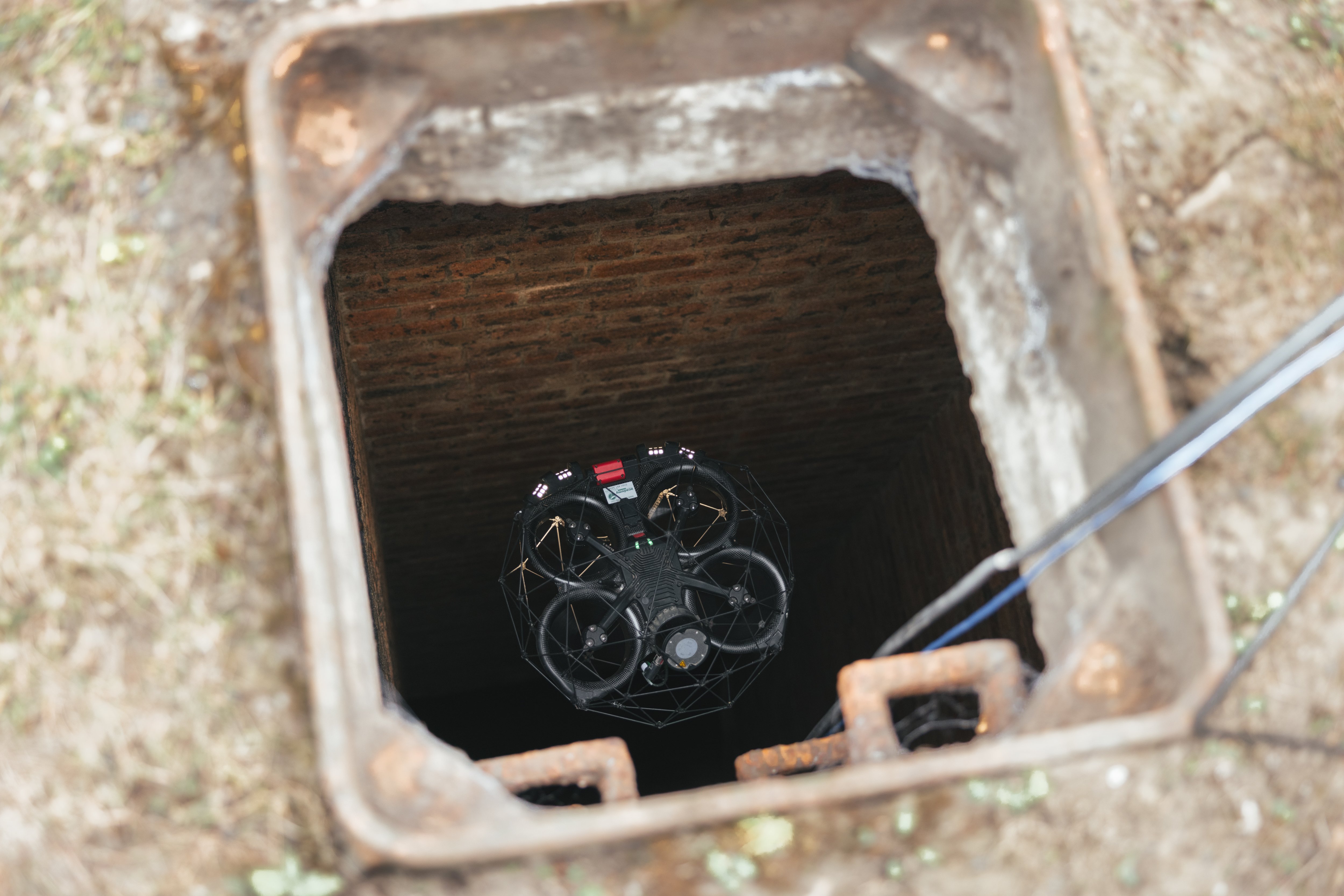
One of the tools Suez RV Osis uses to collect visual data inside pipes is Flyability’s Elios 2, which can provide inspectors with remote access to areas that present dangers to inspectors for direct entry.
“We have been using Flyability’s Elios drones since they first came out. We have found them perfect for sewer inspections.”
- Phillipe Bonnin, Drone Development Manager at Suez RV Osis
The Elios 2 sits in a cage, which allows it to collide with walls or small obstacles without the risk of damaging the drone—or the structure. The latter point is important, since Suez RV Osis is often operating in confined spaces with brittle masonry that could break if struck too hard, potentially causing the entire structure to collapse.
[Related read: 8 Key Benefits of Indoor Drones for Sewer Inspections]
The Elios 2 allows the Suez team to get 100% coverage of its sewer networks, and it also accelerates the rate at which it can do inspections.
Using traditional methods, Suez inspectors can inspect about 400-600 meters (1,312-1,968 feet) of wastewater infrastructure a day. But with the Elios 2, it can inspect up to 900 meters (2,952 feet) a day, increasing its inspection speed by anywhere from 50% to more than double what it can achieve using traditional methods.
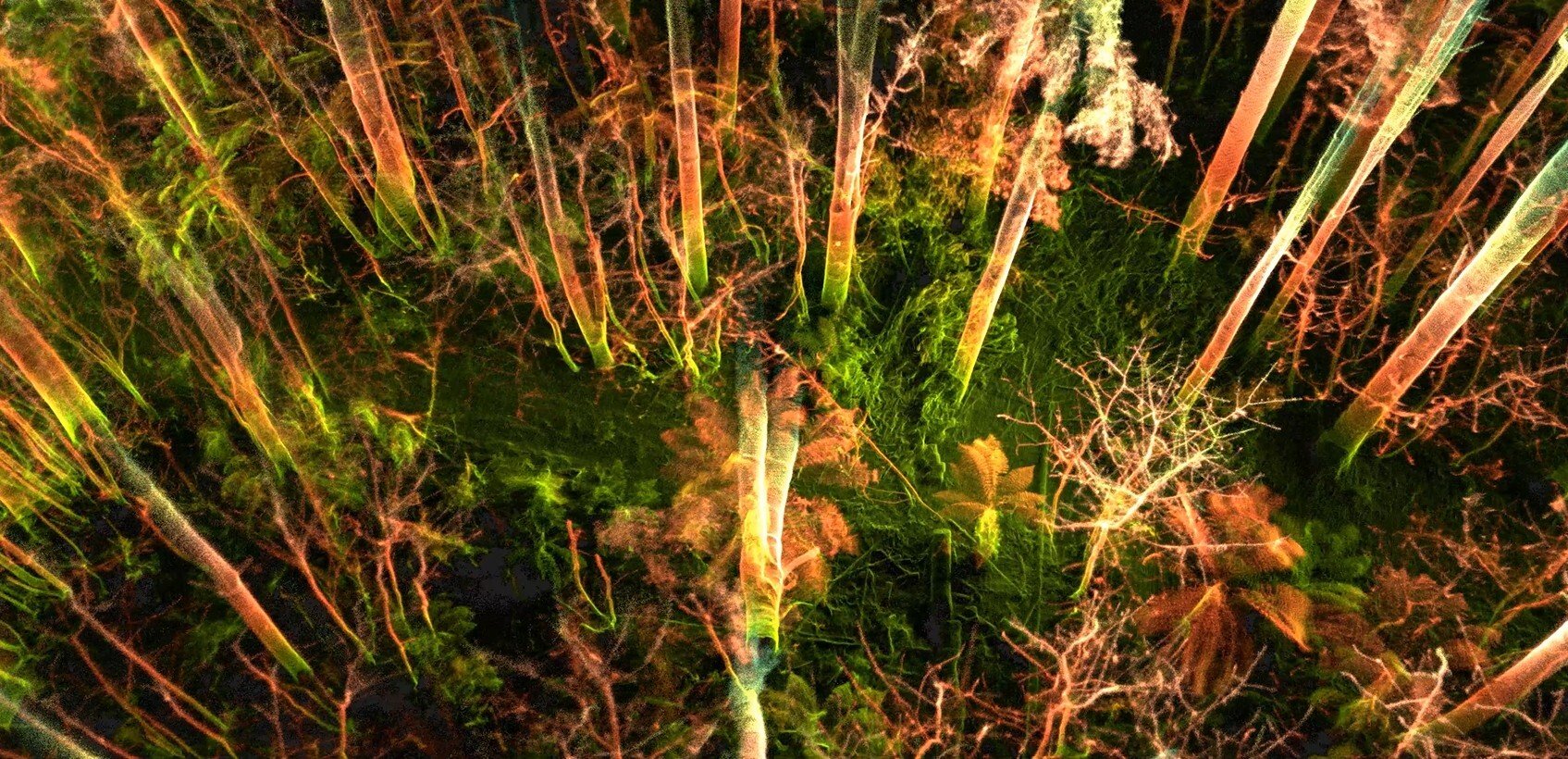
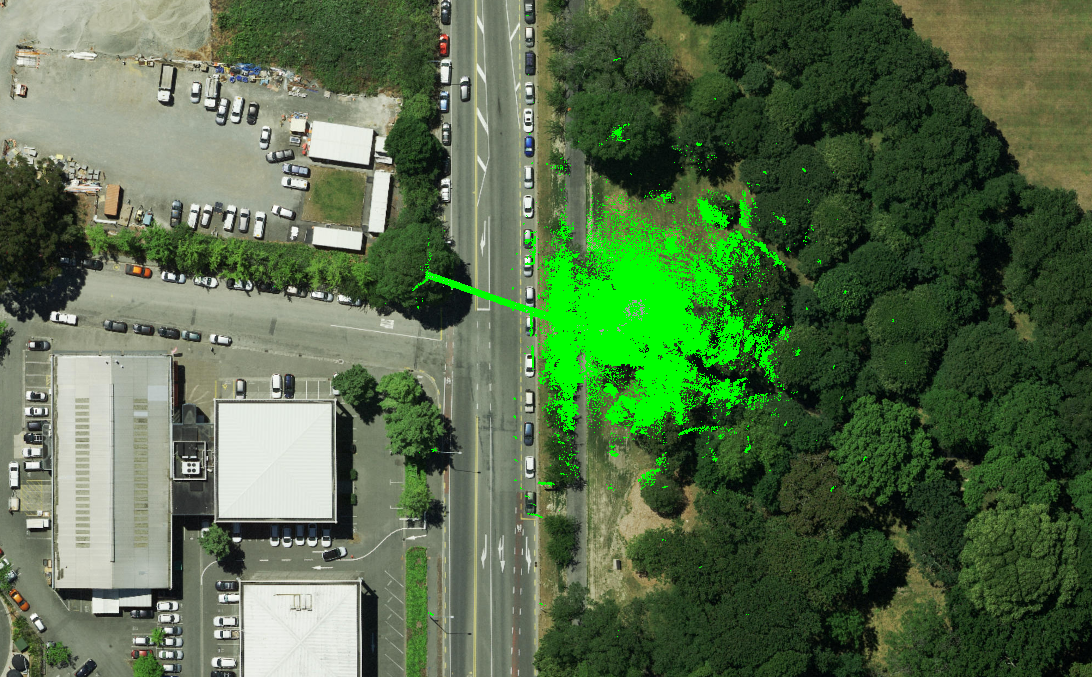
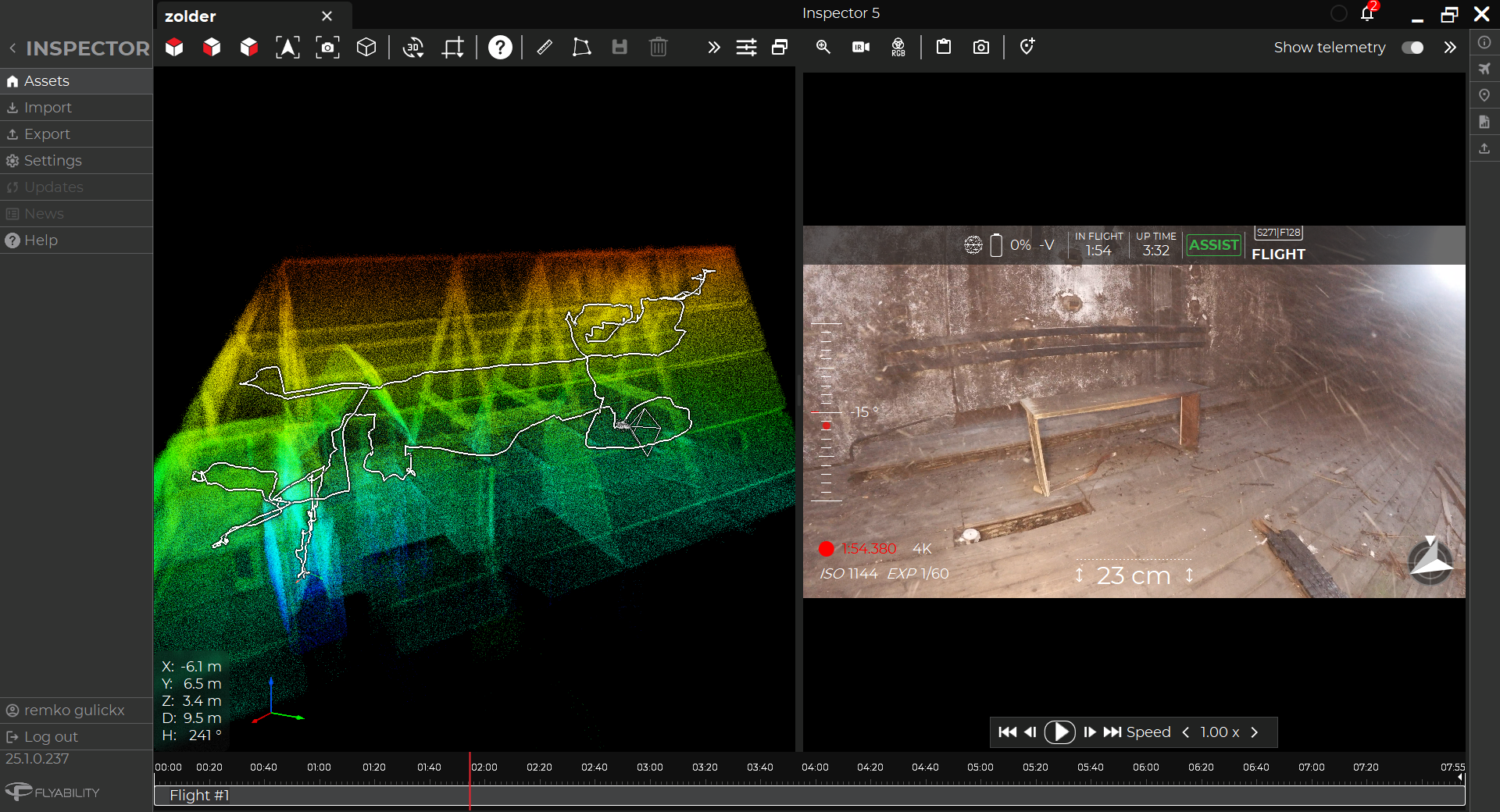
RV Osis has also been experimenting with using Flyability’s new software Inspector 3.0 to pinpoint the location of defects found in visual footage collected by the Elios 2.
Using sparse points clouds generated by the software, inspectors can pinpoint the specific place in a pipe that requires maintenance and share that information with other stakeholders in the maintenance process. The precision of the locational data provided by Inspector 3.0 allows RV Osis’ clients to dig right to the place that requires maintenance, without having to waste time digging to the wrong place.
How Suez Plans Drone Missions For Sewer Inspections
Although drones are useful for collecting visual data, they are just one tool in the inspection toolbox for the team at Suez RV Osis.

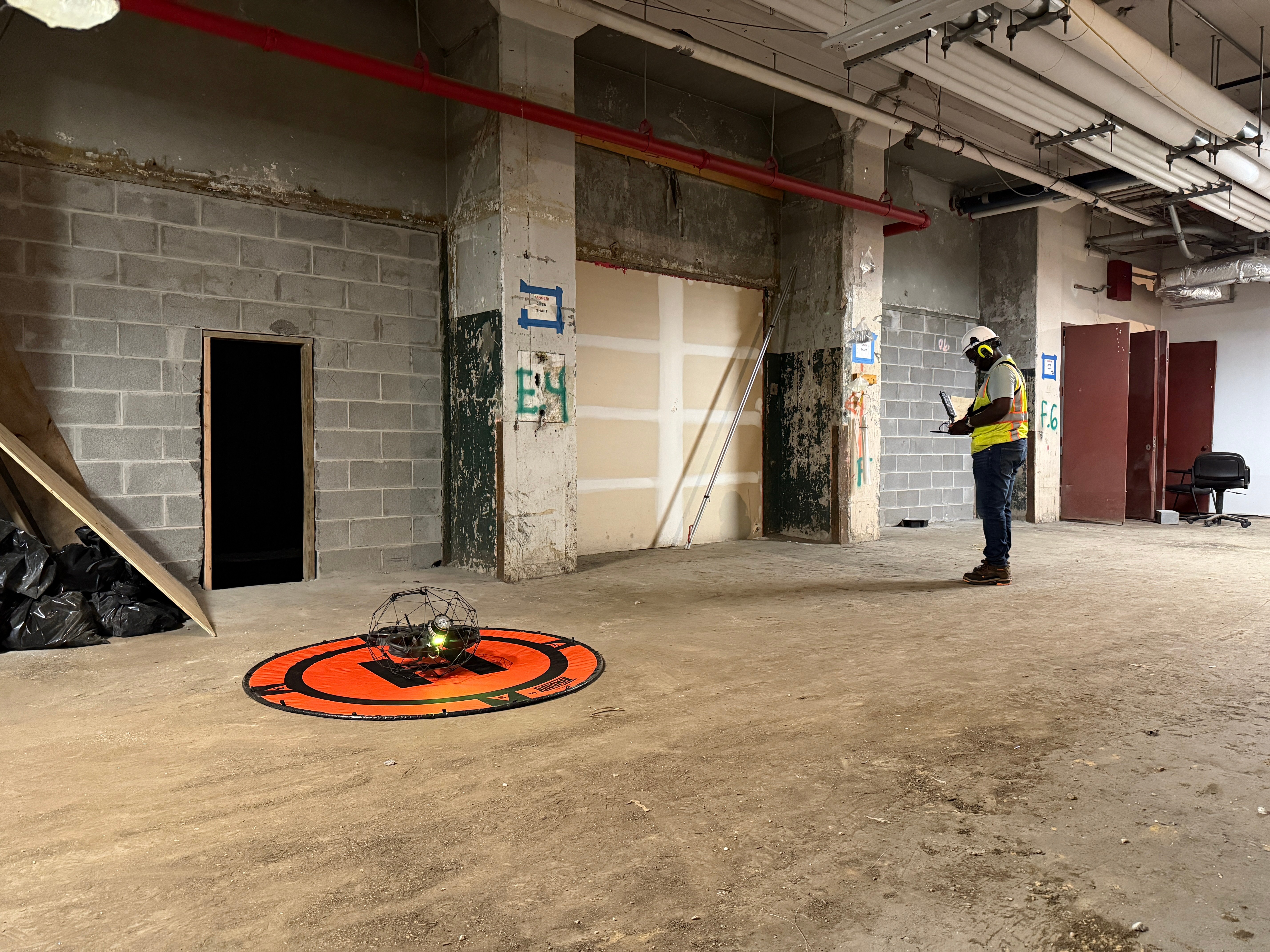
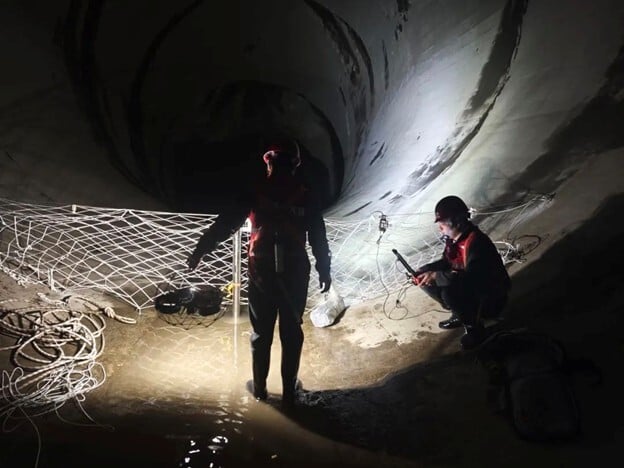
A drone pilot flies the Elios 2 inside a sewer during an inspection
The key skills that make RV Osis a leader in its field are what they do with the visual data they collect: diagnosing defaults by reviewing that data, and providing maintenance recommendations, as needed.
At RV Osis, the term “inspection flight” encompasses a series of steps taken by the inspection team:
-
Step 1: Upstream work & planning. To start out, pilots plan the flight with local inspection teams, including considerations about access, security, and the extent or need of aerial equipment (i.e., drones).
-
Step 2: The flight. When conducting an inspection flight, the drone pilot works closely with the wastewater inspector overseeing the inspection, ensuring that they’re getting all the visual data they need.
-
Step 3: Downstream work & reporting. After all the data has been collected for the inspection, inspectors process the data following a specific series of steps, including the use of photogrammetry to create 3D models where needed. This data is used to draft an official report following the national requirements, which includes the findings from the inspection.
To gain greater access within a sewer system Suez personnel will often use a range extender, which allows them to fly 150-200 meters (490-656 feet) within a pipe.
While in flight, inspectors look for structural and functional issues.
Structural issues are things like spalling, corrosion, cracks, or root penetrations in the system, and functional issues are problems related to the accumulation of sediment, sludge, or anything else that might get in the way of the proper operation of the system.
“The Elios 2 performs particularly well for inspecting underground structures like sewage systems thanks to the incomparable luminosity of its numerous LED lights. The lighting coupled with its high picture quality enables a flawless analysis of everything we need when we’re conducting a sewer inspection.”
- Phillipe Bonnin, Drone Development Manager at Suez RV Osis
Benefits Of The Elios 2 For Sewer Inspections
Here are the benefits the Suez team has realized by using the Elios 2 for sewer inspections:
-
Coverage. The Elios 2 helps inspectors get 100% coverage in Suez’s sewer inspections.
-
Speed. Using the Elios 2, Suez inspectors can increase the amount of wastewater infrastructure they inspect a day by anywhere from 50% to more than double what they can achieve using traditional methods.
-
Image quality. Because of its powerful lighting and high quality camera, the Elios 2 can provide Suez inspectors with the detail they need to make key maintenance decisions.
-
Data localization. Using Inspector 3.0, Suez RV Osis personnel are able to accurately pinpoint the location of defects, which is required by national regulations. This information is important for helping address a collapse, since maintenance workers will need to dig in order to fix the issue, making it crucial to know precisely where to dig in order to reach the area that needs to be repaired.
-
Personnel reduction. While a manual inspection can require as many as five people, using the Elios 2 allows Suez to reduce the total number of people needed for an inspection, sometimes to as few as just two people.


-Jan-16-2026-10-59-56-8006-AM.png)
.jpg)
.png)