Resources
Search our content by topic, type, industry, or whatever keyword you like.
Filter by Industries, Categories or Both.

Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
203585154711
125% more data in gold mine stope surveys with the Elios 3
-Jan-16-2026-10-59-56-8006-AM.png)
Case studies
|
Maritime
|
Oil & Gas
Maritime Oil & Gas
199902388079
CAN-USA and Shell Redefine Offshore Inspections with the...
.jpg)
Factsheets
|
Maritime
Maritime
204229780871
Discover Maritime Drones for Remote UT and Visual...

Factsheets
|
Oil & Gas
Oil & Gas
205365949272
Discover Oil and Gas Drones for remote NDT inspections
.jpg)
Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
203272401011
Inspecting Indoor Waterparks with the Elios 3
.png)
Case studies
|
Sewer
Sewer
202599713641
From Days of Work to a 30-Minute Flight for Oil Water...


Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
201807163781
Drone inspection cuts 300 hours of work in emergency...
-1.png)
Blog
|
Maritime
Maritime
201735712790
Get Certified with ABS to use the Elios 3 UT Drone for...

Webinar
200078497304
Flyability Cloud: Colorization, Feature Updates, and Live...

News
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
200936278284
Jaguar Land Rover Boosts Factory Safety and Efficiency by...



Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
199476167513
Inspecting Elevator Shafts with the Elios 3 in New york


News
|
Oil & Gas
Oil & Gas
198920126373
Saudi Aramco award the use of caged drones for internal...

News
|
Maritime
|
Oil & Gas
Maritime Oil & Gas
196863570522
From Ropes to Drones - A look into Shell and CAN-USA's use...

Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
197588999746
From 8 Hours to 20 Minutes for an Ore Pass Inspection with...










News
|
Maritime
|
Oil & Gas
|
Mining
Maritime Oil & Gas Mining
195106999201
Flyability Launches Tether Power Unit for the Elios 3 for...

Factsheets
|
Sewer
Sewer
194809428911
How Are Drones Reinventing Sewer Management Worldwide?

News
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
195050335881
The Elios 3 Wins Major Hong Kong Construction Safety Award


Factsheets
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
186969916440
Why are Power Plants Investing in Inspection Drones [Free...

Blog
|
Chemicals
|
Infrastructure
Chemicals Infrastructure
194410465623
Making inspections 50% faster for Nippon Steel Technology...




Webinar
|
Mining
{name=Mining, label=Mining}
192646748966
Uncovering the Role of Surveying Drones in Mining

Case studies
|
Food & Beverage
Food & Beverage
193189468336
ROI of Drone Inspections: How Cargill Successfully Deploys...

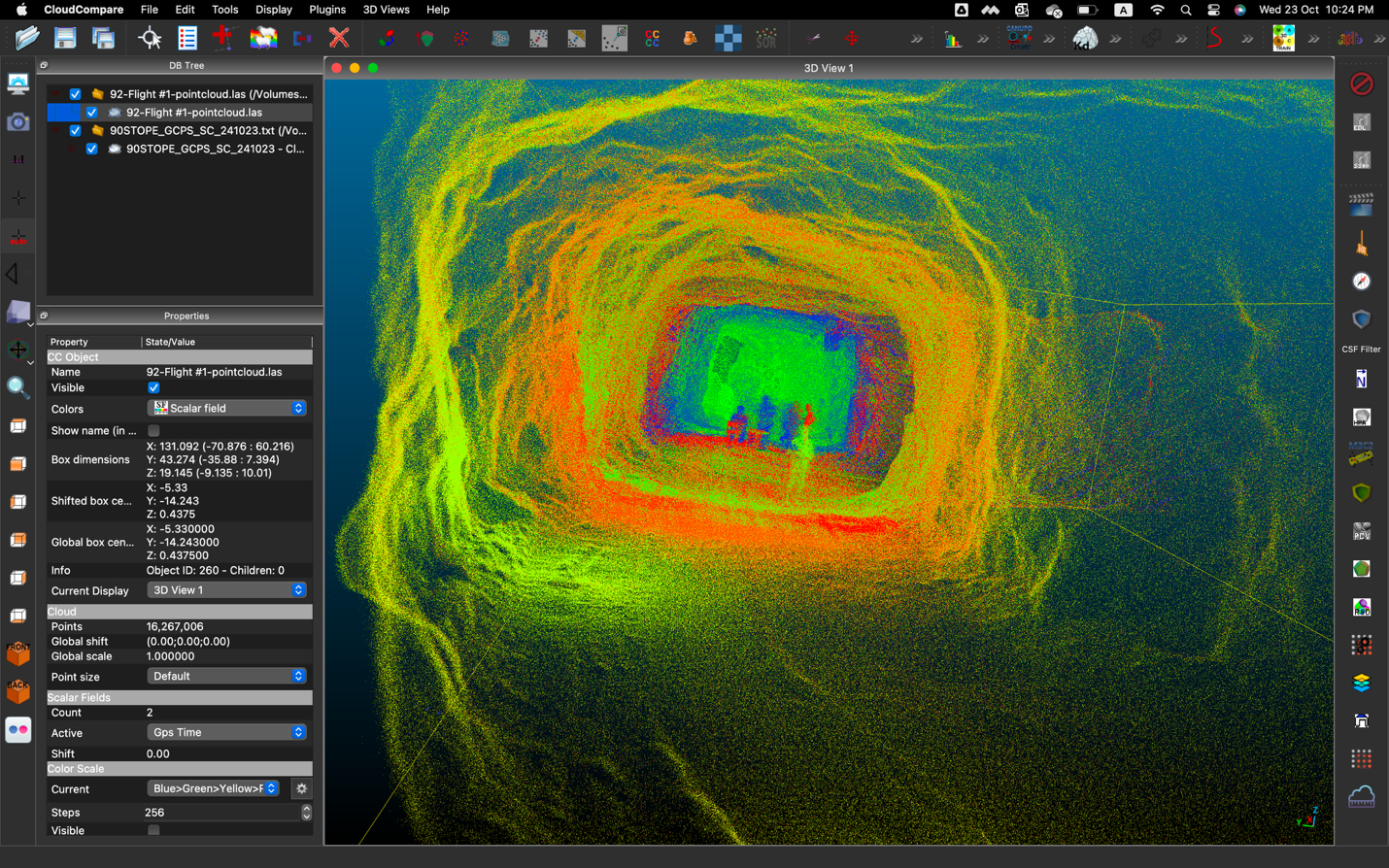
Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
192769032195
Saving $500,000 for Post-Blast Inspections at an...
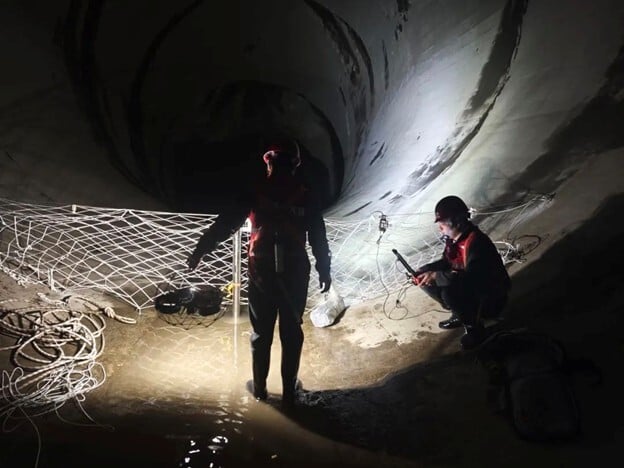


Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
192747228479
7-Minute Drone Penstock Inspections with the Elios 3

News
|
Maritime
Maritime
192510000948
Flyability wins the Safety and the Innovation Award from...

News
|
Mining
Mining
191707878750
Flyability announces new high-capacity batteries amid...
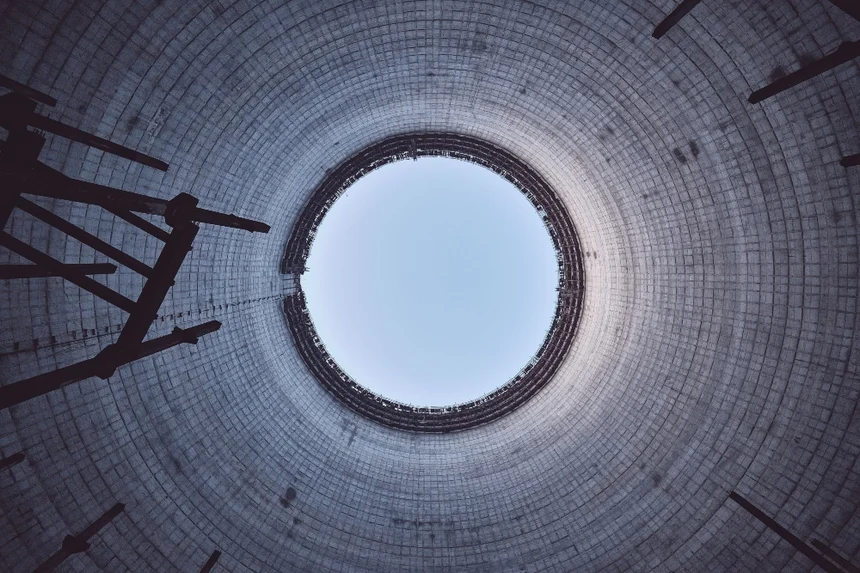

Blog
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
191709422714
How Drones are Improving Cooling Tower Inspections
White papers
|
Mining
Mining
190956009311
Guide: Volume Measurements with Leica Cyclone 3DR

Factsheets
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
186858295829
Penstock inspections with the Elios 3 UT drone
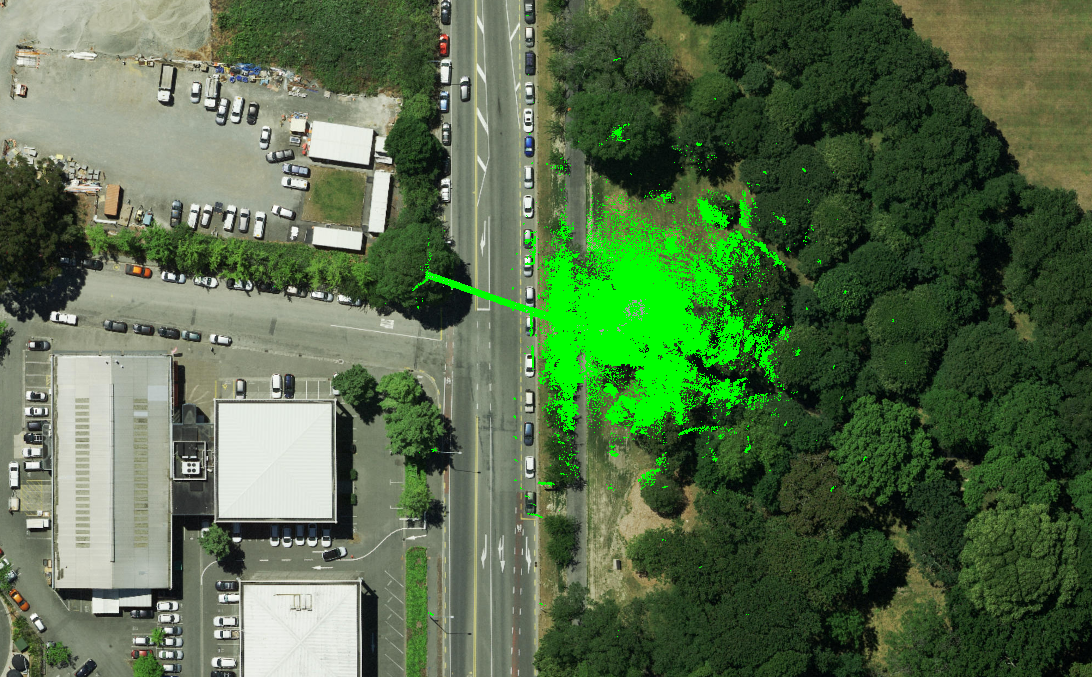

Case studies
|
Sewer
Sewer
190355450670
Inspecting 260 meters of stormwater drains with the Elios 3...
Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
190181392672
Safety First: Flying the Elios 3 Drone Inside a Burnt...

Factsheets
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
186856049847
Boiler Inspections with the Elios 3 drone

Factsheets
|
Power Generation
|
Nuclear
Power Generation Nuclear
187153919644
Condenser inspections with the Elios 3 UT drone

Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
189292963632
Saving 450,000 Euros on Boiler Inspections with the Elios 3...
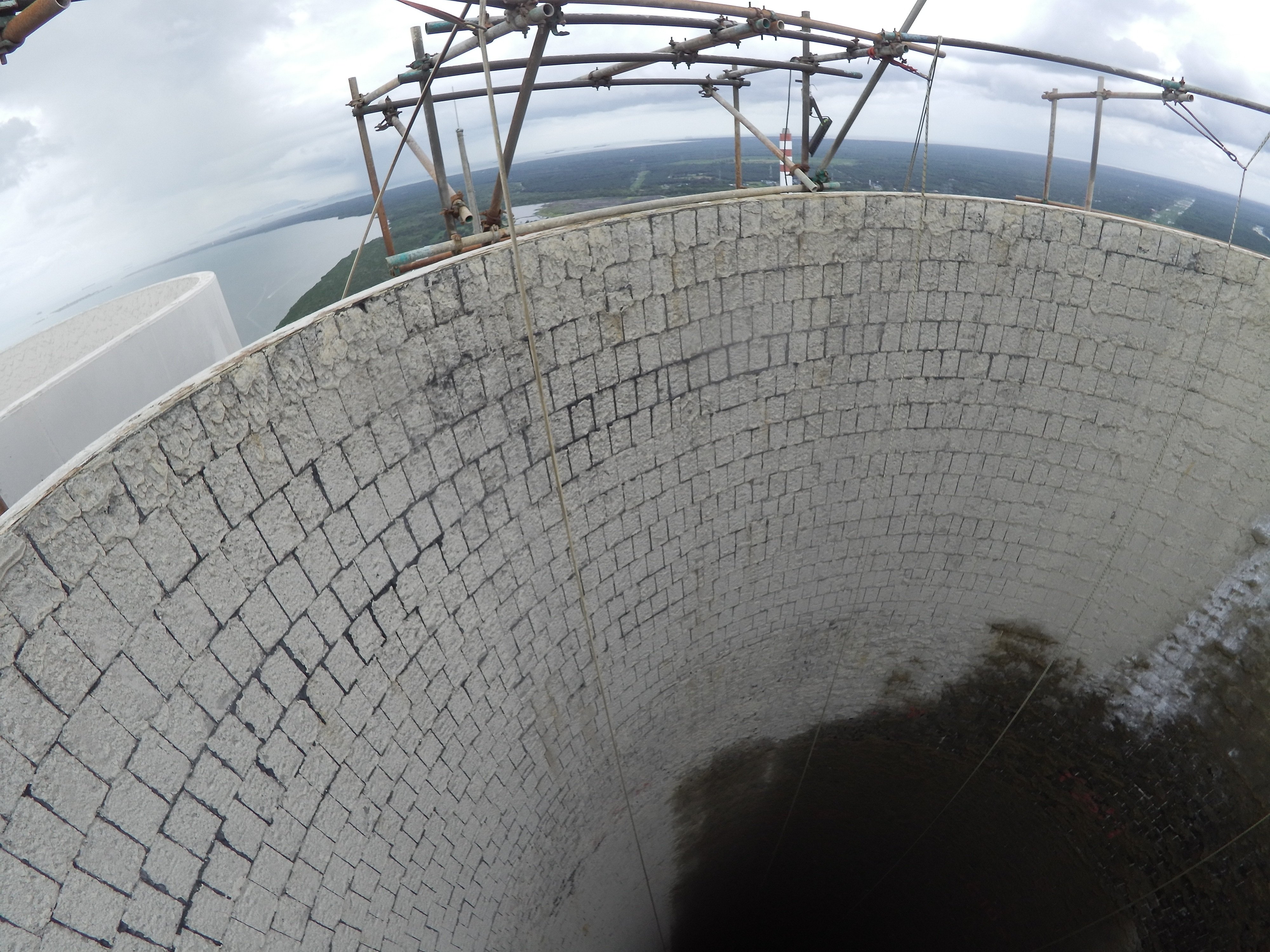

Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
188852414099
Saving 20% on Stack Inspections with the Elios 3


Blog
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
188723047959
Lighting Up: The Benefits of Drones in Power Generation

News
|
Maritime
Maritime
188478880636
Flyability Awarded Innovation Endorsement Certification by...

Factsheets
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
187969593231
Wind turbine blade inspections with the Elios 3 drone


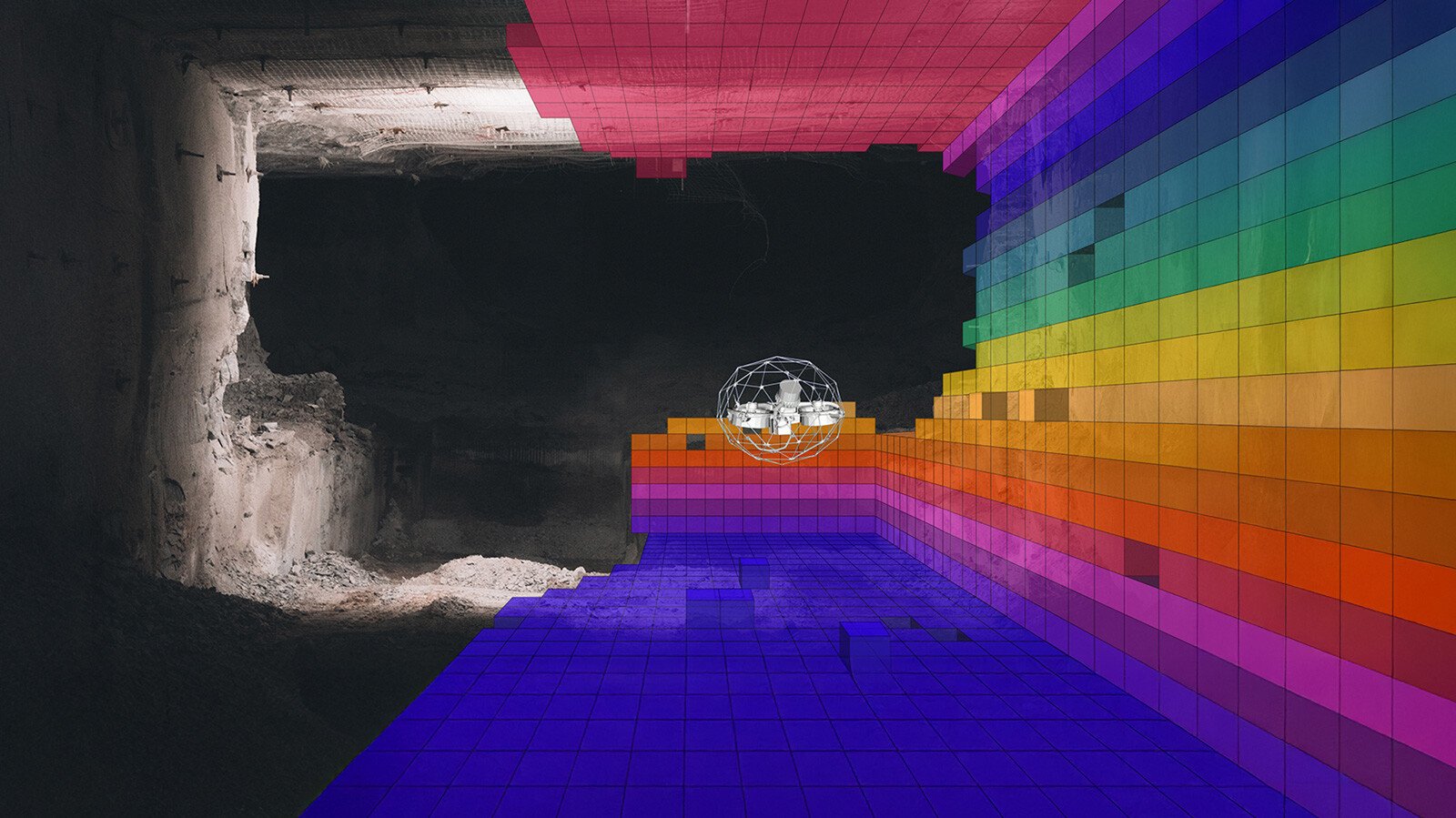

Webinar
|
Power Generation
{name=Power Generation, label=Power Generation}
187222447652
Wind Turbines and the Elios 3: Seeing More

Blog
|
Power Generation
|
Nuclear
Power Generation Nuclear
186336255113
10 Elios 3s and Counting: How Dominion Energy Set Up a...

White papers
|
Mining
|
Infrastructure
Mining Infrastructure
187493394294
Whitepaper: Accuracy Report on the Elios 3's LiDAR Payloads

White papers
|
Cement
|
Infrastructure
Cement Infrastructure
187491266838
Guide: Manual for Scan to BIM with the Elios 3
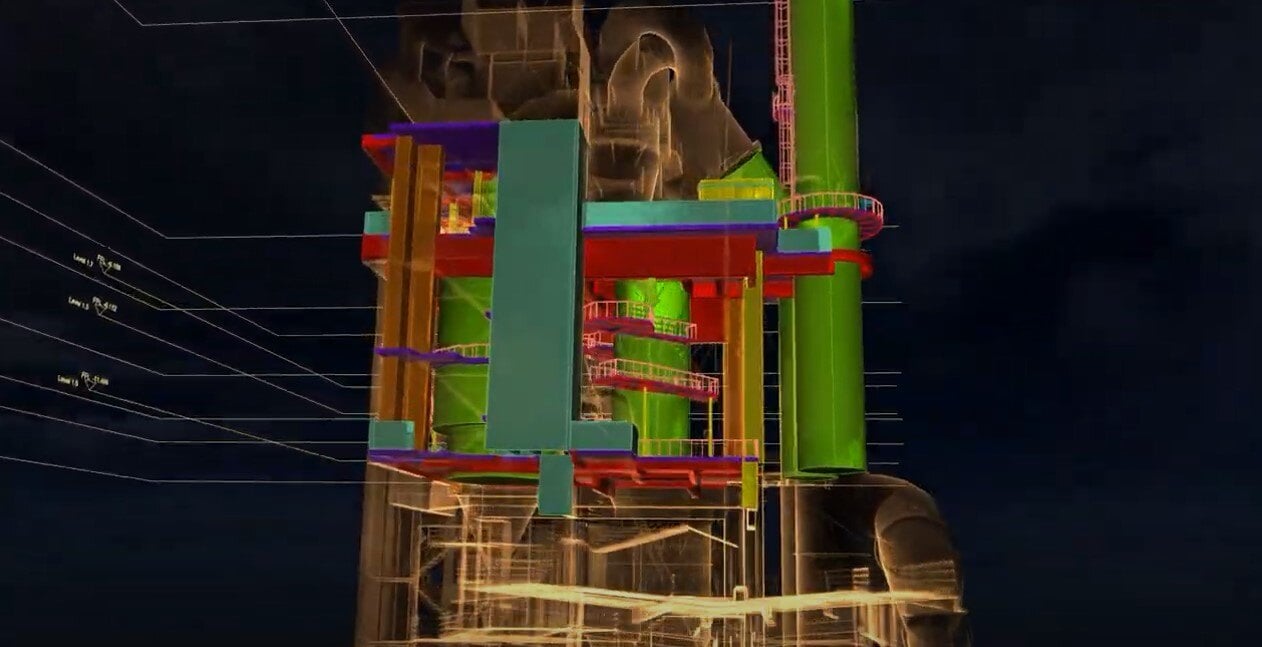
White papers
|
Cement
|
Infrastructure
Cement Infrastructure
187486153893
Whitepaper: Assessing the Elios 3’s for Scan to BIM

Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
187449484869
Drones for Mining in South Africa: An Interview with...

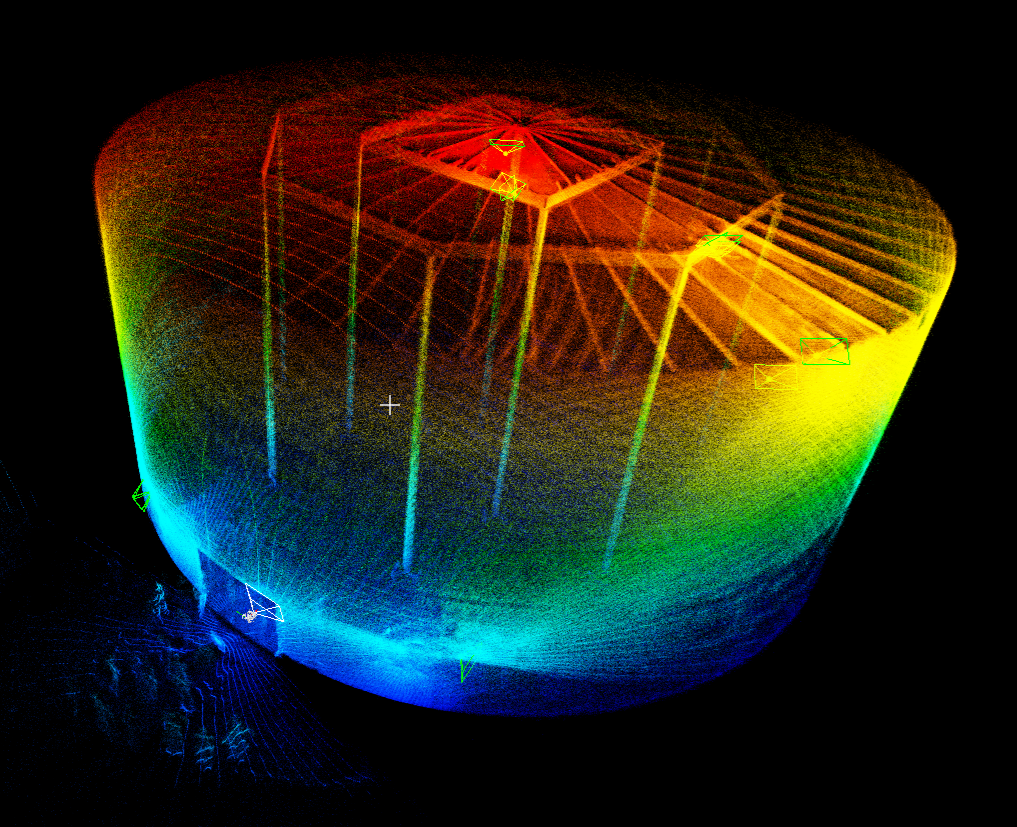
Blog
|
Power Generation
|
Oil & Gas
|
Mining
Power Generation Oil & Gas Mining
187446134570
Videos: 6 Ways to Use the Elios 3 Drone for 3D Models

White papers
|
Mining
|
Cement
Mining Cement
187320446109
Guide: Measuring Volumes in Complex Environments

White papers
|
Mining
|
Cement
Mining Cement
187217986636
Whitepaper: The Elios 3 Compared to Terrestrial Laser...

Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
187271248737
How VZU Plzen Achieved an 80% Reduction in Penstock...
-3.jpg)
Webinar
|
Power Generation
{name=Power Generation, label=Power Generation}
186327732064
Drones in Power Generation: The Elios 3 Inspecting Boilers,...

Case studies
|
Maritime
|
Oil & Gas
Maritime Oil & Gas
186347658382
Saving $600,000 On COT Inspections With The Elios 3 UT

Case studies
|
Power Generation
|
Nuclear
Power Generation Nuclear
186296854181
Cutting Condenser Inspections From 8 Days To 8 Hours


News
|
Maritime
Maritime
185838361381
Flyability's Elios 3 UT Wins Safety Award at Offshore...

News
|
Sewer
Sewer
185141898377
Flyability and WinCan Announce Custom Integration for Elios...
.png)
Webinar
|
Power Generation
{name=Power Generation, label=Power Generation}
184616941159
Powered Up: The Elios 3 in Nuclear Energy


Blog
|
Chemicals
|
Oil & Gas
|
Mining
Chemicals Oil & Gas Mining
185059614726
What Does Intrinsically Safe Mean?

Blog
|
Chemicals
|
Oil & Gas
|
Mining
Chemicals Oil & Gas Mining
185021452565
What Does ATEX Mean?

Blog
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
184753357166
How Indoor Drones at Nuclear Sites Reduce Radiation Exposure

Case studies
|
Oil & Gas
Oil & Gas
184567772756
Cutting Costs by 60% for Pipe Rack Inspections with the...


Blog
|
Chemicals
Chemicals
183852952963
7 Key Benefits of Drone Inspections in the Chemical Industry

Blog
|
Maritime
Maritime
183719002486
Interview: Class Certification for Maritime Drone...




Blog
|
Oil & Gas
Oil & Gas
181881010280
7 Key Benefits of Drone Inspections in Oil and Gas
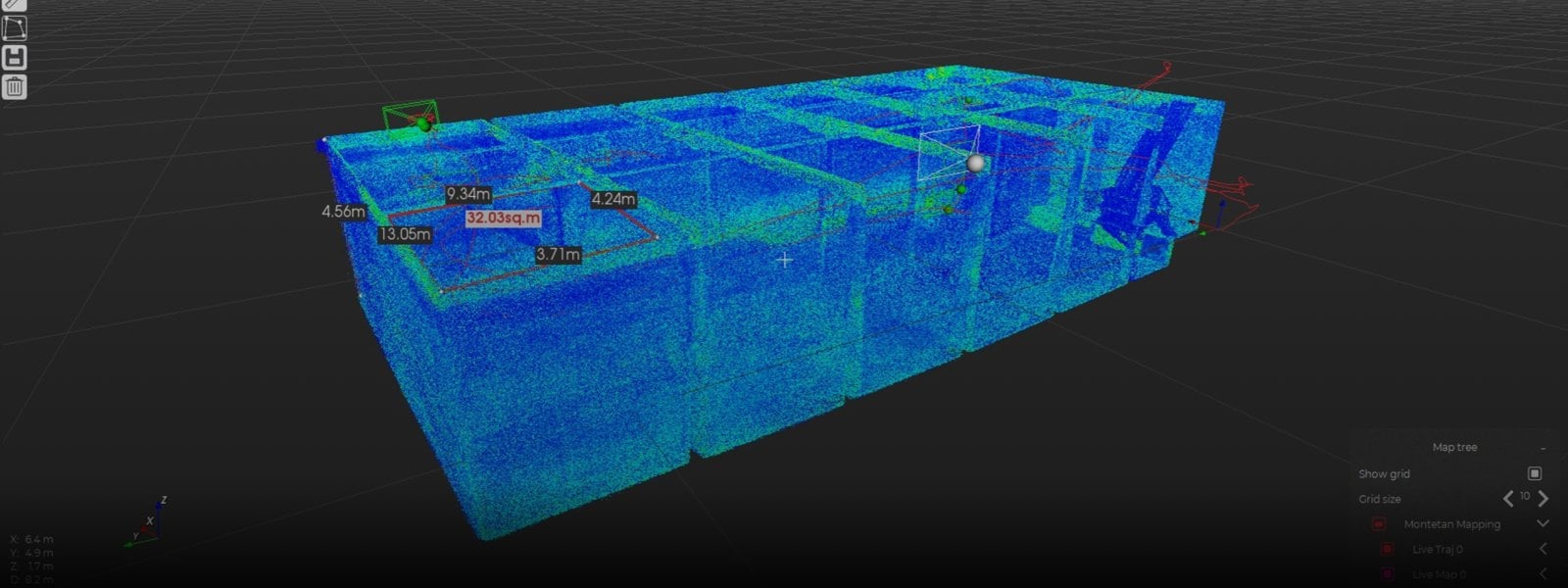



Case studies
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
180501521031
How Much Radiation Can the Elios 3 Handle? Testing at a DoE...



News
|
Cement
Cement
177403710036
Building Expertise: Flyability and Holcim's North America...

Webinar
|
Infrastructure
{name=Infrastructure, label=Infrastructure}
174912905880
Unlocking Scan to BIM with the Elios 3
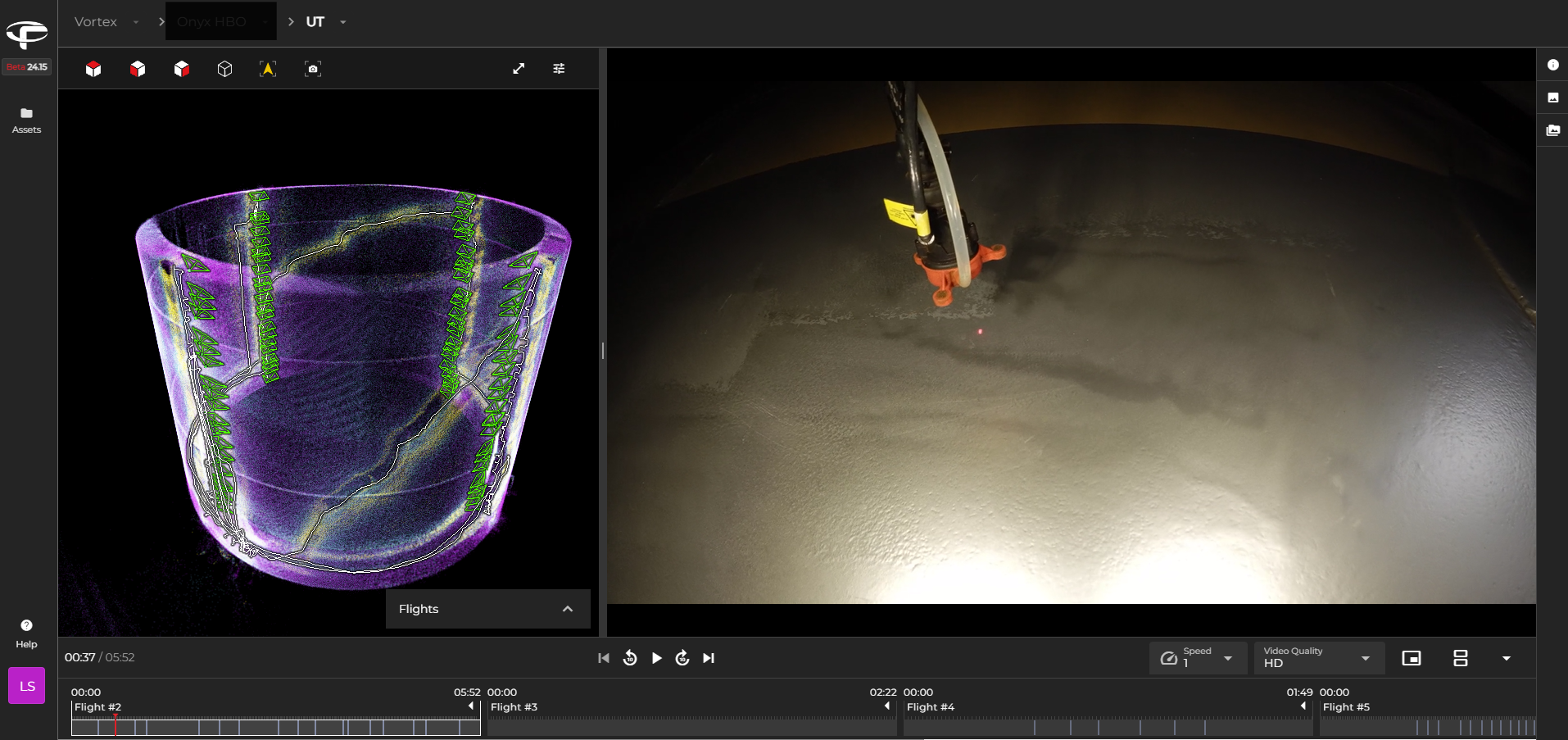
Case studies
|
Power Generation
|
Oil & Gas
Power Generation Oil & Gas
176364570281
Tank Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement With The Elios 3


Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
175751758009
A Storage Bin Inspection with the Elios 3 at a mine


Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
173959040527
Drone wind turbine blade inspections with the Elios 3

Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
173843256620
Investigating a collapsed tunnel after a landslide in the...

Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
173334266236
Drone Scan to BIM: the Elios 3 digitizes a cement plant

Blog
|
Mining
Mining
172508753466
Drones for Mining: Safety, Efficiency, and Data Collection...

Webinar
|
Oil & Gas
{name=Oil & Gas, label=Oil & Gas}
171466793731
Discover the Elios 3 UT Payload
Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
145632795500
Testing the Elios 3 Surveying Payload: Mapping a 600m...




Case studies
|
General
General
166292775793
Underground drones for emergency response: investigating a...




Blog
|
Power Generation
|
General
Power Generation General
164799472751
Boiler Inspections: A Complete Guide

Blog
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
164772679838
Bridge Inspections —Everything You Need to Know

Blog
|
Chemicals
|
Oil & Gas
Chemicals Oil & Gas
164752004924
A Complete Guide to Corrosion Monitoring

Blog
|
General
General
164725112604
What Does a Drone Cage Do? Use Cases, Types & Indoor...

Blog
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
164743513000
A Guide to How Drones are Used for Inspections
Blog
|
General
General
164721831248
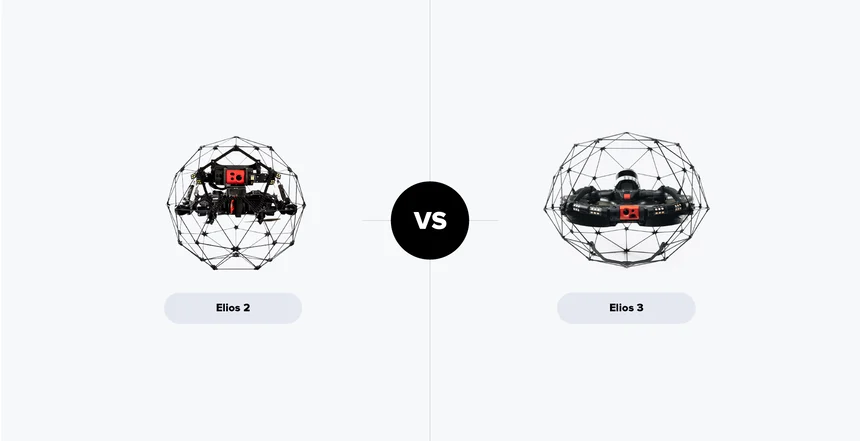
Elios 3 vs. Elios 2: How do the Flyability drones compare?

Blog
|
Sewer
|
Maritime
|
Mining
|
General
Sewer Maritime Mining General
164719776790
What Is a GPS-DENIED Drone?


Blog
|
Mining
Mining
164665724584
How Mine Drones Are Improving Safety and Optimizing Mining






Blog
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
164583719465
POWER PLANT MAINTENANCE: WHAT IS REQUIRED AND HOW DRONES...



Blog
|
Sewer
Sewer
164385558606
The Reality of Sewer Inspections—Everything You Need to Know



Blog
|
Power Generation
|
Oil & Gas
|
General
Power Generation Oil & Gas General
164254076452
What Is Turnaround Time? What Is Downtime?



Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
163246809670
A drone stack inspection with the Elios 3 UT

Case studies
|
General
General
160689626759
Automating flight merging at a sugar refinery with the...
Case studies
|
General
General
163862259590
How can the Asset Management extension reinvent your Elios...
Infographics
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
161622486043
Elios 3 Applications in Power Generation



Webinar
|
Oil & Gas
{name=Oil & Gas, label=Oil & Gas}
160655216437
Discover the Elios 3 UT Payload

Case studies
|
Maritime
Maritime
158873985867
The Elios 3 UT Payload: avoiding 15,000 hours of work at...

Blog
|
Power Generation
|
Chemicals
|
Maritime
|
Oil & Gas
Power Generation Chemicals Maritime Oil & Gas
158837901938
How UT drone inspections elevate safety and efficiency in...
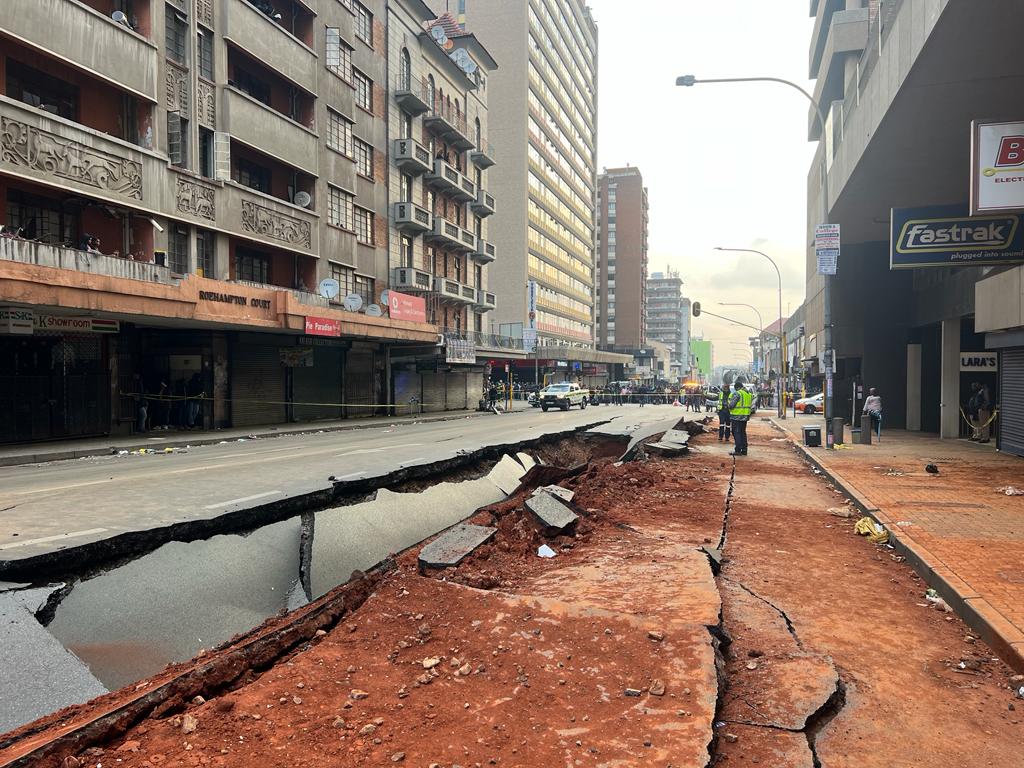


Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
156557512279
Disaster response: the Elios 3 in the Johannesburg gas...


News
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
156556943377
The Elios 3 RAD Wins Innovation Award at 2023 World Nuclear...
Case studies
|
Sewer
Sewer
154883483751
Bringing safer confined space sewer inspections to Sydney...
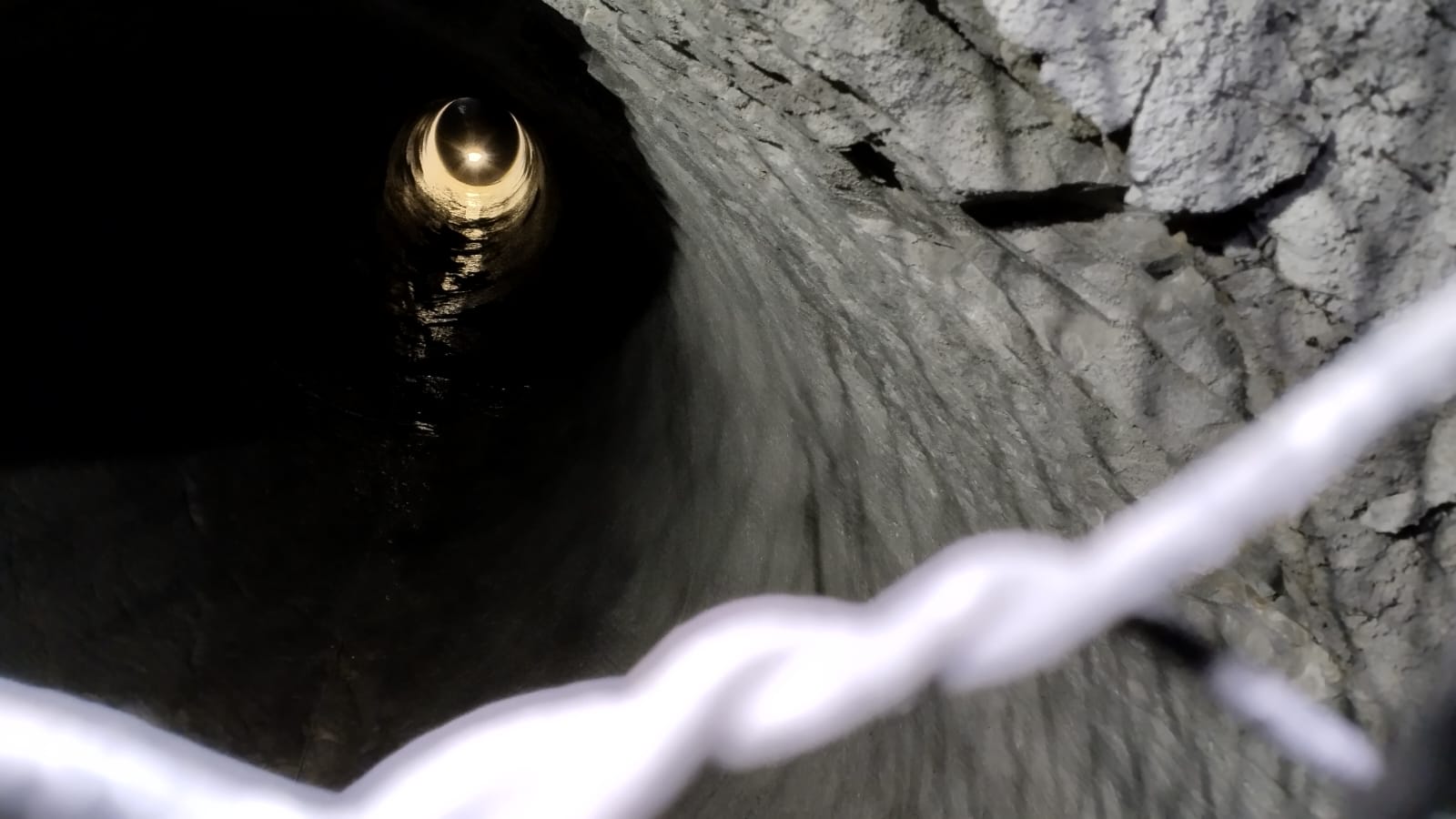

Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
154326323980
Optimizing confined space inspections: A success case with...
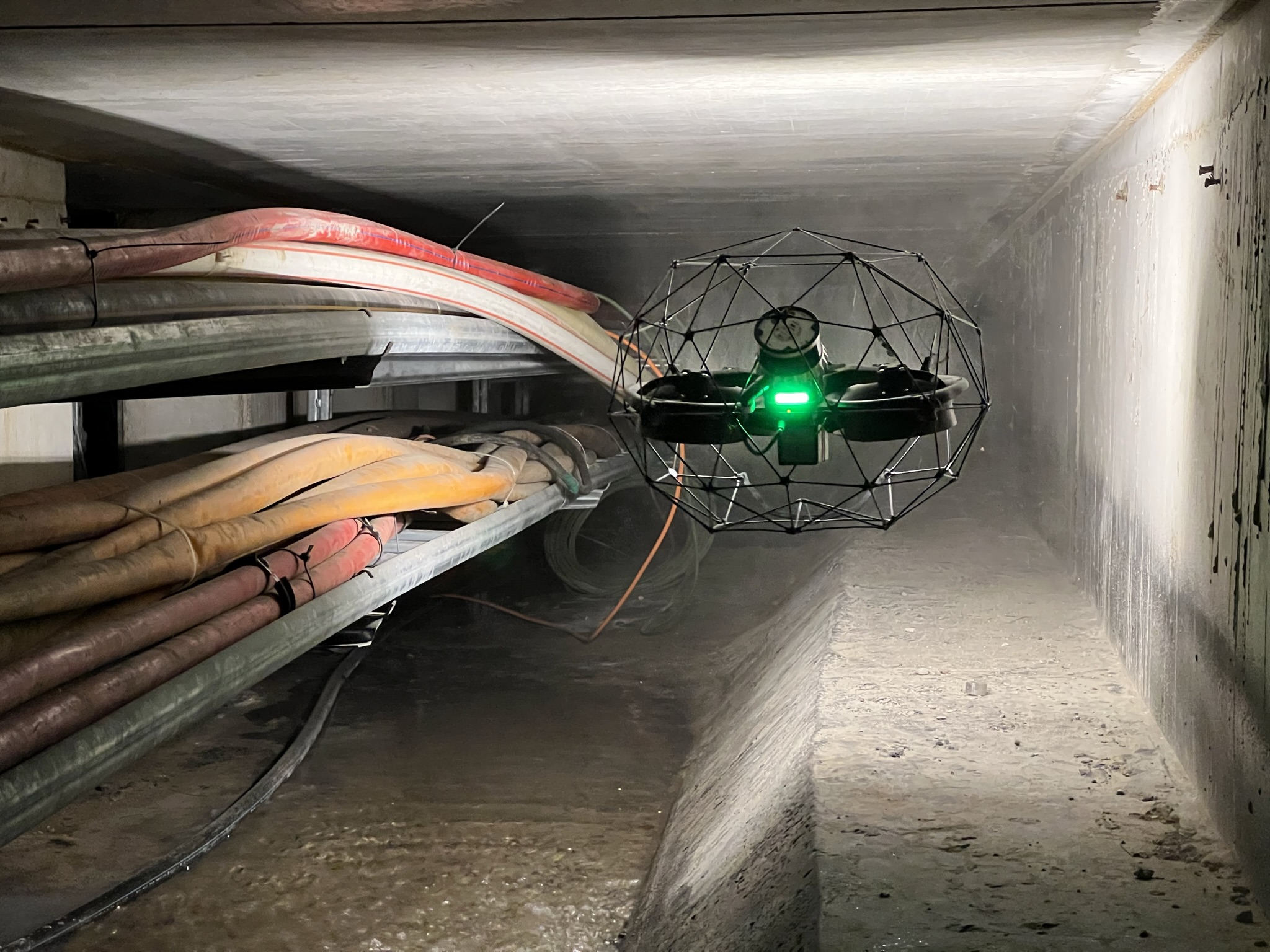

Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
154010151284
Mapping 13 kilometers of underground technical galleries in...
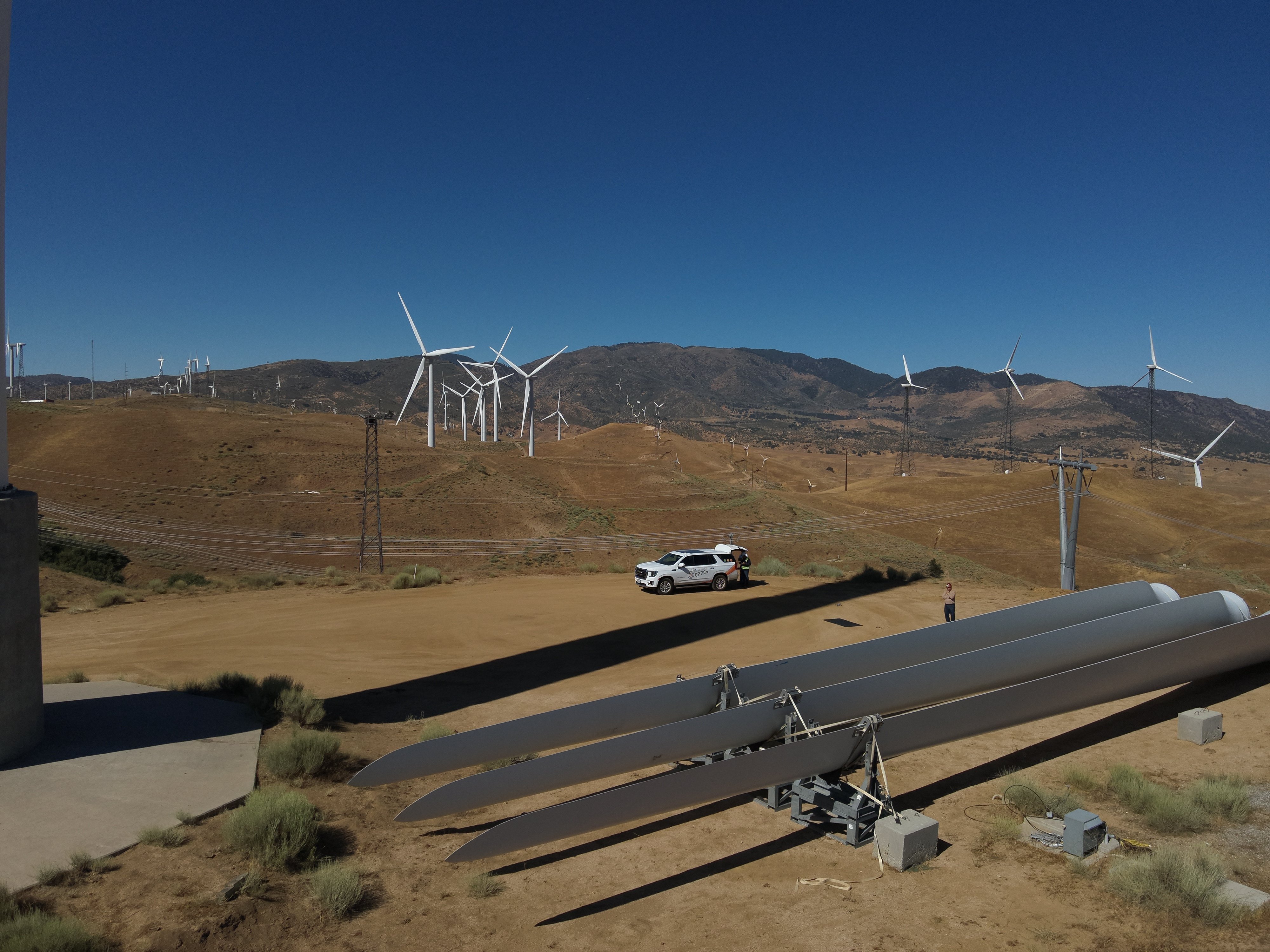

Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
153217186454
Saving over $1 million: wind turbine inspections with the...

Case studies
|
Public Safety
Public Safety
152854151297
Bringing the Elios 2 and Elios 3 to firefighting

Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
152606600547
Surveying a disused coal plant with the Elios 3

Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
152594999356
Power station inspections in Hong Kong with the Elios
Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
150814375275
Surveying Old Workings in a Mine with the Elios 3
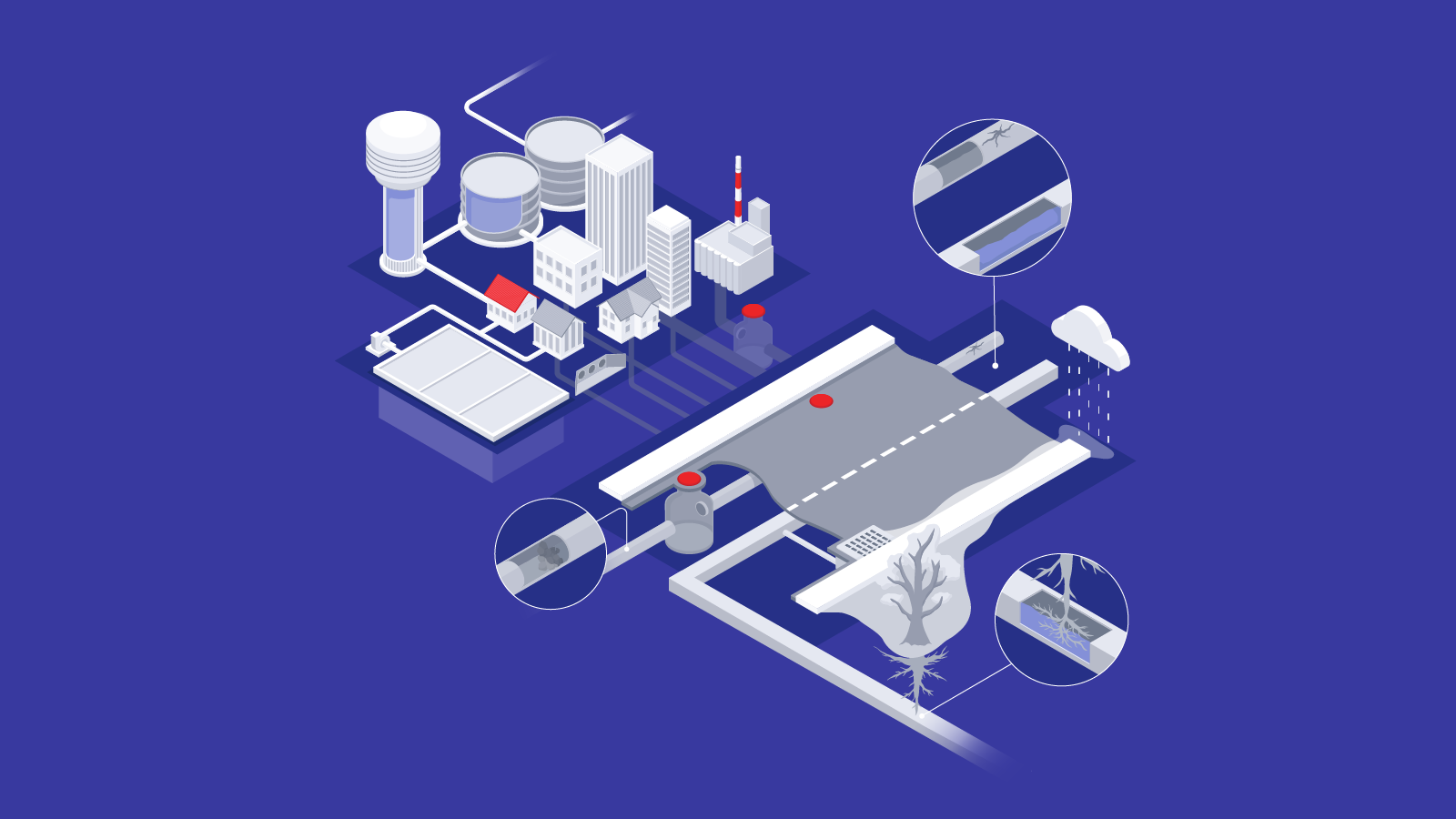

Blog
|
Sewer
|
Mining
|
General
Sewer Mining General
147423405988
Taking the pressure off pilots: Return-to-Signal for the...
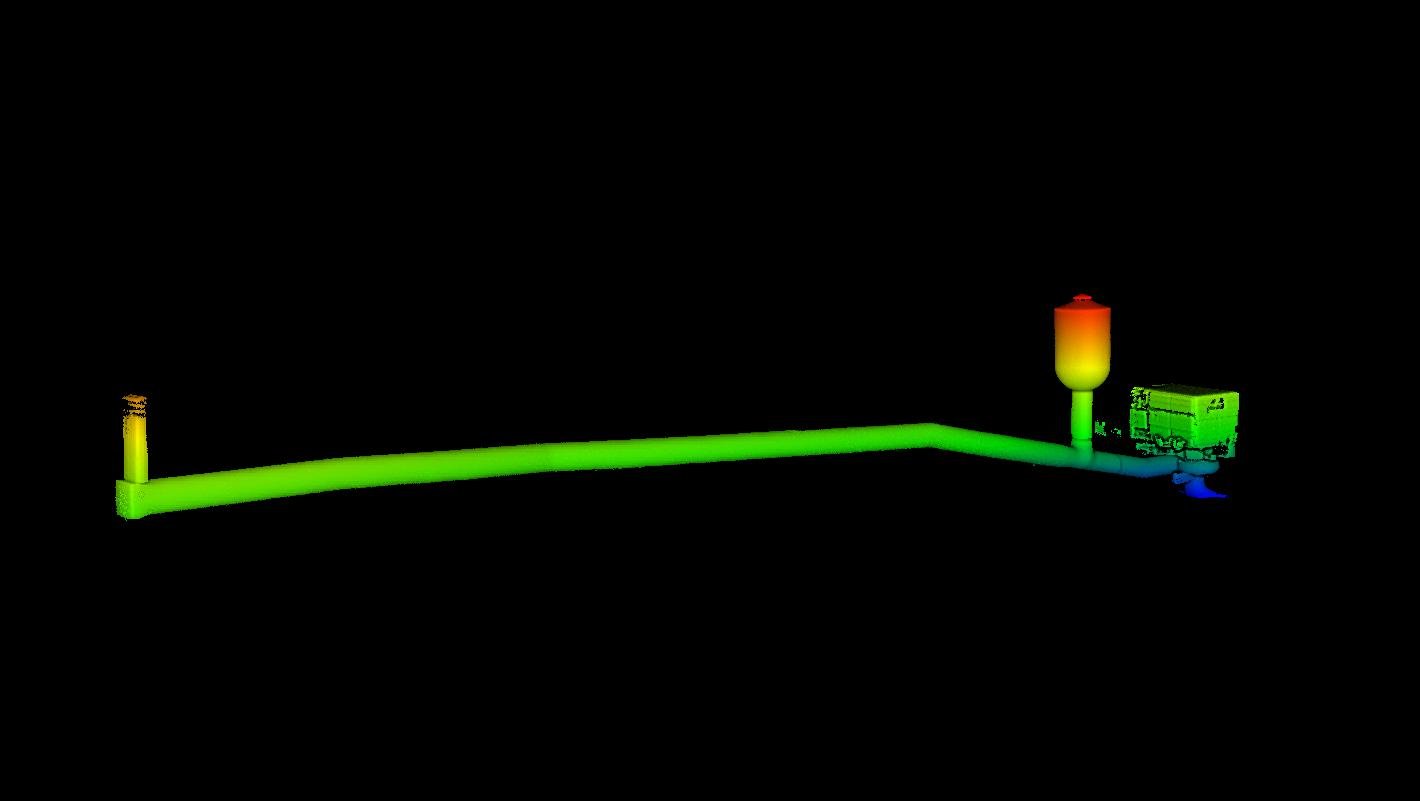
Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
147553752151
Analyzing a 35-meter dam surge tank with the Elios 3 in...
Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
146815429187
Testing The Elios 3 Surveying Payload at ICL Boulby Mine

Case studies
|
Cement
Cement
146466826811
Using the Elios 3 drone to monitor stockpiles at a cement...

Case studies
|
Power Generation
|
Nuclear
Power Generation Nuclear
145290841353
Unlocking NDT inspections for power generation with the...

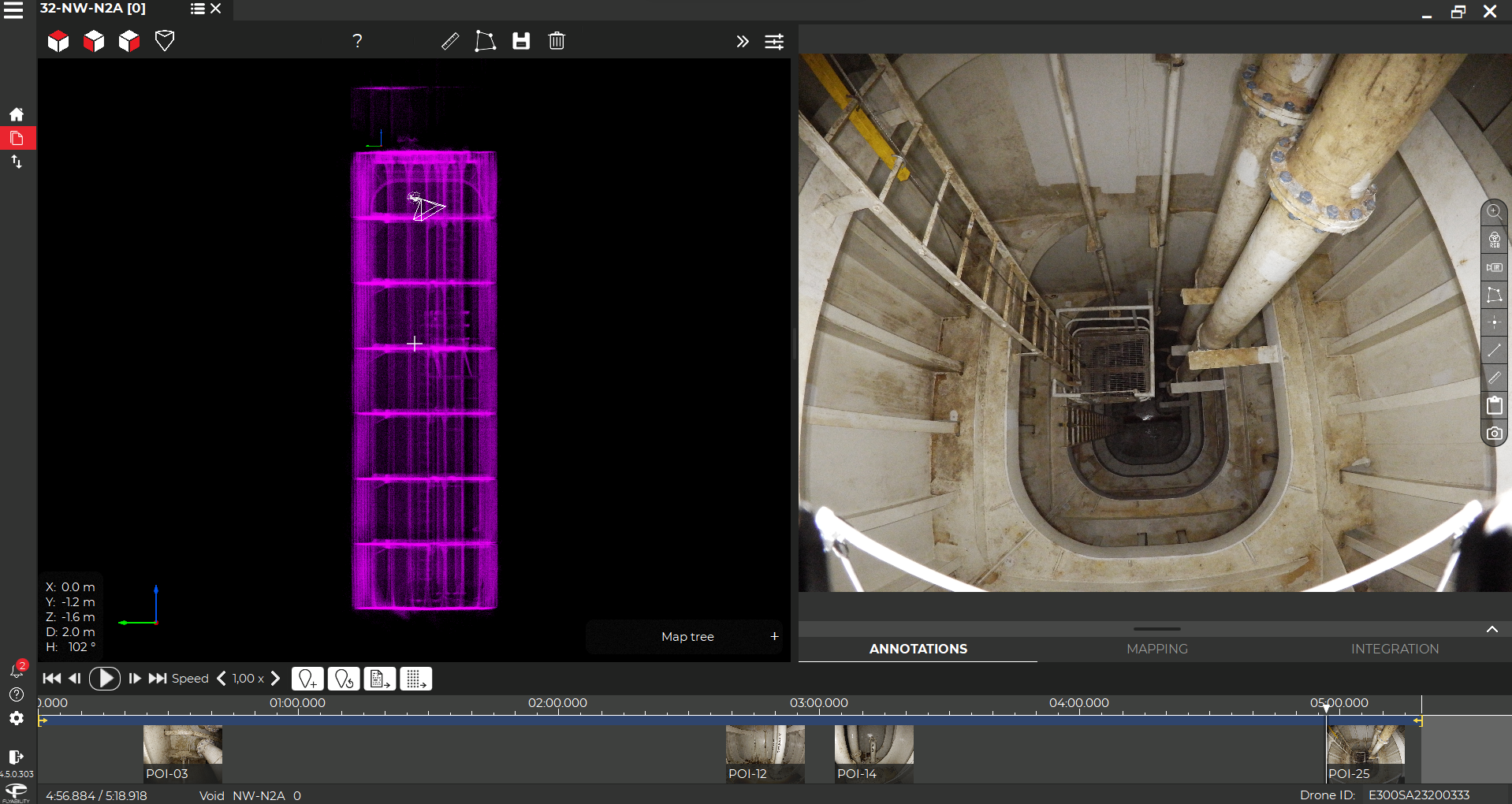
Case studies
|
Maritime
Maritime
144058337121
Inspecting 63 tanks with 2 drones in 2 weeks

Blog
|
Mining
|
General
Mining General
143595028225
How to create a georeferenced 3D model

Case studies
|
Maritime
Maritime
142671208983
Remote Hull inspection saves $1 million with the Elios 3

Webinar
|
Mining
{name=Mining, label=Mining}
100011716008
How Drones Are Being Used in Mining: Addressing ATEX Issues...

Webinar
|
Cement
{name=Cement, label=Cement}
142276091564
Discover the Elios 3 Surveying Payload

Webinar
|
Cement
{name=Cement, label=Cement}
143712670045
From 0 to Fleet: How Holcim adopted the Elios 3 for cement...

News
|
Cement
Cement
139845917464
Plants of Tomorrow Drone Days: Advancing Innovation in...


Blog
|
Sewer
|
Oil & Gas
|
Mining
|
Cement
Sewer Oil & Gas Mining Cement
139324176498
Which Elios 3 LiDAR payload is right for you? The Standard...

Webinar
|
Power Generation
{name=Power Generation, label=Power Generation}
134533606488
Radioactive: The Elios 3 for Nuclear Inspections

Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
136096724512
Eliminating downtime for a train station roof inspection...


Case studies
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
133210084904
Interview: Elios drones at Sellafield, Europe's largest...

Case studies
|
Cement
Cement
130581808237
Identifying chimney tower faults with the Elios 3 at a...
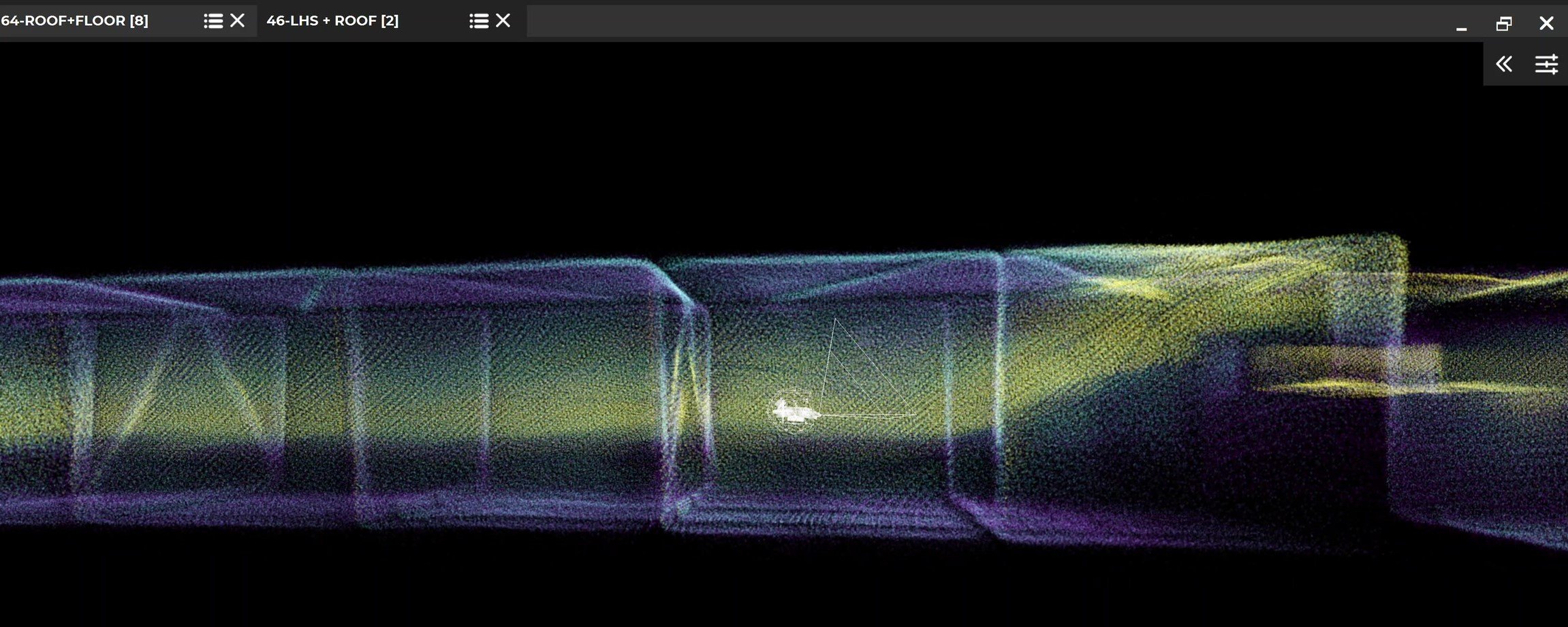
Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
130436053279
Inspecting a railway bridge inside and out with the Elios 3


Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
125072056375
Using the Elios 3 to improve site safety on a mine in...

Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
124157182340
Mining More Efficiently at Glencore Kidd Operations With...

Case studies
|
Sewer
Sewer
123756979336
Veolia Water increase safety and efficiency of their...


Webinar
|
Oil & Gas
{name=Oil & Gas, label=Oil & Gas}
118083418243
Elios Drones in the Oil & Gas industry: Digitalizing Asset...

Case studies
|
Oil & Gas
Oil & Gas
116558412724
TEXO Case Study: Inspection of Oil Tanks on an FPSO

Case studies
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
115168022934
How the Elios 3 RAD payload is detecting radiation hotspots

News
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
115599057758
Flyability launches a radiation survey meter payload for...


News
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
104316492821
Flyability and Mirion Technologies announce collaboration...
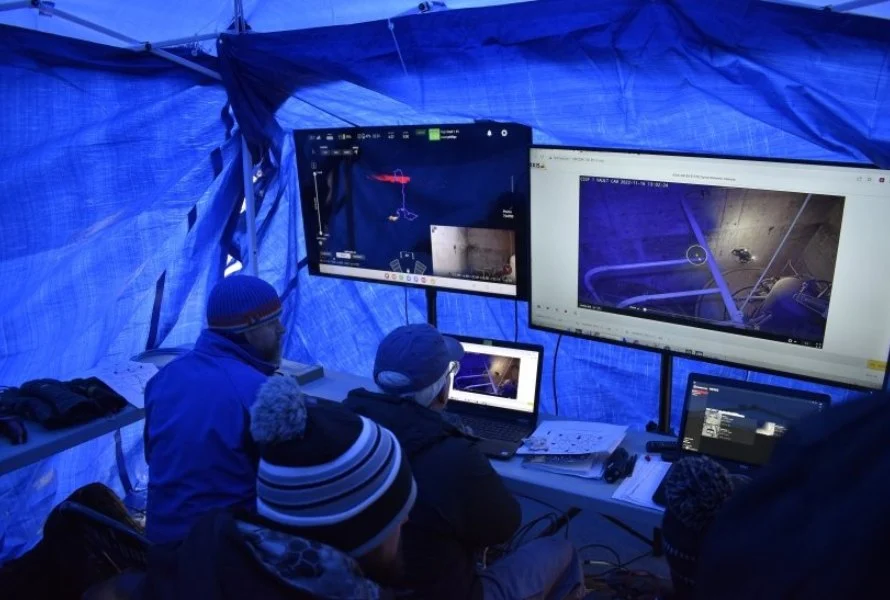

News
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
99023789955
In Historic Mission, DOE Site Uses Elios 3 to 3D Map...
Case studies
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
99056168704
Elios 3 Used to 3D Map Irradiated Storage Vault at DOE Site
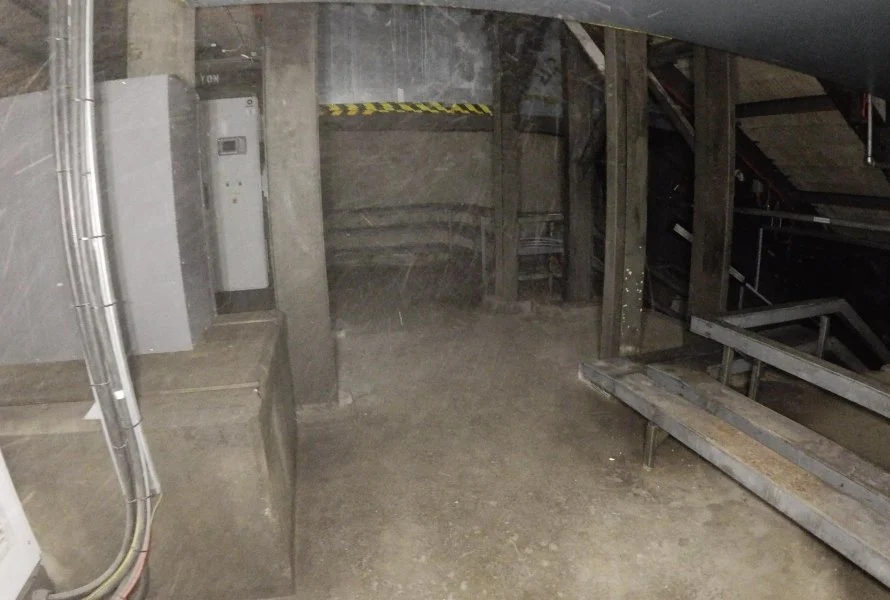

Webinar
79839535243
How to Make Survey-Grade 3D Models with the Elios 3 and...
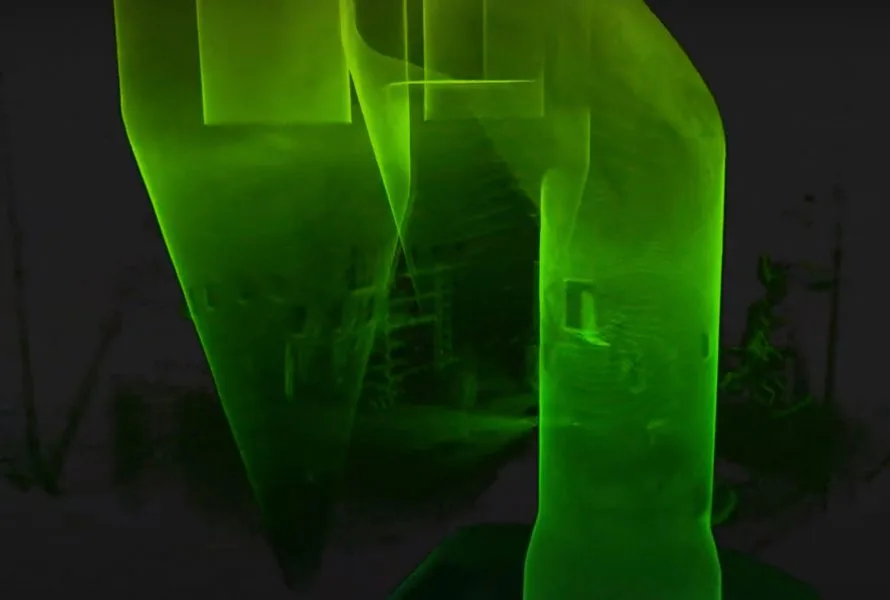

Case studies
|
Cement
Cement
86441577065
Elios 3 Makes Digital Twins of New Cement Plant to Track...
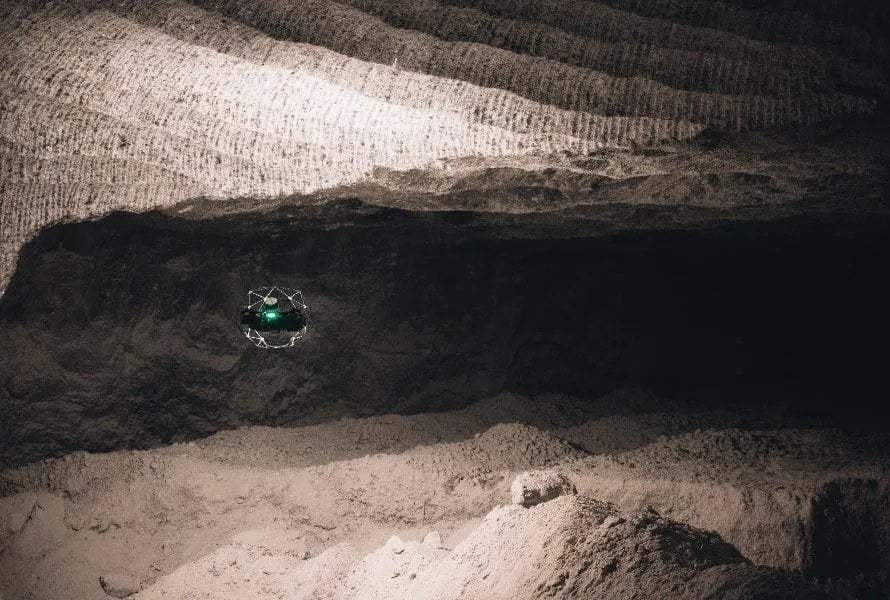
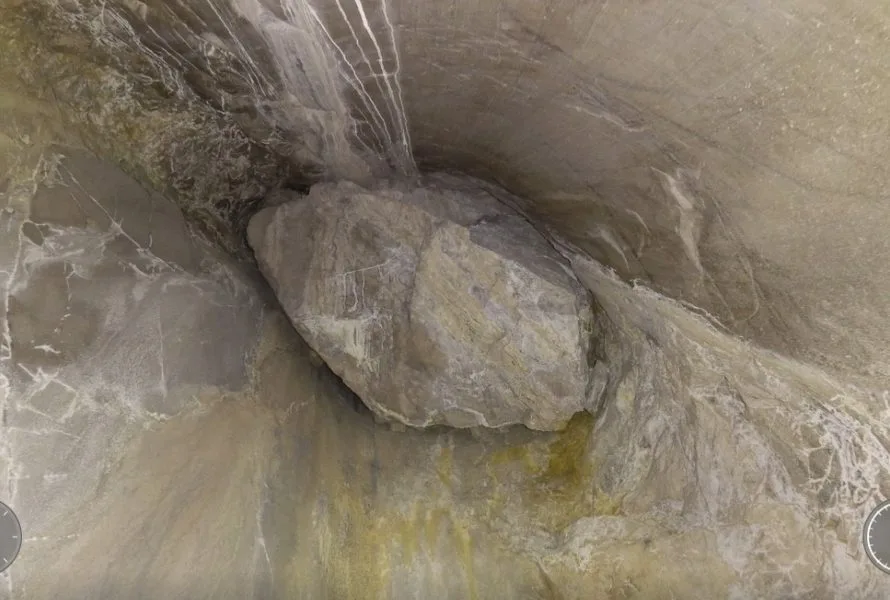


Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
83333686068
3D Maps from Elios 3 Help Mining Operation Find Cause of...
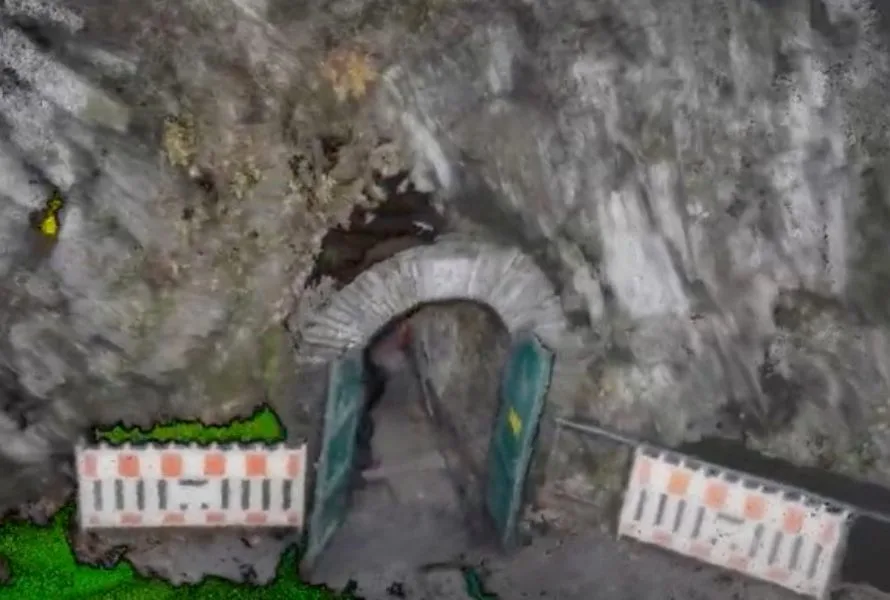

Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
72501121816
Elios 3 Helps Luxembourg 3D Map Slate Mine Turned into...
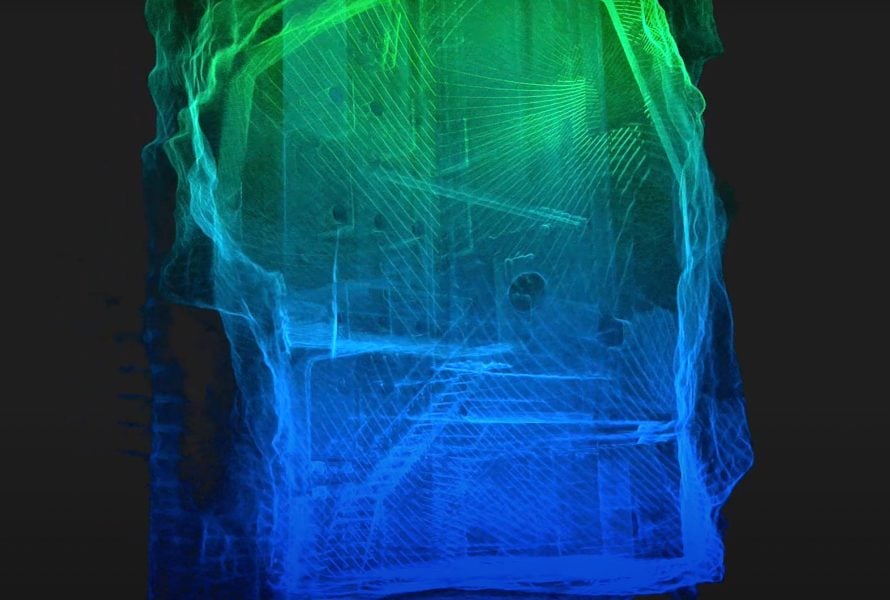

Case studies
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
72503766622
Vattenfall Uses Elios 3 to Map No Go Zones in...
Case studies
|
Cement
Cement
82147951626
Major Cement Company Improves Stockpile Measurement with...
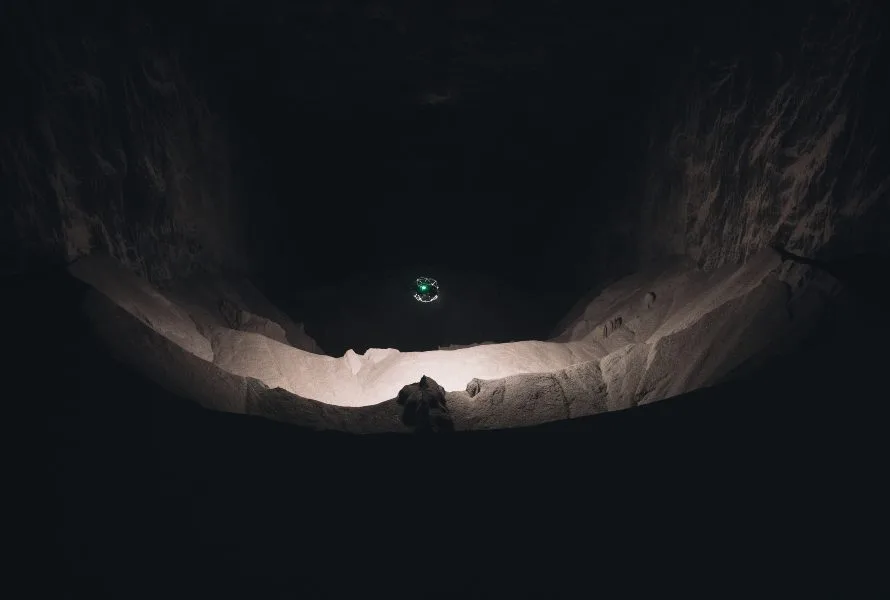

Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
72526459443
Elios 3 Stockpile Measurements Improve Safety & Accuracy at...

Webinar
79615074948
Remote Drone Inspections: How to Do an Inspection with a...


Case studies
|
Sewer
Sewer
72486101850
Elios 3’s Indoor 3D Mapping Helps City of Lausanne in Water...



Case studies
|
Maritime
Maritime
65866322606
Flyability's Elios Cuts Downtime by 80% in Drilling Rig...


News
|
Sewer
Sewer
64331569520
WinCan and Flyability partner on end-to-end solution for...




Webinar
|
Power Generation
{name=Power Generation, label=Power Generation}
57047516306
How Indoor Drones Help Reduce Radiation Exposure: New...

Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
57531353177
Testing the Elios drone at a High Altitude Mine Located in...




News
|
Mining
Mining
56282237259
Team CERBERUS wins DARPA Subterranean Challenge, takes home...
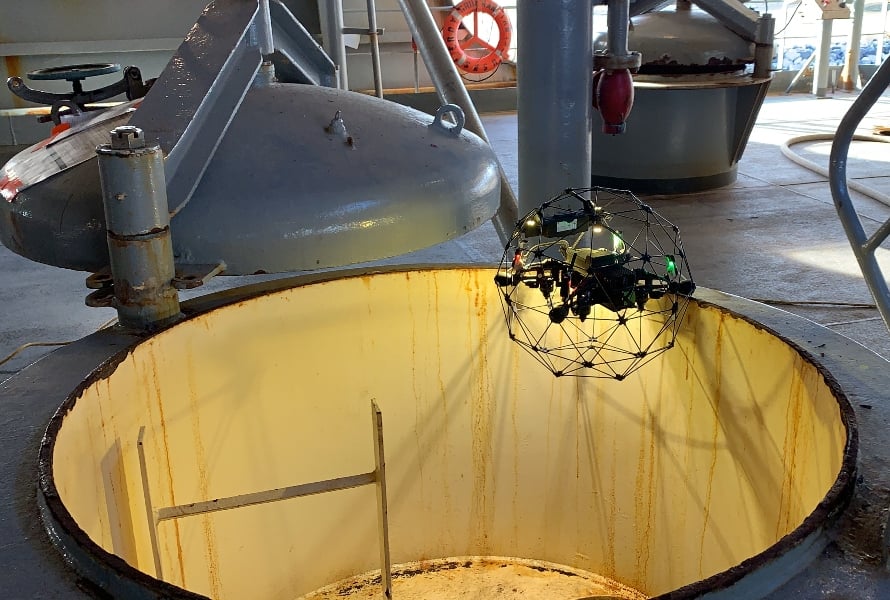



Case studies
|
Maritime
Maritime
49959985240
DroneUp Saves 700+ Hours in ABS Tank Inspection with Elios 2
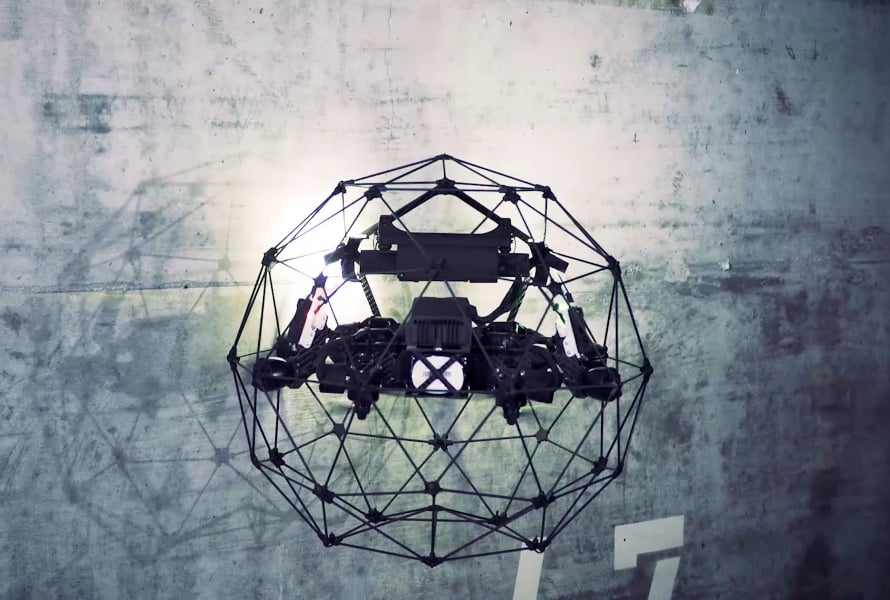
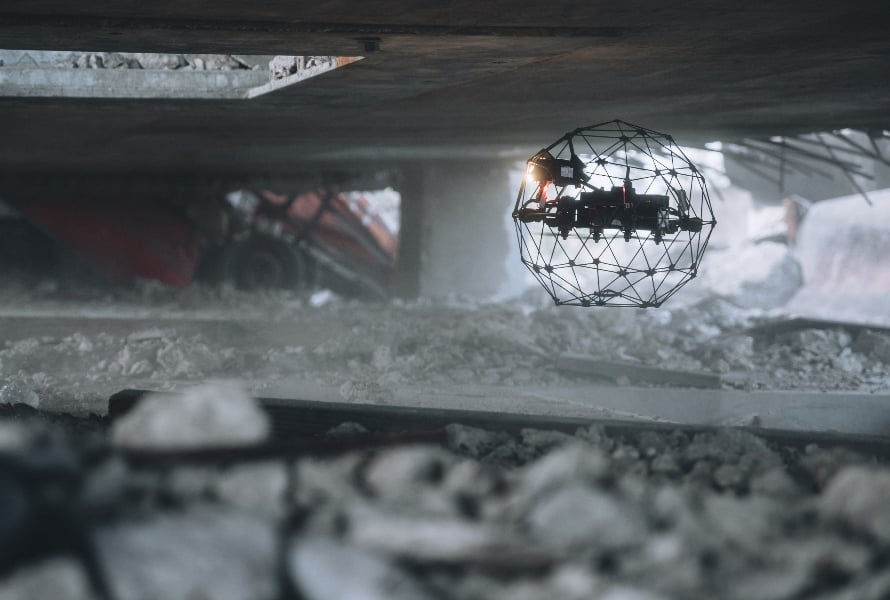
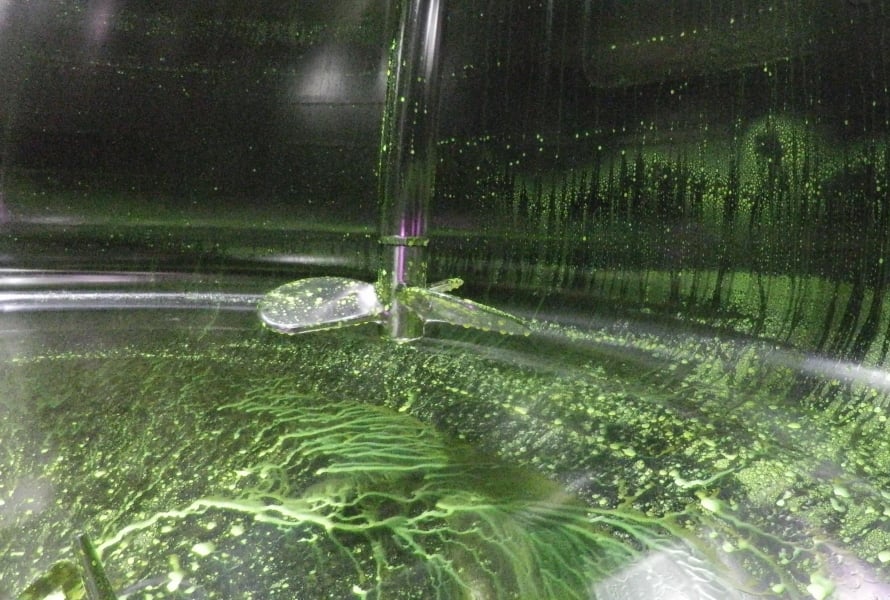






Case studies
|
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceuticals
46457055268
Major Pharmaceutical Company Saves Using the Elios 2 for...
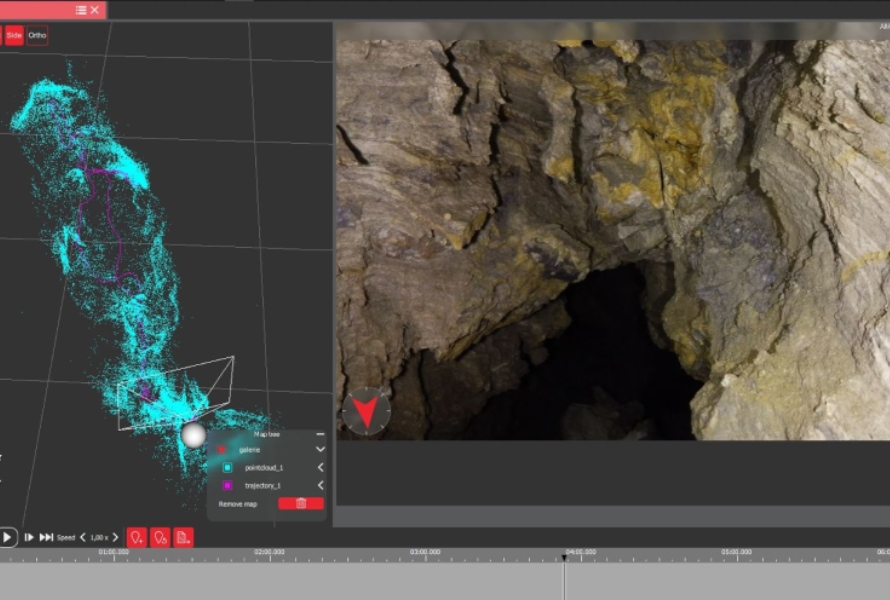

Case studies
|
Sewer
Sewer
44997426538
Sewer Inspections by Drone: How Suez RV Osis Uses the Elios...
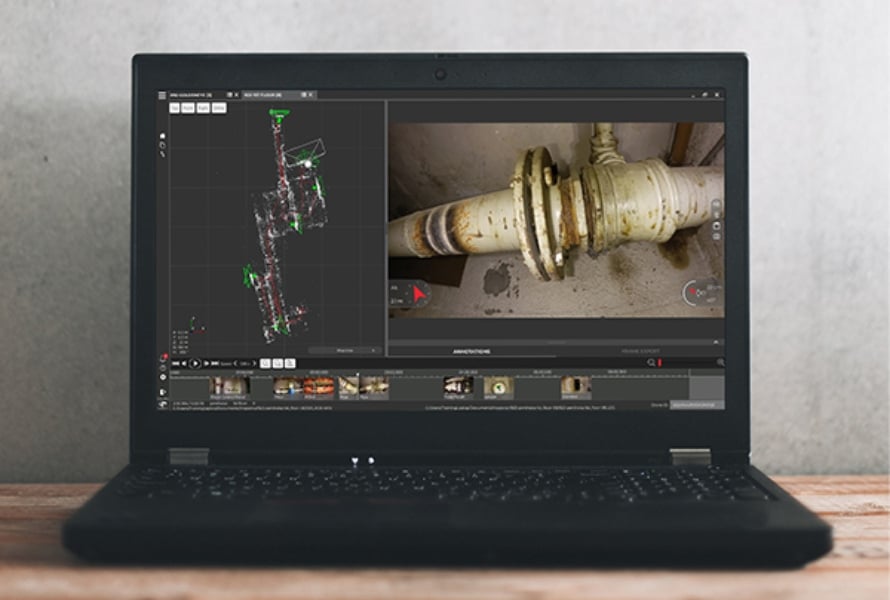

Webinar
41020798670
Drone Inspections: How to Manage Data for All Stakeholders...

Webinar
41020798669
Outdoor Drone Inspections: Case Studies and Best Practices...

Case studies
|
Public Safety
Public Safety
43598557721
Marine Firefighters of Marseille Test the Elios 2 for Ship...

Webinar
41019254489
Indoor Drone Inspections: Case Studies and Best Practices...

Webinar
41020798668
Drone Inspections: Insourcing vs. Outsourcing Your Drone...


Webinar
41020798667
The Benefits of Drone Inspections: How Inspectors Are Using...



Webinar
38266946266
[SK] Elios 2 Use Cases in South Korea (Airsens Co LTD) -...

Webinar
38461011305
Discover How Inspector 3.0 Will Change The Way You Look At...

Webinar
37617369207
How to Conduct Inspections in High Risk Environments—2 of 2

News
|
Nuclear
Nuclear
37373600133
Elios Drone Tested at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant

Webinar
36301190647
How to Conduct Inspections in High Risk Environments—1 of 2

Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
36162191521
Drone Reduces Time Needed for Scrubber Inspection by 98%,...

Webinar
36415259434
[FR] Comment réaliser des inspections en milieux confinés...
/featured-diesel-tank-inspection.jpg)



Webinar
34303338813
HOW TO GET THE MOST OUT OF YOUR DRONE'S BATTERY LIFE—ADVICE...

Case studies
|
Food & Beverage
Food & Beverage
33505264514
Grain Bin Inspections See Improved Safety, 95% Cost...

Webinar
30895349173
DRONES IN MARINE & OFFSHORE: IMPROVING SAFETY AND REDUCING...

Webinar
|
Oil & Gas
{name=Oil & Gas, label=Oil & Gas}
30443935200
How to Mitigate Intrinsic Safety




Webinar
|
Power Generation
{name=Power Generation, label=Power Generation}
28944780058
Drones in Power Generation: How Exelon Clearsight Uses...
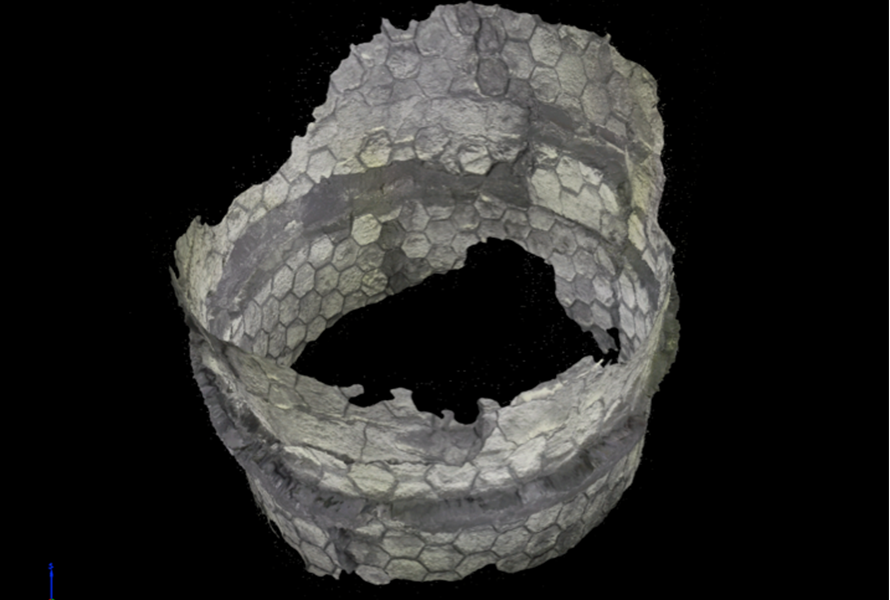
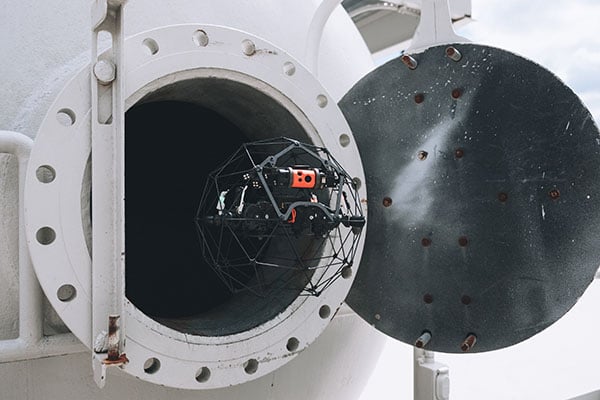
Webinar
|
Oil & Gas
{name=Oil & Gas, label=Oil & Gas}
28419143347
DRONES IN OIL & GAS: HOW CHEVRON USES DRONES TO IMPROVE...

Webinar
28178284817
[IT] - COME EFFETTUARE ISPEZIONI SICURE IN SPAZI CONFINATI...

Webinar
28168774149
[DE] - WIE MAN IN SCHWER ZUGÄNGLICHEN BEREICHEN SICHERER...



Webinar
28203529759
LEARN HOW API AND ASME EXPERTS ARE WORKING TO EXPAND DRONE...


Webinar
28168774118
[ES] - CÓMO REALIZAR INSPECCIONES DE ESPACIOS CONFINADOS...


Case studies
|
Power Generation
Power Generation
24381357273
$420,000 Saved in Elios Test by Argentinian Energy Company
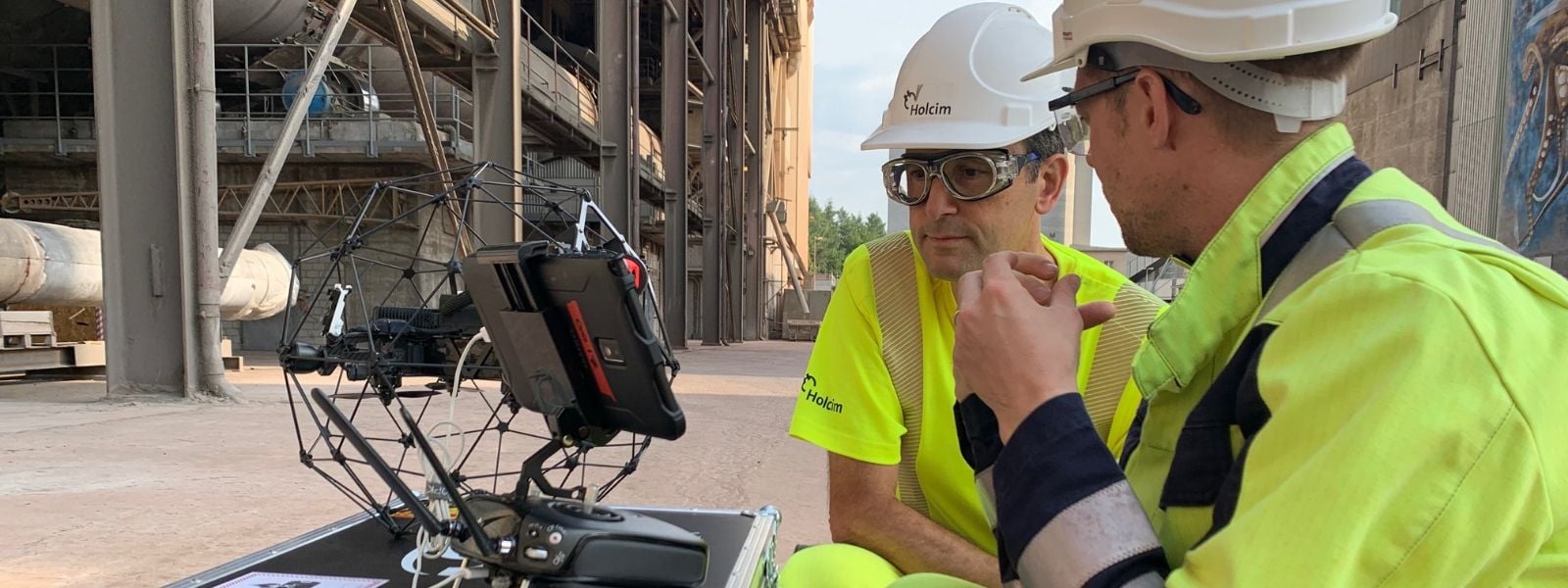
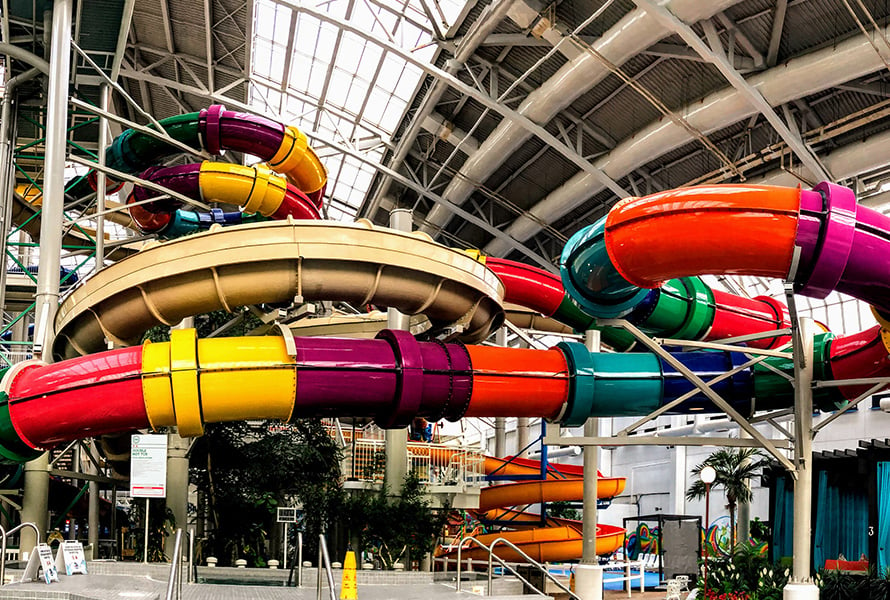













Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
8352842433
Amusement Park Inspections: Faster, Safer, and More...
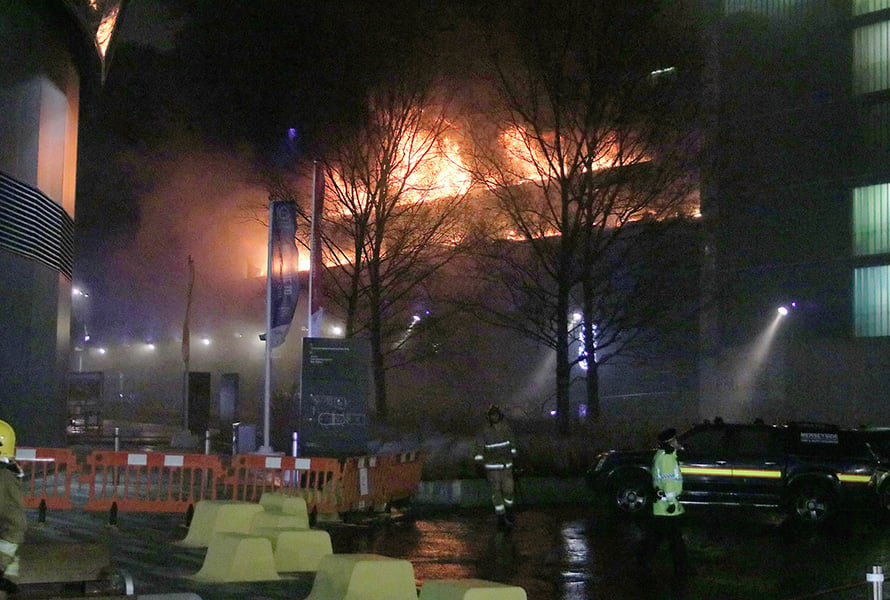


Case studies
|
Public Safety
Public Safety
6842075110
Safe Forensic Investigation in Liverpool Parking Lot...


Case studies
|
Public Safety
Public Safety
6823772291
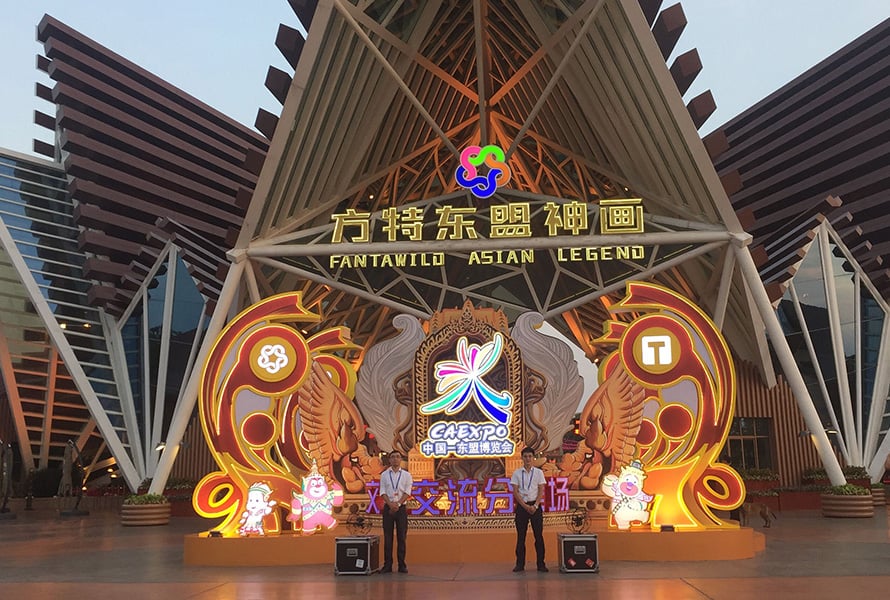
Security inspection reaches new heights at China-ASEAN Expo

Case studies
|
Maritime
Maritime
6629570251
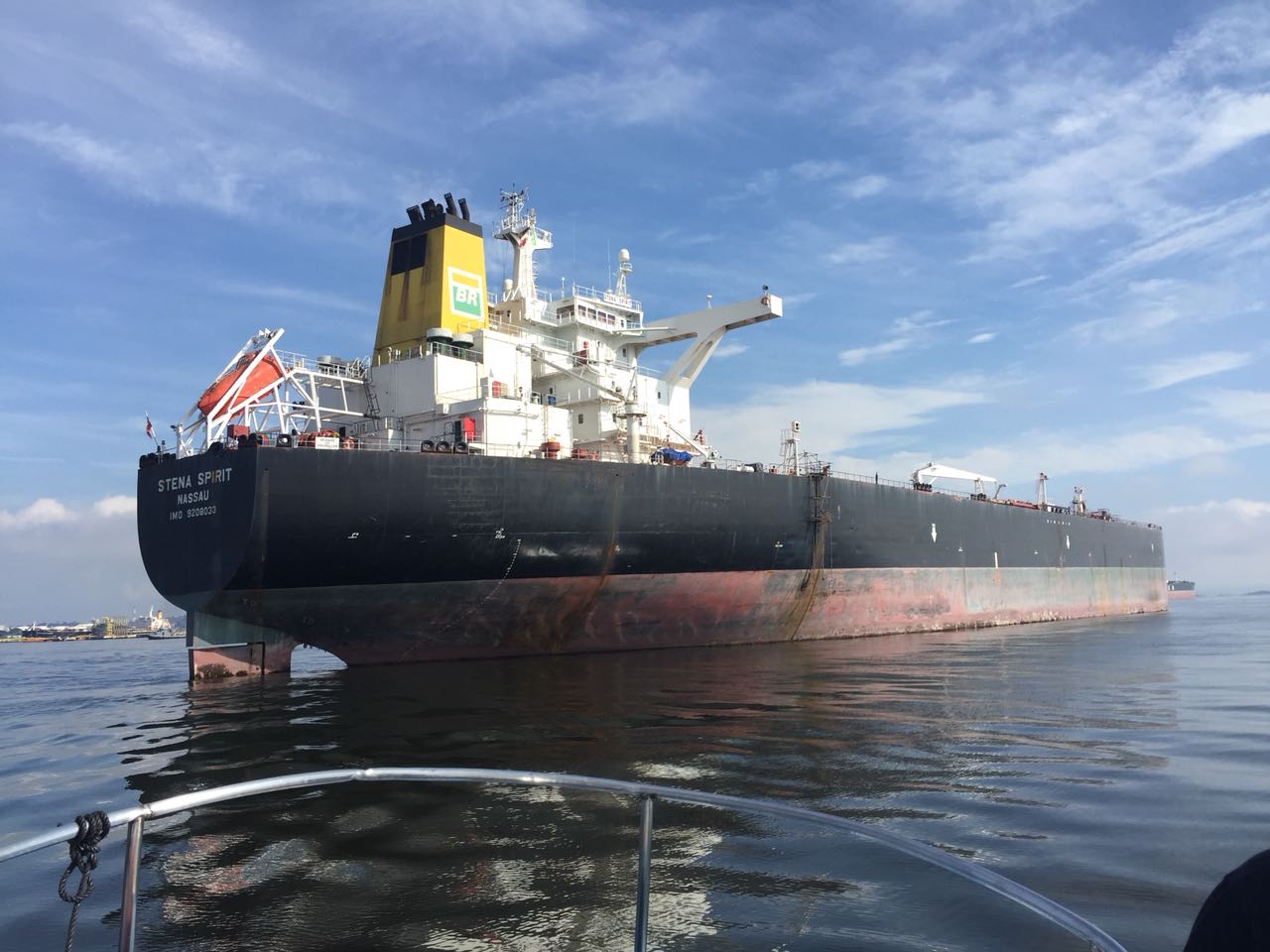
Shipping Inspections Smooth Sailing with Drone Technology





Case studies
|
Sewer
Sewer
6103334755
Inside Barcelona's Sewer System: Drone Inspection Is the...
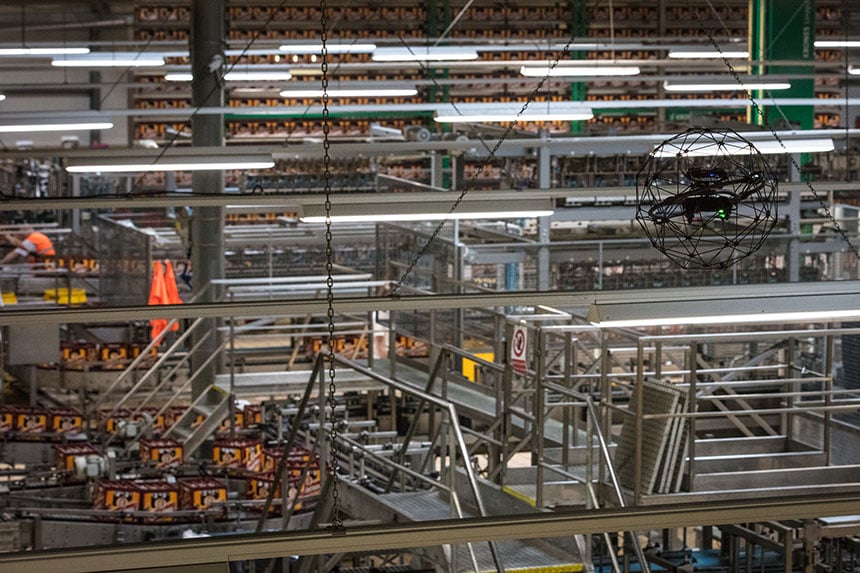

News
|
Food & Beverage
Food & Beverage
5947952137
60,000 Bottles of Beer per Hour: This Collision-Tolerant...

Case studies
|
Food & Beverage
Food & Beverage
5945106275
Pilsner Urquell Keeps Production Running During Inspection...
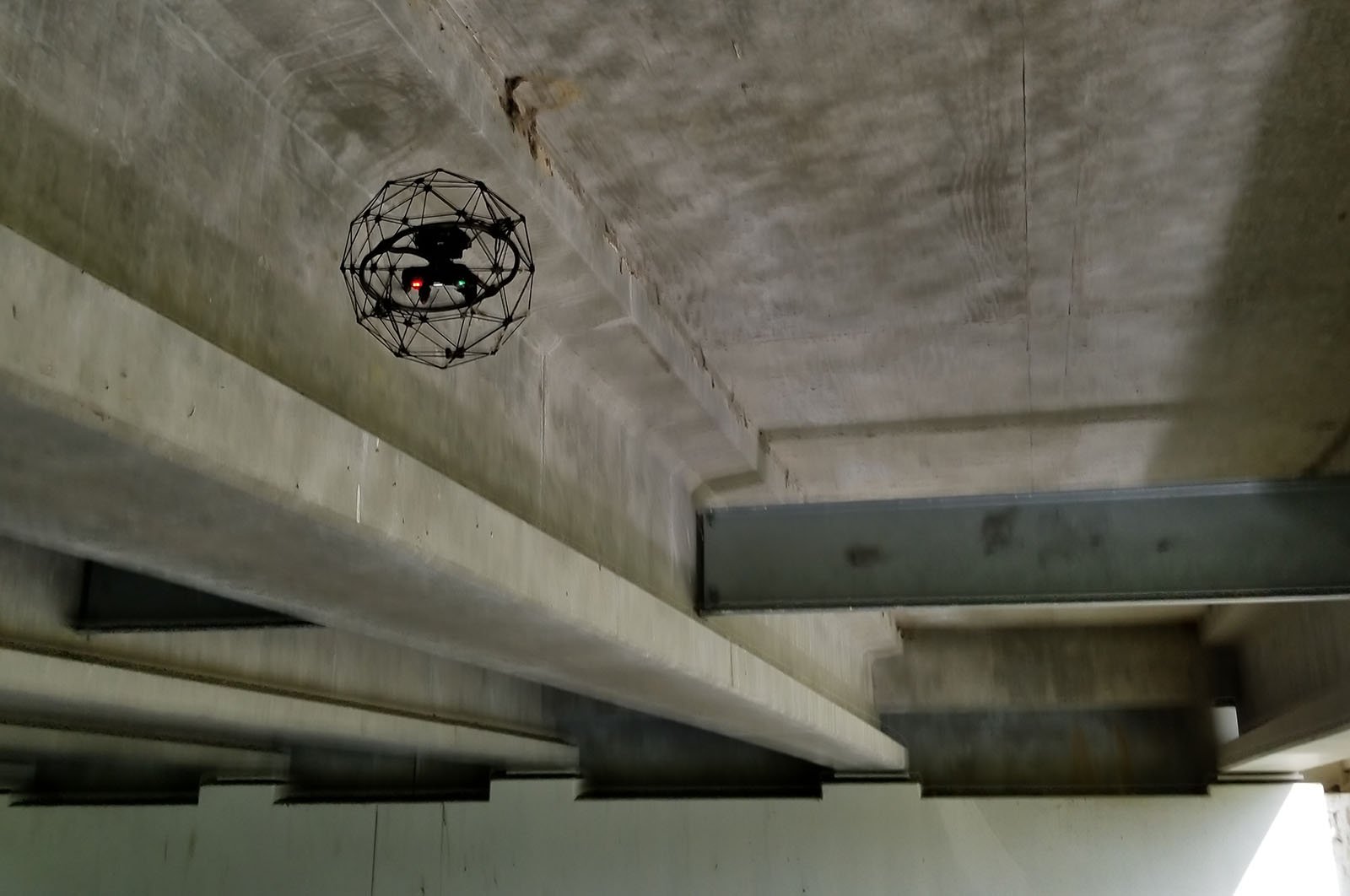











Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
5531676195
Indoor Drones in Bridge Inspection: Between Beams and...
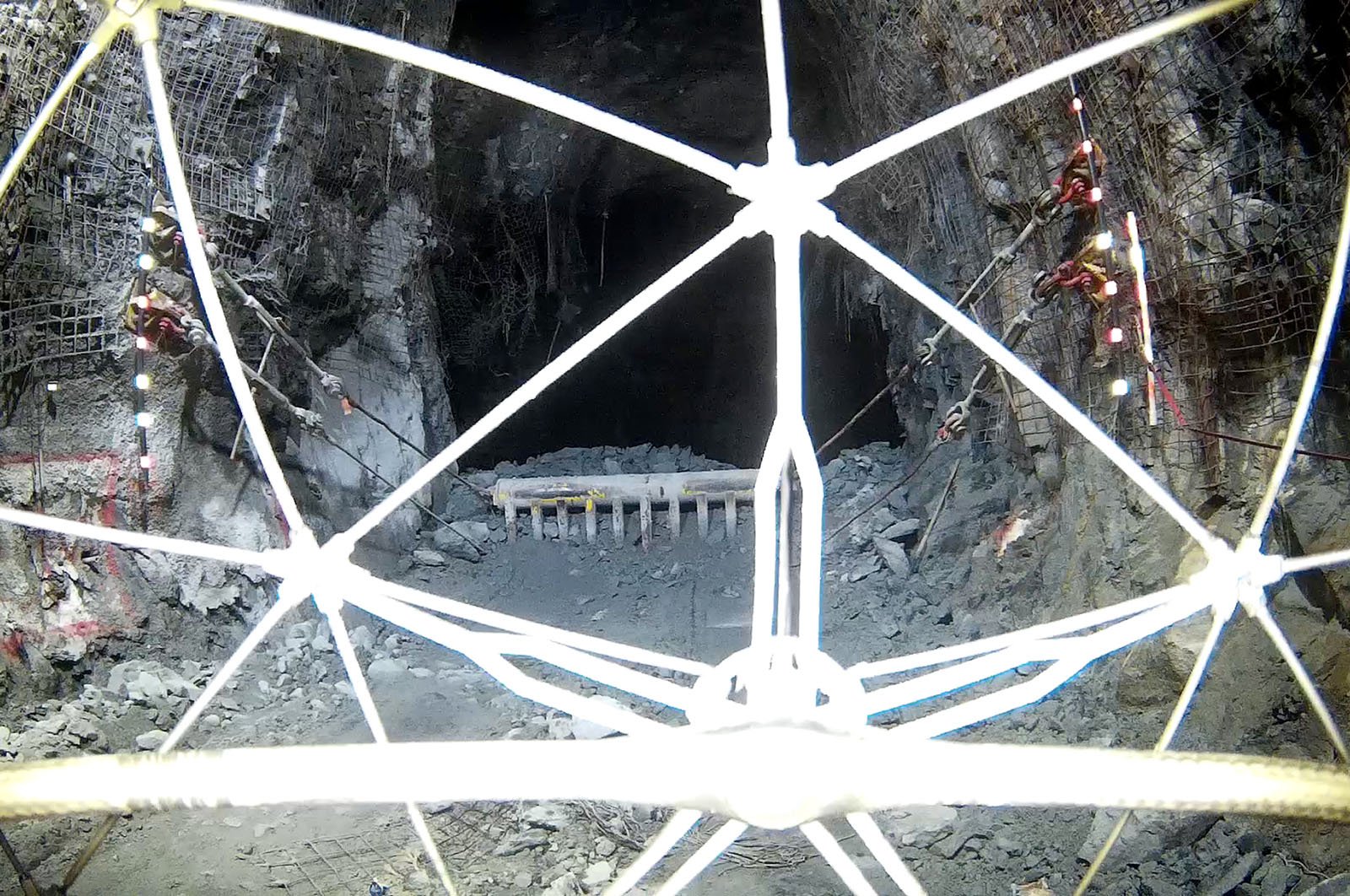

Case studies
|
Mining
Mining
5531400207
Indoor Drone in Underground Mining: Accessing the...
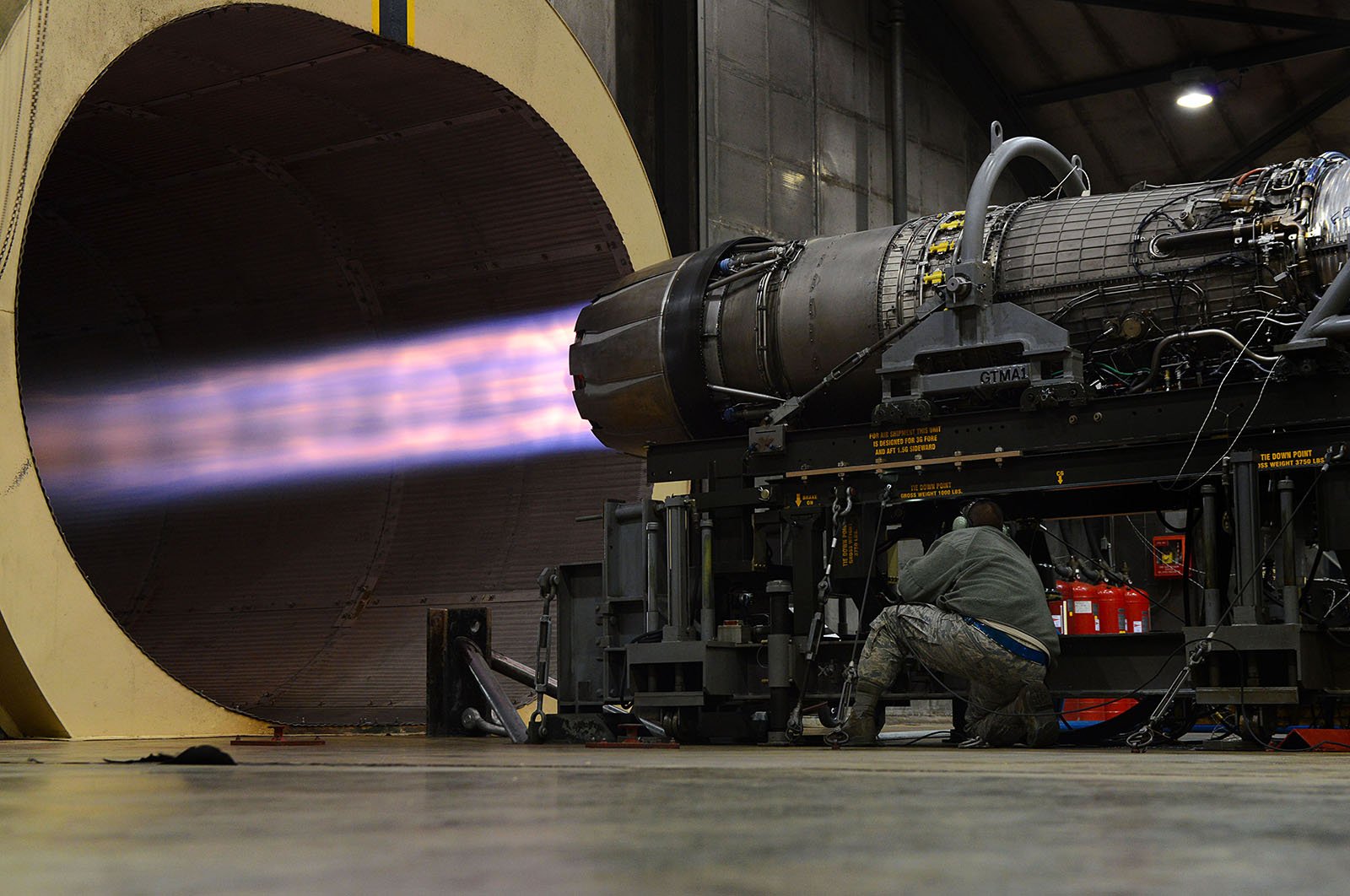

Case studies
|
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
5531390572
Inspection of a jet engine test facility
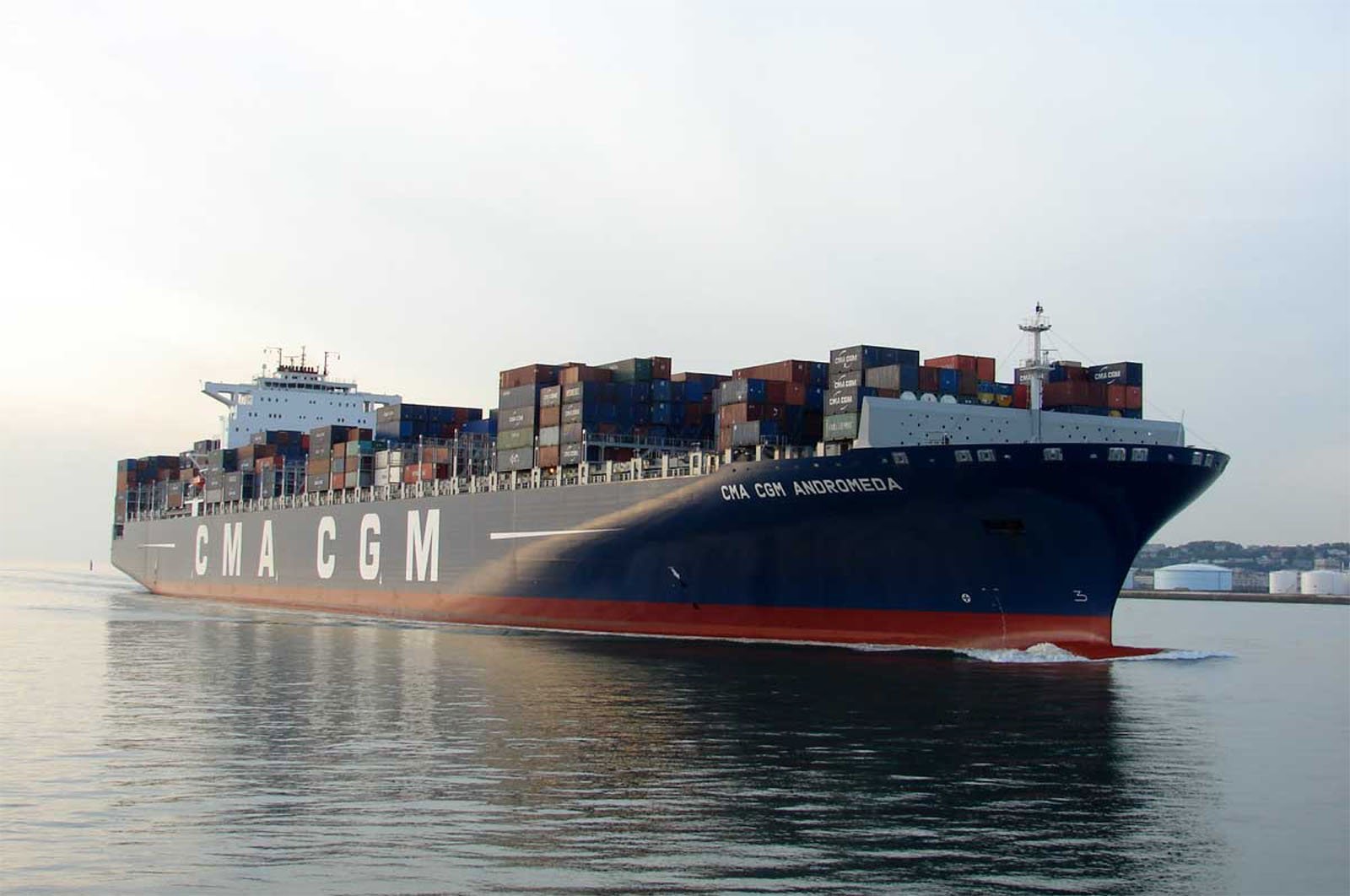

Case studies
|
Maritime
Maritime
5531385620
Inspecting the ballast tank of a container ship








.jpg)












